6EF1
 
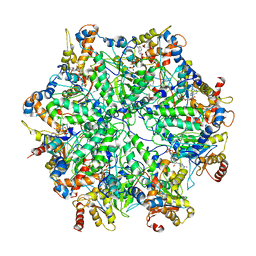 | | Yeast 26S proteasome bound to ubiquitinated substrate (5D motor state) | | 分子名称: | 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 4 homolog, 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6A, 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6B homolog, ... | | 著者 | de la Pena, A.H, Goodall, E.A, Gates, S.N, Lander, G.C, Martin, A. | | 登録日 | 2018-08-15 | | 公開日 | 2018-10-17 | | 最終更新日 | 2024-03-13 | | 実験手法 | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY (4.73 Å) | | 主引用文献 | Substrate-engaged 26Sproteasome structures reveal mechanisms for ATP-hydrolysis-driven translocation.
Science, 362, 2018
|
|
6EF2
 
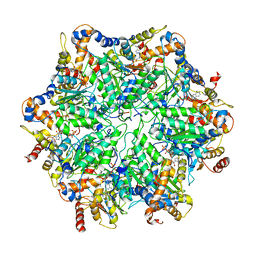 | | Yeast 26S proteasome bound to ubiquitinated substrate (5T motor state) | | 分子名称: | 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 4 homolog, 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6A, 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6B homolog, ... | | 著者 | de la Pena, A.H, Goodall, E.A, Gates, S.N, Lander, G.C, Martin, A. | | 登録日 | 2018-08-15 | | 公開日 | 2018-10-17 | | 最終更新日 | 2024-03-13 | | 実験手法 | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY (4.27 Å) | | 主引用文献 | Substrate-engaged 26Sproteasome structures reveal mechanisms for ATP-hydrolysis-driven translocation.
Science, 362, 2018
|
|
6EF3
 
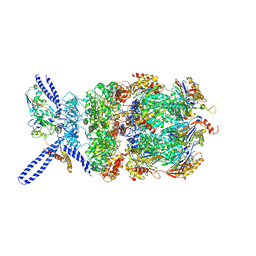 | | Yeast 26S proteasome bound to ubiquitinated substrate (4D motor state) | | 分子名称: | 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 4 homolog, 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6A, 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6B homolog, ... | | 著者 | de la Pena, A.H, Goodall, E.A, Gates, S.N, Lander, G.C, Martin, A. | | 登録日 | 2018-08-15 | | 公開日 | 2018-10-17 | | 最終更新日 | 2024-10-30 | | 実験手法 | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY (4.17 Å) | | 主引用文献 | Substrate-engaged 26Sproteasome structures reveal mechanisms for ATP-hydrolysis-driven translocation.
Science, 362, 2018
|
|
6EF0
 
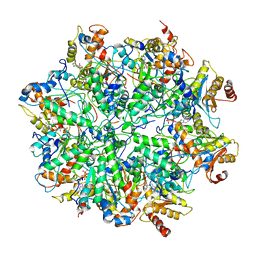 | | Yeast 26S proteasome bound to ubiquitinated substrate (1D* motor state) | | 分子名称: | 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 4 homolog, 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6A, 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6B homolog, ... | | 著者 | de la Pena, A.H, Goodall, E.A, Gates, S.N, Lander, G.C, Martin, A. | | 登録日 | 2018-08-15 | | 公開日 | 2018-10-17 | | 最終更新日 | 2024-03-13 | | 実験手法 | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY (4.43 Å) | | 主引用文献 | Substrate-engaged 26Sproteasome structures reveal mechanisms for ATP-hydrolysis-driven translocation.
Science, 362, 2018
|
|
