+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ja3 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
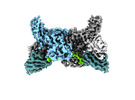
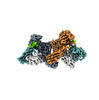
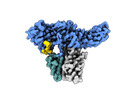
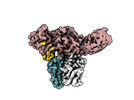
| Title | Structure of beta-arrestin1 in complex with C3aRpp | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  SIGNALING PROTEIN/IMMUNE SYSTEM / SIGNALING PROTEIN/IMMUNE SYSTEM /  GPCR / GPCR /  Arrestin / Arrestin /  SIGNALING PROTEIN / SIGNALING PROTEIN /  SIGNALING PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex SIGNALING PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information V2 vasopressin receptor binding / complement component C3a receptor activity / V2 vasopressin receptor binding / complement component C3a receptor activity /  alpha-1A adrenergic receptor binding / alpha-1A adrenergic receptor binding /  follicle-stimulating hormone receptor binding / Activation of SMO / sensory perception of touch / G alpha (s) signalling events / follicle-stimulating hormone receptor binding / Activation of SMO / sensory perception of touch / G alpha (s) signalling events /  alpha-1B adrenergic receptor binding / complement component C5a receptor activity / follicle-stimulating hormone signaling pathway ... alpha-1B adrenergic receptor binding / complement component C5a receptor activity / follicle-stimulating hormone signaling pathway ... V2 vasopressin receptor binding / complement component C3a receptor activity / V2 vasopressin receptor binding / complement component C3a receptor activity /  alpha-1A adrenergic receptor binding / alpha-1A adrenergic receptor binding /  follicle-stimulating hormone receptor binding / Activation of SMO / sensory perception of touch / G alpha (s) signalling events / follicle-stimulating hormone receptor binding / Activation of SMO / sensory perception of touch / G alpha (s) signalling events /  alpha-1B adrenergic receptor binding / complement component C5a receptor activity / follicle-stimulating hormone signaling pathway / protein phosphorylated amino acid binding / alpha-1B adrenergic receptor binding / complement component C5a receptor activity / follicle-stimulating hormone signaling pathway / protein phosphorylated amino acid binding /  angiotensin receptor binding / AP-2 adaptor complex binding / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / MAP2K and MAPK activation / Ub-specific processing proteases / positive regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process / negative regulation of interleukin-8 production / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / angiotensin receptor binding / AP-2 adaptor complex binding / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / MAP2K and MAPK activation / Ub-specific processing proteases / positive regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process / negative regulation of interleukin-8 production / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis /  Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / clathrin adaptor activity / complement receptor mediated signaling pathway / regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / arrestin family protein binding / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / clathrin adaptor activity / complement receptor mediated signaling pathway / regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / arrestin family protein binding / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis /  blood circulation / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding / azurophil granule membrane / positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / blood circulation / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding / azurophil granule membrane / positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction /  clathrin binding / positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis / clathrin binding / positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis /  stress fiber assembly / negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway / stress fiber assembly / negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway /  pseudopodium / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / positive regulation of receptor internalization / pseudopodium / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / positive regulation of receptor internalization /  phototransduction / positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production / specific granule membrane / phototransduction / positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production / specific granule membrane /  Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection /  clathrin-coated pit / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / clathrin-coated pit / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination /  insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding /  visual perception / visual perception /  GTPase activator activity / Peptide ligand-binding receptors / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / G protein-coupled receptor binding / GTPase activator activity / Peptide ligand-binding receptors / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / G protein-coupled receptor binding /  Regulation of Complement cascade / G protein-coupled receptor activity / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / calcium-mediated signaling / Regulation of Complement cascade / G protein-coupled receptor activity / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / calcium-mediated signaling /  phosphoprotein binding / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / phosphoprotein binding / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade /  endocytosis / positive regulation of angiogenesis / endocytosis / positive regulation of angiogenesis /  chemotaxis / chemotaxis /  protein transport / positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / G alpha (i) signalling events / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / cytoplasmic vesicle / protein transport / positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / G alpha (i) signalling events / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / cytoplasmic vesicle /  postsynaptic membrane / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / basolateral plasma membrane / regulation of apoptotic process / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / transmembrane transporter binding / postsynaptic membrane / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / basolateral plasma membrane / regulation of apoptotic process / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / transmembrane transporter binding /  dendritic spine / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / dendritic spine / positive regulation of MAPK cascade /  transcription coactivator activity / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / protein ubiquitination / transcription coactivator activity / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / protein ubiquitination /  endosome / response to xenobiotic stimulus / endosome / response to xenobiotic stimulus /  inflammatory response / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / inflammatory response / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway /  signaling receptor binding / signaling receptor binding /  ubiquitin protein ligase binding / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / positive regulation of cell population proliferation /  chromatin / Neutrophil degranulation / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of apoptotic process / chromatin / Neutrophil degranulation / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of apoptotic process /  enzyme binding / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / enzyme binding / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II /  nucleus / nucleus /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol cytosolSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat)  Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.94 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.94 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Maharana, J. / Sarma, P. / Yadav, M.K. / Chami, M. / Banerjee, R. / Shukla, A.K. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  India, 4items India, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: Molecular insights into atypical modes of β-arrestin interaction with seven transmembrane receptors. Authors: Jagannath Maharana / Fumiya K Sano / Parishmita Sarma / Manish K Yadav / Longhan Duan / Tomasz M Stepniewski / Madhu Chaturvedi / Ashutosh Ranjan / Vinay Singh / Sayantan Saha / Gargi ...Authors: Jagannath Maharana / Fumiya K Sano / Parishmita Sarma / Manish K Yadav / Longhan Duan / Tomasz M Stepniewski / Madhu Chaturvedi / Ashutosh Ranjan / Vinay Singh / Sayantan Saha / Gargi Mahajan / Mohamed Chami / Wataru Shihoya / Jana Selent / Ka Young Chung / Ramanuj Banerjee / Osamu Nureki / Arun K Shukla /      Abstract: β-arrestins (βarrs) are multifunctional proteins involved in signaling and regulation of seven transmembrane receptors (7TMRs), and their interaction is driven primarily by agonist-induced receptor ...β-arrestins (βarrs) are multifunctional proteins involved in signaling and regulation of seven transmembrane receptors (7TMRs), and their interaction is driven primarily by agonist-induced receptor activation and phosphorylation. Here, we present seven cryo-electron microscopy structures of βarrs either in the basal state, activated by the muscarinic receptor subtype 2 (M2R) through its third intracellular loop, or activated by the βarr-biased decoy D6 receptor (D6R). Combined with biochemical, cellular, and biophysical experiments, these structural snapshots allow the visualization of atypical engagement of βarrs with 7TMRs and also reveal a structural transition in the carboxyl terminus of βarr2 from a β strand to an α helix upon activation by D6R. Our study provides previously unanticipated molecular insights into the structural and functional diversity encoded in 7TMR-βarr complexes with direct implications for exploring novel therapeutic avenues. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ja3.cif.gz 8ja3.cif.gz | 189.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ja3.ent.gz pdb8ja3.ent.gz | 138.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ja3.json.gz 8ja3.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/8ja3 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/8ja3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/8ja3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/8ja3 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 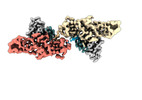 36124MC  8go9C  8j8rC 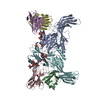 8j8vC 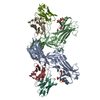 8j8zC 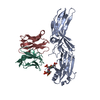 8j97C  8j9kC 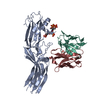 8jafC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Arrestin / Arrestin beta-1 Arrestin / Arrestin beta-1Mass: 40075.152 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) / Gene: Arrb1 / Production host: Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) / Gene: Arrb1 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P29066 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P29066#2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1484.165 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: C-terminal tail / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q16581 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q16581#3: Antibody | Mass: 25512.354 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host: Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli)#4: Antibody | Mass: 23435.064 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host: Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli)Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 46000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 46000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 49.4 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 13438 |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 8834633 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.94 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 164339 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 8GO8 Accession code: 8GO8 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 79.26 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj

























