+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 9brs | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Intact V-ATPase State 2 in synaptophysin knock-out isolated synaptic vesicles | |||||||||
 要素 要素 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / V-ATPase / synaptic vesicle | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報Ion channel transport / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Insulin receptor recycling / eye pigmentation / RHOA GTPase cycle / central nervous system maturation / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / transporter activator activity / negative regulation of autophagic cell death ...Ion channel transport / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Insulin receptor recycling / eye pigmentation / RHOA GTPase cycle / central nervous system maturation / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / transporter activator activity / negative regulation of autophagic cell death / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / plasma membrane proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / endosome to plasma membrane protein transport / intracellular organelle / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / lysosomal lumen acidification / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / endosomal lumen acidification / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / vacuolar transport / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / head morphogenesis / osteoclast development / protein localization to cilium / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / dendritic spine membrane / regulation of cellular pH / vacuolar acidification / ATPase complex / autophagosome membrane / microvillus / regulation of MAPK cascade / ATPase activator activity / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / cilium assembly / transmembrane transporter complex / endomembrane system / regulation of macroautophagy / angiotensin maturation / ATP metabolic process / axon terminus / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton transmembrane transport / ruffle / phagocytic vesicle / RNA endonuclease activity / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / Neutrophil degranulation / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / receptor-mediated endocytosis / secretory granule / transmembrane transport / cilium / small GTPase binding / synaptic vesicle membrane / endocytosis / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / melanosome / synaptic vesicle / apical part of cell / myelin sheath / signaling receptor activity / ATPase binding / cell body / postsynaptic membrane / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / 加水分解酵素; エステル加水分解酵素 / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / early endosome / endosome membrane / endosome / nuclear speck / apical plasma membrane / external side of plasma membrane / axon / lysosomal membrane / centrosome / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein-containing complex / mitochondrion / extracellular space / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  | |||||||||
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 4.4 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Wang, C. / Jiang, W. / Yang, K. / Wang, X. / Guo, Q. / Brunger, A.T. | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 2件 米国, 2件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2024 ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2024タイトル: Structure and topography of the synaptic V-ATPase-synaptophysin complex. 著者: Chuchu Wang / Wenhong Jiang / Jeremy Leitz / Kailu Yang / Luis Esquivies / Xing Wang / Xiaotao Shen / Richard G Held / Daniel J Adams / Tamara Basta / Lucas Hampton / Ruiqi Jian / Lihua Jiang ...著者: Chuchu Wang / Wenhong Jiang / Jeremy Leitz / Kailu Yang / Luis Esquivies / Xing Wang / Xiaotao Shen / Richard G Held / Daniel J Adams / Tamara Basta / Lucas Hampton / Ruiqi Jian / Lihua Jiang / Michael H B Stowell / Wolfgang Baumeister / Qiang Guo / Axel T Brunger /     要旨: Synaptic vesicles are organelles with a precisely defined protein and lipid composition, yet the molecular mechanisms for the biogenesis of synaptic vesicles are mainly unknown. Here we discovered a ...Synaptic vesicles are organelles with a precisely defined protein and lipid composition, yet the molecular mechanisms for the biogenesis of synaptic vesicles are mainly unknown. Here we discovered a well-defined interface between the synaptic vesicle V-ATPase and synaptophysin by in situ cryo-electron tomography and single-particle cryo-electron microscopy of functional synaptic vesicles isolated from mouse brains. The synaptic vesicle V-ATPase is an ATP-dependent proton pump that establishes the proton gradient across the synaptic vesicle, which in turn drives the uptake of neurotransmitters. Synaptophysin and its paralogues synaptoporin and synaptogyrin belong to a family of abundant synaptic vesicle proteins whose function is still unclear. We performed structural and functional studies of synaptophysin-knockout mice, confirming the identity of synaptophysin as an interaction partner with the V-ATPase. Although there is little change in the conformation of the V-ATPase upon interaction with synaptophysin, the presence of synaptophysin in synaptic vesicles profoundly affects the copy number of V-ATPases. This effect on the topography of synaptic vesicles suggests that synaptophysin assists in their biogenesis. In support of this model, we observed that synaptophysin-knockout mice exhibit severe seizure susceptibility, suggesting an imbalance of neurotransmitter release as a physiological consequence of the absence of synaptophysin. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  9brs.cif.gz 9brs.cif.gz | 1.4 MB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb9brs.ent.gz pdb9brs.ent.gz | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 | |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  9brs.json.gz 9brs.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/br/9brs https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/br/9brs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/br/9brs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/br/9brs | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  44842MC  9braC 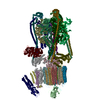 9brqC  9brrC  9brtC 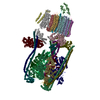 9bruC 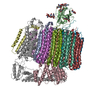 9bryC 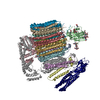 9brzC M: このデータのモデリングに利用したマップデータ C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
-V-type proton ATPase ... , 14種, 30分子 89QRTV6UaeXdcbghijklmno1204537
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 26196.449 Da / 分子数: 3 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: VATE1_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase subunit E 1 / 由来: (天然)  #2: タンパク質 | 分子量: 13674.476 Da / 分子数: 3 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: VATG2_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase subunit G 2 / 由来: (天然)  #3: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 43945.449 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: VATC1_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase subunit C 1 / 由来: (天然)  #4: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 55922.859 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: VATH_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase subunit H / 由来: (天然)  #5: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 96442.500 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 天然 詳細: VPP1_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 1 由来: (天然)  #6: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 9203.020 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: VA0E2_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase subunit e 2 / 由来: (天然)  #8: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 13389.262 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: VATF_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase subunit F / 由来: (天然)  #9: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 40341.934 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: VA0D1_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase subunit d 1 / 由来: (天然)  #10: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 51046.215 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: VAS1_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase subunit S1 / 由来: (天然)  #12: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 21618.553 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 天然 詳細: VATO_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase 21 kDa proteolipid subunit 由来: (天然)  #13: タンパク質 | 分子量: 15815.833 Da / 分子数: 9 / 由来タイプ: 天然 詳細: VATL_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase 16 kDa proteolipid subunit 由来: (天然)  #14: タンパク質 | 分子量: 68402.875 Da / 分子数: 3 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: VATA_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A / 由来: (天然)  #15: タンパク質 | 分子量: 56611.570 Da / 分子数: 3 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: VATB2_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase subunit B / 由来: (天然)  #16: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 28419.117 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: VATD_MOUSE V-type proton ATPase subunit D / 由来: (天然)  |
|---|
-タンパク質 , 2種, 2分子 fp
| #7: タンパク質 | 分子量: 11000.004 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: RNK_MOUSE Ribonuclease kappa / 由来: (天然)  参照: UniProt: Q8K3C0, 加水分解酵素; エステル加水分解酵素 |
|---|---|
| #11: タンパク質 | 分子量: 39128.789 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 詳細: RENR_MOUSE Renin receptor / 由来: (天然)  |
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: CELL / 3次元再構成法: 単粒子再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 | 名称: Synaptophysin knock-out mouse brain isolated glutamatergic synaptic vesicles タイプ: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: all / 由来: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 実験値: NO |
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  |
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.4 |
| 試料 | 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES 詳細: The specimen state should be an intact subcellular component. |
| 急速凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: TFS KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2000 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 800 nm |
| 撮影 | 電子線照射量: 50 e/Å2 フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- 解析
解析
| ソフトウェア | 名称: PHENIX / バージョン: 1.21.1_5286: / 分類: 精密化 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMソフトウェア |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF補正 | タイプ: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3次元再構成 | 解像度: 4.4 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 30487 / 対称性のタイプ: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 原子モデル構築 | プロトコル: FLEXIBLE FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 拘束条件 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー













 PDBj
PDBj











