[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-44845: V0-only V-ATPase in synaptophysin gene knock-out mouse brain isol... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | V0-only V-ATPase in synaptophysin gene knock-out mouse brain isolated synaptic vesicles | |||||||||
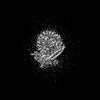
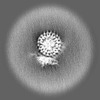
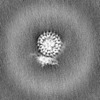
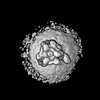
 Map data Map data | Full map of V0-only V-ATPase in SYP-KO ISVs. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | V0only V-ATPase / synaptic vesicle / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationIon channel transport / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Insulin receptor recycling / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production ...Ion channel transport / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Insulin receptor recycling / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production / RHOA GTPase cycle / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / endosome to plasma membrane protein transport / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / lysosomal lumen acidification / endosomal lumen acidification / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / head morphogenesis / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / osteoclast development / vacuolar acidification / dendritic spine membrane / ATPase activator activity / regulation of MAPK cascade / autophagosome membrane / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / cilium assembly / regulation of macroautophagy / transporter activator activity / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / angiotensin maturation / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / Neutrophil degranulation / endomembrane system / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / RNA endonuclease activity / proton transmembrane transport / receptor-mediated endocytosis / axon terminus / small GTPase binding / melanosome / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / synaptic vesicle membrane / signaling receptor activity / ATPase binding / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / early endosome / postsynaptic membrane / apical plasma membrane / endosome / endosome membrane / nuclear speck / external side of plasma membrane / axon / lysosomal membrane / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / centrosome / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / Golgi apparatus / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang C / Jiang W / Yang K / Wang X / Guo Q / Brunger AT | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Structure and topography of the synaptic V-ATPase-synaptophysin complex. Authors: Chuchu Wang / Wenhong Jiang / Jeremy Leitz / Kailu Yang / Luis Esquivies / Xing Wang / Xiaotao Shen / Richard G Held / Daniel J Adams / Tamara Basta / Lucas Hampton / Ruiqi Jian / Lihua ...Authors: Chuchu Wang / Wenhong Jiang / Jeremy Leitz / Kailu Yang / Luis Esquivies / Xing Wang / Xiaotao Shen / Richard G Held / Daniel J Adams / Tamara Basta / Lucas Hampton / Ruiqi Jian / Lihua Jiang / Michael H B Stowell / Wolfgang Baumeister / Qiang Guo / Axel T Brunger /     Abstract: Synaptic vesicles are organelles with a precisely defined protein and lipid composition, yet the molecular mechanisms for the biogenesis of synaptic vesicles are mainly unknown. Here we discovered a ...Synaptic vesicles are organelles with a precisely defined protein and lipid composition, yet the molecular mechanisms for the biogenesis of synaptic vesicles are mainly unknown. Here we discovered a well-defined interface between the synaptic vesicle V-ATPase and synaptophysin by in situ cryo-electron tomography and single-particle cryo-electron microscopy of functional synaptic vesicles isolated from mouse brains. The synaptic vesicle V-ATPase is an ATP-dependent proton pump that establishes the proton gradient across the synaptic vesicle, which in turn drives the uptake of neurotransmitters. Synaptophysin and its paralogues synaptoporin and synaptogyrin belong to a family of abundant synaptic vesicle proteins whose function is still unclear. We performed structural and functional studies of synaptophysin-knockout mice, confirming the identity of synaptophysin as an interaction partner with the V-ATPase. Although there is little change in the conformation of the V-ATPase upon interaction with synaptophysin, the presence of synaptophysin in synaptic vesicles profoundly affects the copy number of V-ATPases. This effect on the topography of synaptic vesicles suggests that synaptophysin assists in their biogenesis. In support of this model, we observed that synaptophysin-knockout mice exhibit severe seizure susceptibility, suggesting an imbalance of neurotransmitter release as a physiological consequence of the absence of synaptophysin. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44845.map.gz emd_44845.map.gz | 86.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44845-v30.xml emd-44845-v30.xml emd-44845.xml emd-44845.xml | 28.3 KB 28.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_44845.png emd_44845.png | 156.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44845.cif.gz emd-44845.cif.gz | 7.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44845_additional_1.map.gz emd_44845_additional_1.map.gz emd_44845_additional_2.map.gz emd_44845_additional_2.map.gz emd_44845_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44845_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44845_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44845_half_map_2.map.gz | 81.9 MB 71.3 MB 84.5 MB 84.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44845 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44845 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44845 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44845 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9bryMC  9braC  9brqC  9brrC  9brsC  9brtC  9bruC  9brzC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44845.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44845.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Full map of V0-only V-ATPase in SYP-KO ISVs. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
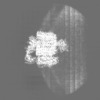
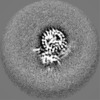
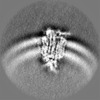
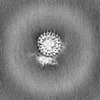
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1064 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
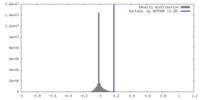
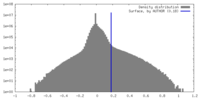
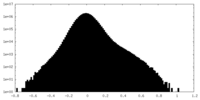
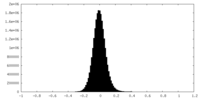
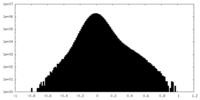
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: EMhancer full map of V0-only V-ATPase in SYP-KO ISVs.
| File | emd_44845_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | EMhancer full map of V0-only V-ATPase in SYP-KO ISVs. | ||||||||||||
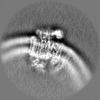
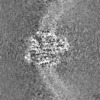
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Unsharpened map
| File | emd_44845_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened map | ||||||||||||
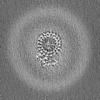
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B of V0-only V-ATPase in SYP-KO ISVs.
| File | emd_44845_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B of V0-only V-ATPase in SYP-KO ISVs. | ||||||||||||
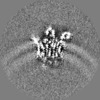
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A of V0-only V-ATPase in SYP-KO ISVs.
| File | emd_44845_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A of V0-only V-ATPase in SYP-KO ISVs. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Syptophysin gene knock-out mouse brain isolated glutamatergic syn...
+Supramolecule #1: Syptophysin gene knock-out mouse brain isolated glutamatergic syn...
+Macromolecule #1: V-type proton ATPase subunit S1
+Macromolecule #2: V-type proton ATPase 21 kDa proteolipid subunit c''
+Macromolecule #3: V-type proton ATPase subunit d 1
+Macromolecule #4: Ribonuclease kappa
+Macromolecule #5: V-type proton ATPase 16 kDa proteolipid subunit c
+Macromolecule #6: Renin receptor cytoplasmic fragment
+Macromolecule #7: V-type proton ATPase subunit e 2
+Macromolecule #8: V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a 1
+Macromolecule #11: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
+Macromolecule #12: beta-D-mannopyranose
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | cell |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
| Details | The specimen state should be an intact subcellular component. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 53390 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: RANDOM ASSIGNMENT |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | The initial model is the model of wild-type V0-only V-ATPase. For fitting and refinement details, see https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07610-x. |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-9bry: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)