+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9dgg | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
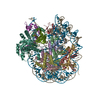
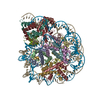
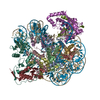
| Title | ncPRC1RYBP bound to unmodified nucleosome | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | NUCLEAR PROTEIN/DNA / DNA complex protein / NUCLEAR PROTEIN-DNA complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhistone H2AK119 ubiquitin ligase activity / PRC1 complex / regulation of kidney development / RING-like zinc finger domain binding / segment specification / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / ubiquitin-protein transferase activator activity / regulation of adaxial/abaxial pattern formation / embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis / somatic stem cell division ...histone H2AK119 ubiquitin ligase activity / PRC1 complex / regulation of kidney development / RING-like zinc finger domain binding / segment specification / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / ubiquitin-protein transferase activator activity / regulation of adaxial/abaxial pattern formation / embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis / somatic stem cell division / sex chromatin / positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus / PcG protein complex / SUMOylation of DNA methylation proteins / gastrulation with mouth forming second / SUMOylation of RNA binding proteins / anterior/posterior axis specification / positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / DNA methylation-dependent constitutive heterochromatin formation / negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / germ cell development / RUNX1 interacts with co-factors whose precise effect on RUNX1 targets is not known / humoral immune response / hemopoiesis / MLL1 complex / negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / cellular response to interleukin-1 / cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus / ubiquitin ligase complex / : / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / heterochromatin / positive regulation of B cell proliferation / SUMOylation of transcription cofactors / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of PTEN gene transcription / promoter-specific chromatin binding / apoptotic signaling pathway / euchromatin / brain development / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation / structural constituent of chromatin / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / mitotic cell cycle / nucleosome assembly / regulation of gene expression / gene expression / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / in utero embryonic development / nuclear body / protein ubiquitination / chromatin remodeling / protein heterodimerization activity / chromatin binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.98 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Godinez-Lopez, V. / Valencia-Sanchez, M.I. / Armache, J.P. / Armache, K.-J. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Read-write mechanisms of H2A ubiquitination by Polycomb repressive complex 1. Authors: Victoria Godínez López / Marco Igor Valencia-Sánchez / Stephen Abini-Agbomson / Jonathan F Thomas / Rachel Lee / Pablo De Ioannes / Brian A Sosa / Jean-Paul Armache / Karim-Jean Armache /  Abstract: Epigenetic inheritance of silent chromatin domains is fundamental to cellular memory during embryogenesis, but it must overcome the dilution of repressive histone modifications during DNA replication. ...Epigenetic inheritance of silent chromatin domains is fundamental to cellular memory during embryogenesis, but it must overcome the dilution of repressive histone modifications during DNA replication. One such modification, histone H2A lysine 119 monoubiquitination (H2AK119Ub), needs to be re-established by the Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1) E3 ligase to restore the silent Polycomb domain. However, the exact mechanism behind this restoration remains unknown. Here, combining cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and functional approaches, we characterize the read-write mechanism of the non-canonical PRC1-containing RYBP (ncPRC1). This mechanism, which functions as a positive-feedback loop in epigenetic regulation, emphasizes the pivotal role of ncPRC1 in restoring H2AK119Ub. We observe an asymmetrical binding of ncPRC1 to H2AK119Ub nucleosomes, guided in part by the N-terminal zinc-finger domain of RYBP binding to residual H2AK119Ub on nascent chromatin. This recognition positions the RING domains of RING1B and BMI1 on the unmodified nucleosome side, enabling recruitment of the E2 enzyme to ubiquitinate H2AK119 within the same nucleosome (intra-nucleosome read-write) or across nucleosomes (inter-nucleosome read-write). Collectively, our findings provide key structural and mechanistic insights into the dynamic interplay of epigenetic regulation, highlighting the significance of ncPRC1 in H2AK119Ub restoration to sustain repressive chromatin domains. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9dgg.cif.gz 9dgg.cif.gz | 364.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9dgg.ent.gz pdb9dgg.ent.gz | 270.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9dgg.json.gz 9dgg.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dg/9dgg https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dg/9dgg ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dg/9dgg ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dg/9dgg | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  46823MC  9dbyC  9ddeC  9dg3C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 6 types, 10 molecules AEBFCGDHKL
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15435.126 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: G103A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #2: Protein | Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #3: Protein | Mass: 14093.436 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: G100R Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #4: Protein | Mass: 13979.291 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: S33T Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #7: Protein | | Mass: 37006.062 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BMI1, PCGF4, RNF51 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BMI1, PCGF4, RNF51 / Production host:  #8: Protein | | Mass: 37706.371 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RNF2, BAP1, DING, HIPI3, RING1B / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RNF2, BAP1, DING, HIPI3, RING1B / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q99496, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 57982.918 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 57488.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 4 molecules 
| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: ncPRC1RYBP bound to unmodified nucleosome / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#8 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1600 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 44.01 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 3304 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1394967 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.98 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 205635 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 PDBj
PDBj