+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9j22 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | structure of human urea transport protein slc14A1 with urea | ||||||
 Components Components | Urea transporter 1 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / human urea transport protein slc14A1 | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationurea channel activity / water transmembrane transporter activity / urea transport / : / urea transmembrane transporter activity / urea transmembrane transport / establishment of localization in cell / transmembrane transport / basolateral plasma membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.75 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | He, J. / Wang, F. / Zhong, C. / Zhang, P. / Liu, Z. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2025 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2025Title: Structural basis of the bifunctionality of Marinobacter salinexigens ZYF650 glucosylglycerol phosphorylase in glucosylglycerol catabolism. Authors: Di Lu / Keke Zhang / Chen Cheng / Danni Wu / Lei Yin / Quan Luo / Meiyun Shi / Honglei Ma / Xuefeng Lu /  Abstract: 2-O-α-Glucosylglycerol (GG) is a natural heteroside synthesized by many cyanobacteria and a few heterotrophic bacteria under salt stress conditions. Bacteria produce GG in response to stimuli and ...2-O-α-Glucosylglycerol (GG) is a natural heteroside synthesized by many cyanobacteria and a few heterotrophic bacteria under salt stress conditions. Bacteria produce GG in response to stimuli and degrade it once the stimulus diminishes. Heterotrophic bacteria utilize GG phosphorylase (GGP), a member of the GH13_18 family, via a two-step process consisting of phosphorolysis and hydrolysis for GG catabolism. However, the precise mechanism by which GGP degrades GG remains elusive. We determined the 3D structure of a recently identified GGP (MsGGP) of the deep-sea bacterium Marinobacter salinexigens ZYF650, in complex with glucose and glycerol, α-d-glucose-1-phosphate (αGlc1-P), and orthophosphate (inorganic phosphate) at resolutions of 2.5, 2.7, and 2.7 Å, respectively. Notably, the first αGlc1-P complex structure in the GH13_18 family, the complex of MsGGP and αGlc1-P, validates that GGP catalyzes GG decomposition through consecutive phosphorolysis and hydrolysis. In addition, the structure reveals the mechanism of high stereoselectivity on αGlc1-P. Glu231 and Asp190 were identified as the catalytic residues. Interestingly, these structures closely resemble each other, indicating minimal conformational changes upon binding end-product glucose and glycerol, or the intermediate αGlc1-P. The structures also indicate that the substrates may follow a specific trajectory and a precise order toward the active center in close proximity and in a geometrically favorable orientation for catalysis in a double displacement mechanism. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9j22.cif.gz 9j22.cif.gz | 206.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9j22.ent.gz pdb9j22.ent.gz | 166.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9j22.json.gz 9j22.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j2/9j22 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j2/9j22 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j2/9j22 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j2/9j22 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  61086MC  9j1uC  9j24C  9j25C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
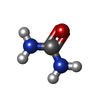
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42566.145 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SLC14A1, HUT11, JK, RACH1, UT1, UTE / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SLC14A1, HUT11, JK, RACH1, UT1, UTE / Production host:  Baculoviridae sp. (virus) / References: UniProt: Q13336 Baculoviridae sp. (virus) / References: UniProt: Q13336#2: Chemical | ChemComp-URE / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-PLM / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of human urea transport protein slc14A1 with urea Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Baculoviridae sp. (virus) Baculoviridae sp. (virus) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: YES / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| EM embedding | Material: water |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 80 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.21rc1_5127: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.75 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 348046 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj