[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9q95: CryoEM structure of bacterial transcription intermediate complex ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9q95 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM structure of bacterial transcription intermediate complex mediated by activator PspF containing nifH promoter DNA containing mismatch from -10 to -1 | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / sigma factor / complex / AAA+ / DNA-binding protein | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of cellular response to stress / DNA-binding transcription activator activity / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / phosphorelay signal transduction system / sigma factor activity / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding ...regulation of cellular response to stress / DNA-binding transcription activator activity / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / phosphorelay signal transduction system / sigma factor activity / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / nucleotidyltransferase activity / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription elongation factor complex / transcription antitermination / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / cell motility / DNA-templated transcription initiation / protein-DNA complex / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / response to heat / protein-containing complex assembly / transcription regulator complex / sequence-specific DNA binding / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / protein dimerization activity / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / response to antibiotic / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA-templated transcription / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Klebsiella pneumoniae (bacteria) Klebsiella pneumoniae (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.8 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gao, F. / Zhang, X. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025Title: Subunit specialization in AAA+ proteins and substrate unfolding during transcription complex remodeling. Authors: Forson Gao / Fuzhou Ye / Martin Buck / Xiaodong Zhang /  Abstract: Bacterial RNA polymerase (RNAP) is a multisubunit enzyme that copies DNA into RNA in a process known as transcription. Bacteria use σ factors to recruit RNAP to promoter regions of genes that need ...Bacterial RNA polymerase (RNAP) is a multisubunit enzyme that copies DNA into RNA in a process known as transcription. Bacteria use σ factors to recruit RNAP to promoter regions of genes that need to be transcribed, with 60% bacteria containing at least one specialized σ factor, σ. σ recruits RNAP to promoters of genes associated with stress responses and forms a stable closed complex that does not spontaneously isomerize to the open state where promoter DNA is melted out and competent for transcription. The σ-mediated open complex formation requires specific AAA+ proteins (TPases ssociated with diverse cellular ctivities) known as bacterial enhancer-binding proteins (bEBPs). We have now obtained structures of new intermediate states of bEBP-bound complexes during transcription initiation, which elucidate the mechanism of DNA melting driven by ATPase activity of bEBPs and suggest a mechanistic model that couples the Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) hydrolysis cycle within the bEBP hexamer with σ unfolding. Our data reveal that bEBP forms a nonplanar hexamer with the hydrolysis-ready subunit located at the furthest/highest point of the spiral hexamer relative to the RNAP. ATP hydrolysis induces conformational changes in bEBP that drives a vectoral transiting of the regulatory N terminus of σ into the bEBP hexamer central pore causing the partial unfolding of σ, while forming specific bEBP contacts with promoter DNA. Furthermore, our data suggest a mechanism of the bEBP AAA+ protein that is distinct from the hand-over-hand mechanism proposed for many other AAA+ proteins, highlighting the versatile mechanisms utilized by the large protein family. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9q95.cif.gz 9q95.cif.gz | 759 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9q95.ent.gz pdb9q95.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9q95.json.gz 9q95.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q9/9q95 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q9/9q95 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q9/9q95 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q9/9q95 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  52918MC  9q91C  9q92C  9q93C  9q94C  9q96C  9q97C 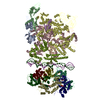 9q98C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 7 molecules 321645M
| #1: Protein | Mass: 31016.430 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | | Mass: 53978.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Klebsiella pneumoniae (bacteria) / Gene: rpoN, KPN_03612 / Production host: Klebsiella pneumoniae (bacteria) / Gene: rpoN, KPN_03612 / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules NT
| #3: DNA chain | Mass: 9826.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
|---|---|
| #4: DNA chain | Mass: 9858.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 4 types, 5 molecules ABCDE
| #5: Protein | Mass: 36558.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #6: Protein | | Mass: 150820.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: rpoB, groN, nitB, rif, ron, stl, stv, tabD, b3987, JW3950 Production host:  #7: Protein | | Mass: 152415.719 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #8: Protein | | Mass: 10249.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 15 molecules 
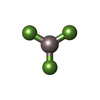



| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #10: Chemical | ChemComp-AF3 / #11: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Subtracted refinement map of conformation 1 of PspF(1-275)-sigma54 bound to nifH DNA (-28 to +35) containing mismatch from -11 to -8. Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#8 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 65353 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION Details: Composite map, 6.8A resolution for global consensus map Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 6.8 Å Stereochemistry target values: REAL-SPACE (WEIGHTED MAP SUM AT ATOM CENTERS) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




























 PDBj
PDBj











































