[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8tln: STRUCTURAL COMPARISON SUGGESTS THAT THERMOLYSIN AND RELATED NEUTR... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8tln | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
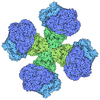
| Title | STRUCTURAL COMPARISON SUGGESTS THAT THERMOLYSIN AND RELATED NEUTRAL PROTEASES UNDERGO HINGE-BENDING MOTION DURING CATALYSIS | |||||||||
 Components Components | THERMOLYSIN | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE(METALLOPROTEINASE) | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationthermolysin / metalloendopeptidase activity / proteolysis / extracellular region / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Resolution: 1.6 Å X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Resolution: 1.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Tronrud, D. / Matthews, B.W. | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1992 Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1992Title: Structural comparison suggests that thermolysin and related neutral proteases undergo hinge-bending motion during catalysis. Authors: Holland, D.R. / Tronrud, D.E. / Pley, H.W. / Flaherty, K.M. / Stark, W. / Jansonius, J.N. / McKay, D.B. / Matthews, B.W. #1:  Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 1982 Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 1982Title: Structure of Thermolysin Refined at 1.6 Angstroms Resolution Authors: Holmes, M.A. / Matthews, B.W. #2:  Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1982 Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1982Title: Structure of a Mercaptan-Thermolysin Complex Illustrates Mode of Inhibition of Zinc Proteases by Substrate-Analogue Mercaptans Authors: Monzingo, A.F. / Matthews, B.W. #3:  Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1981 Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1981Title: Binding of Hydroxamic Acid Inhibitors to Crystalline Thermolysin Suggests a Pentacoordinate Zinc Intermediate in Catalysis Authors: Holmes, M.A. / Matthews, B.W. #4:  Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 1979 Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 1979Title: Binding of the Biproduct Analog L-Benzylsuccinic Acid to Thermolysin Determined by X-Ray Crystallography Authors: Bolognesi, M.C. / Matthews, B.W. #5:  Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 1977 Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 1977Title: Comparison of the Structures of Carboxypeptidase a and Thermolysin Authors: Kester, W.R. / Matthews, B.W. #6:  Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 1977 Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 1977Title: A Crystallographic Study of the Complex of Phosphoramidon with Thermolysin. A Model for the Presumed Catalytic Transition State and for the Binding of Extended Substrates Authors: Weaver, L.H. / Kester, W.R. / Matthews, B.W. #7:  Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1977 Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1977Title: Crystallographic Study of the Binding of Dipeptide Inhibitors to Thermolysin. Implications for the Mechanism of Catalysis Authors: Kester, W.R. / Matthews, B.W. #8:  Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1976 Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1976Title: Role of Calcium in the Thermal Stability of Thermolysin Authors: Dahlquist, F.W. / Long, J.W. / Bigbee, W.L. #9:  Journal: Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA / Year: 1975 Journal: Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA / Year: 1975Title: Evidence of Homologous Relationship between Thermolysin and Neutral Protease a of Bacillus Subtilis Authors: Levy, P.L. / Pangburn, M.K. / Burstein, Y. / Ericsson, L.H. / Neurath, H. / Walsh, K.A. #10:  Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 1974 Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 1974Title: The Conformation of Thermolysin Authors: Matthews, B.W. / Weaver, L.H. / Kester, W.R. #11:  Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1974 Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 1974Title: Binding of Lanthanide Ions to Thermolysin Authors: Matthews, B.W. / Weaver, L.H. #12:  Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 1972 Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 1972Title: The Structure of Thermolysin,an Electron Density Map at 2.3 Angstroms Resolution Authors: Colman, P.M. / Jansonius, J.N. / Matthews, B.W. #13:  Journal: Nature New Biol. / Year: 1972 Journal: Nature New Biol. / Year: 1972Title: Amino-Acid Sequence of Thermolysin Authors: Titani, K. / Hermodson, M.A. / Ericsson, L.H. / Walsh, K.A. / Neurath, H. #14:  Journal: Nature New Biol. / Year: 1972 Journal: Nature New Biol. / Year: 1972Title: Three Dimensional Structure of Thermolysin Authors: Matthews, B.W. / Jansonius, J.N. / Colman, P.M. / Schoenborn, B.P. / Duporque, D. #15:  Journal: Nature New Biol. / Year: 1972 Journal: Nature New Biol. / Year: 1972Title: Structure of Thermolysin Authors: Matthews, B.W. / Colman, P.M. / Jansonius, J.N. / Titani, K. / Walsh, K.A. / Neurath, H. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8tln.cif.gz 8tln.cif.gz | 80.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8tln.ent.gz pdb8tln.ent.gz | 59.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8tln.json.gz 8tln.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tl/8tln https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tl/8tln ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tl/8tln ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tl/8tln | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
| ||||||||
| Atom site foot note | 1: RESIDUE PRO E 51 IS A CIS PROLINE. | ||||||||
| Components on special symmetry positions |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules E
| #1: Protein | Mass: 34362.305 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 6 types, 165 molecules 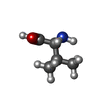








| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-VAL / | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-LYS / | ||||||
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / | #6: Chemical | ChemComp-DMS / | #7: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
-Details
| Nonpolymer details | RESIDUES 1321 AND 1322 FORM A DIPEPTIDE (VAL-LYS) BOUND IN THE ACTIVE SITE OF THE MOLECULE. IT IS ...RESIDUES 1321 AND 1322 FORM A DIPEPTIDE (VAL-LYS) BOUND IN THE ACTIVE SITE OF THE MOLECULE. IT IS PRESUMED THAT THE ORIGIN OF THIS DIPEPTIDE IS THE C-TERMINAL TWO RESIDUES OF THE PROTEIN. SINCE THE C-TERMINUS APPEARS AT FULL OCCUPANCY, MOLECULES NOT INCORPORAT |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION X-RAY DIFFRACTION |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.43 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 49.29 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal grow | *PLUS pH: 7.2 / Method: unknown | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of the solutions | *PLUS
|
-Data collection
| Radiation | Scattering type: x-ray |
|---|---|
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | *PLUS Highest resolution: 1.6 Å / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.163 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: TNT / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Resolution: 1.6→20 Å / Rfactor obs: 0.165 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.6→20 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Software | *PLUS Name: TNT / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | *PLUS Rfactor obs: 0.165 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints | *PLUS
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj