[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
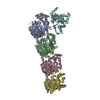
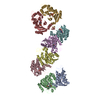
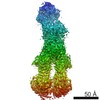
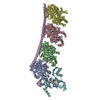
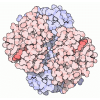
Yorodumi- SASDEY5: Albumin-insulin detemir 2:12 complex, P1 symmetry (Human Albumin ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDEY5 |
|---|---|
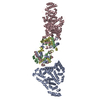
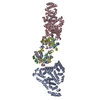
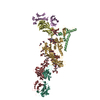
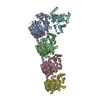
 Sample Sample | Albumin-insulin detemir 2:12 complex, P1 symmetry
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbilirubin transport / Ciprofloxacin ADME / exogenous protein binding / cellular response to calcium ion starvation / enterobactin binding / Heme biosynthesis / HDL remodeling / molecular carrier activity / negative regulation of mitochondrial depolarization / Heme degradation ...bilirubin transport / Ciprofloxacin ADME / exogenous protein binding / cellular response to calcium ion starvation / enterobactin binding / Heme biosynthesis / HDL remodeling / molecular carrier activity / negative regulation of mitochondrial depolarization / Heme degradation / Prednisone ADME / negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / Signaling by Insulin receptor / negative regulation of feeding behavior / IRS activation / Insulin processing / regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / Aspirin ADME / antioxidant activity / positive regulation of respiratory burst / Regulation of gene expression in beta cells / negative regulation of acute inflammatory response / alpha-beta T cell activation / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / negative regulation of protein secretion / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / fatty acid homeostasis / Signal attenuation / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / negative regulation of lipid catabolic process / Scavenging of heme from plasma / toxic substance binding / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / Recycling of bile acids and salts / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / transport vesicle / nitric oxide-cGMP-mediated signaling / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Insulin receptor recycling / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / neuron projection maintenance / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / platelet alpha granule lumen / positive regulation of glycolytic process / fatty acid binding / cellular response to starvation / endosome lumen / positive regulation of cytokine production / acute-phase response / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / positive regulation of D-glucose import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of protein secretion / insulin receptor binding / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / positive regulation of cell differentiation / Regulation of insulin secretion / wound healing / Cytoprotection by HMOX1 / positive regulation of neuron projection development / hormone activity / response to nutrient levels / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / regulation of synaptic plasticity / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / Golgi lumen / vasodilation / cognition / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / glucose metabolic process / insulin receptor signaling pathway / Platelet degranulation / cell-cell signaling / pyridoxal phosphate binding / glucose homeostasis / protein-folding chaperone binding / regulation of protein localization / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / positive regulation of cell growth / protease binding / secretory granule lumen / blood microparticle / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / positive regulation of cell migration / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway Similarity search - Function |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol / Year: 2019 Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol / Year: 2019Title: Solution structures of long-acting insulin analogues and their complexes with albumin. Authors: Line A Ryberg / Pernille Sønderby / Fabian Barrientos / Jens T Bukrinski / Günther H J Peters / Pernille Harris /  Abstract: The lipidation of peptide drugs is one strategy to obtain extended half-lives, enabling once-daily or even less frequent injections for patients. The half-life extension results from a combination of ...The lipidation of peptide drugs is one strategy to obtain extended half-lives, enabling once-daily or even less frequent injections for patients. The half-life extension results from a combination of self-association and association with human serum albumin (albumin). The self-association and association with albumin of two insulin analogues, insulin detemir and insulin degludec, were investigated by small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) in phenolic buffers. Detemir shows concentration-dependent self-association, with an equilibrium between hexamer, dihexamer, trihexamer and larger species, while degludec appears as a dihexamer independent of concentration. The solution structure of the detemir trihexamer has a bent shape. The stoichiometry of the association with albumin was studied using DLS. For albumin-detemir the molar stoichiometry was determined to be 1:6 (albumin:detemir ratio) and for albumin-degludec it was between 1:6 and 1:12 (albumin:degludec ratio). Batch SAXS measurements of a 1:6 albumin:detemir concentration series revealed a concentration dependence of complex formation. The data allowed the modelling of a complex between albumin and a detemir hexamer and a complex consisting of two albumins binding to opposite ends of a detemir dihexamer. Measurements of size-exclusion chromatography coupled to SAXS revealed a complex between a degludec dihexamer and albumin. Based on the results, equilibria for the albumin-detemir and albumin-degludec mixtures are proposed. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Data source
| SASBDB page |  SASDEY5 SASDEY5 |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- External links
External links
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
|---|
-Models
| Model #2462 |  Type: atomic / Chi-square value: 1.008 / P-value: 0.000003  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|---|
| Model #2463 |  Type: dummy / Radius of dummy atoms: 2.70 A / Chi-square value: 0.828 / P-value: 0.000106  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: Albumin-insulin detemir 2:12 complex, P1 symmetry / Specimen concentration: 15.6 mg/ml / Entity id: 1320 / 1321 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 8.8 mM Na2HPO4, 10.6 mM m-cresol, 12.2 mM phenol, 140.9 mM glycerol, 56.9 mM NaCl pH: 7.4 |
| Entity #1320 | Type: protein Description: Human Albumin (Recombumin(R) Alpha, Albumedix Ltd.) Formula weight: 66.472 / Num. of mol.: 1 / References: UniProt: P02768 Sequence: DAHKSEVAHR FKDLGEENFK ALVLIAFAQY LQQCPFEDHV KLVNEVTEFA KTCVADESAE NCDKSLHTLF GDKLCTVATL RETYGEMADC CAKQEPERNE CFLQHKDDNP NLPRLVRPEV DVMCTAFHDN EETFLKKYLY EIARRHPYFY APELLFFAKR YKAAFTECCQ ...Sequence: DAHKSEVAHR FKDLGEENFK ALVLIAFAQY LQQCPFEDHV KLVNEVTEFA KTCVADESAE NCDKSLHTLF GDKLCTVATL RETYGEMADC CAKQEPERNE CFLQHKDDNP NLPRLVRPEV DVMCTAFHDN EETFLKKYLY EIARRHPYFY APELLFFAKR YKAAFTECCQ AADKAACLLP KLDELRDEGK ASSAKQRLKC ASLQKFGERA FKAWAVARLS QRFPKAEFAE VSKLVTDLTK VHTECCHGDL LECADDRADL AKYICENQDS ISSKLKECCE KPLLEKSHCI AEVENDEMPA DLPSLAADFV ESKDVCKNYA EAKDVFLGMF LYEYARRHPD YSVVLLLRLA KTYETTLEKC CAAADPHECY AKVFDEFKPL VEEPQNLIKQ NCELFEQLGE YKFQNALLVR YTKKVPQVST PTLVEVSRNL GKVGSKCCKH PEAKRMPCAE DYLSVVLNQL CVLHEKTPVS DRVTKCCTES LVNRRPCFSA LEVDETYVPK EFNAETFTFH ADICTLSEKE RQIKKQTALV ELVKHKPKAT KEQLKAVMDD FAAFVEKCCK ADDKETCFAE EGKKLVAASQ AALGL |
| Entity #1321 | Type: protein / Description: Insulin detemir (Levemir(R), Novo Nordisk A/S) / Formula weight: 5.9 / Num. of mol.: 12 / References: UniProt: P01308 Sequence: GIVEQCCTSI CSLYQLENYC NFVNQHLCGS HLVEALYLVC GERGFFYTPK |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: MAX IV I911-4 / City: Lund / 国: Sweden  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.091 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 1.962 mm / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.091 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 1.962 mm | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Pilatus 1M / Type: Dectris / Pixsize x: 172 mm | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scan |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller