+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ots | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
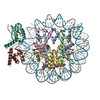
| Title | OCT4 and MYC-MAX co-bound to a nucleosome | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMad-Max complex / cell fate commitment involved in formation of primary germ layer / positive regulation of metanephric cap mesenchymal cell proliferation / positive regulation of acinar cell proliferation / acinar cell proliferation / negative regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / SCF ubiquitin ligase complex binding / NK T cell proliferation / cardiac cell fate determination / Myc-Max complex ...Mad-Max complex / cell fate commitment involved in formation of primary germ layer / positive regulation of metanephric cap mesenchymal cell proliferation / positive regulation of acinar cell proliferation / acinar cell proliferation / negative regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / SCF ubiquitin ligase complex binding / NK T cell proliferation / cardiac cell fate determination / Myc-Max complex / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG repress genes related to differentiation / Formation of the anterior neural plate / endodermal-mesodermal cell signaling / regulation of asymmetric cell division / endodermal cell fate specification / regulation of somatic stem cell population maintenance / regulation of cell cycle process / Binding of TCF/LEF:CTNNB1 to target gene promoters / cellular response to interferon-alpha / RNA polymerase II transcription repressor complex / heart induction / Specification of primordial germ cells / myotube differentiation / positive regulation of B cell apoptotic process / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG activate genes related to proliferation / RUNX3 regulates WNT signaling / TFAP2 (AP-2) family regulates transcription of cell cycle factors / Specification of the neural plate border / Transcriptional regulation of pluripotent stem cells / negative regulation of cell division / negative regulation of monocyte differentiation / Germ layer formation at gastrulation / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound / response to growth factor / response to alkaloid / B cell apoptotic process / transcription regulator activator activity / protein-DNA complex disassembly / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / negative regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade / fibroblast apoptotic process / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / Regulation of NFE2L2 gene expression / regulation of telomere maintenance / miRNA binding / positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation / skeletal system morphogenesis / middle ear morphogenesis / Signaling by ALK / branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis / negative regulation of gene expression via chromosomal CpG island methylation / pigmentation / rRNA metabolic process / E-box binding / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / positive regulation of telomere maintenance / skeletal muscle cell differentiation / MLL1 complex / blastocyst development / somatic stem cell population maintenance / anatomical structure morphogenesis / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / BMP signaling pathway / chromosome organization / positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / Cyclin E associated events during G1/S transition / core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / telomere organization / Interleukin-7 signaling / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Meiotic synapsis / negative regulation of miRNA transcription / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / DNA methylation / bioluminescence / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / SMAD2/SMAD3:SMAD4 heterotrimer regulates transcription / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / innate immune response in mucosa Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Michael, A.K. / Stoos, L. / Kempf, G. / Cavadini, S. / Thoma, N. | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  France, 2items France, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Cooperation between bHLH transcription factors and histones for DNA access. Authors: Alicia K Michael / Lisa Stoos / Priya Crosby / Nikolas Eggers / Xinyu Y Nie / Kristina Makasheva / Martina Minnich / Kelly L Healy / Joscha Weiss / Georg Kempf / Simone Cavadini / Lukas ...Authors: Alicia K Michael / Lisa Stoos / Priya Crosby / Nikolas Eggers / Xinyu Y Nie / Kristina Makasheva / Martina Minnich / Kelly L Healy / Joscha Weiss / Georg Kempf / Simone Cavadini / Lukas Kater / Jan Seebacher / Luca Vecchia / Deyasini Chakraborty / Luke Isbel / Ralph S Grand / Florian Andersch / Jennifer L Fribourgh / Dirk Schübeler / Johannes Zuber / Andrew C Liu / Peter B Becker / Beat Fierz / Carrie L Partch / Jerome S Menet / Nicolas H Thomä /     Abstract: The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family of transcription factors recognizes DNA motifs known as E-boxes (CANNTG) and includes 108 members. Here we investigate how chromatinized E-boxes are engaged ...The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family of transcription factors recognizes DNA motifs known as E-boxes (CANNTG) and includes 108 members. Here we investigate how chromatinized E-boxes are engaged by two structurally diverse bHLH proteins: the proto-oncogene MYC-MAX and the circadian transcription factor CLOCK-BMAL1 (refs. ). Both transcription factors bind to E-boxes preferentially near the nucleosomal entry-exit sites. Structural studies with engineered or native nucleosome sequences show that MYC-MAX or CLOCK-BMAL1 triggers the release of DNA from histones to gain access. Atop the H2A-H2B acidic patch, the CLOCK-BMAL1 Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) dimerization domains engage the histone octamer disc. Binding of tandem E-boxes at endogenous DNA sequences occurs through direct interactions between two CLOCK-BMAL1 protomers and histones and is important for circadian cycling. At internal E-boxes, the MYC-MAX leucine zipper can also interact with histones H2B and H3, and its binding is indirectly enhanced by OCT4 elsewhere on the nucleosome. The nucleosomal E-box position and the type of bHLH dimerization domain jointly determine the histone contact, the affinity and the degree of competition and cooperativity with other nucleosome-bound factors. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ots.cif.gz 8ots.cif.gz | 361.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ots.ent.gz pdb8ots.ent.gz | 265 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ots.json.gz 8ots.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8ots_validation.pdf.gz 8ots_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8ots_full_validation.pdf.gz 8ots_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8ots_validation.xml.gz 8ots_validation.xml.gz | 43.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8ots_validation.cif.gz 8ots_validation.cif.gz | 68.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ot/8ots https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ot/8ots ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ot/8ots ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ot/8ots | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  17183MC  8osjC  8oskC  8oslC 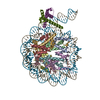 8ottC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 7 types, 11 molecules AEBFCGDHKMN
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15719.445 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H3A, H3FA, HIST1H3B, H3FL, HIST1H3C, H3FC, HIST1H3D, H3FB, HIST1H3E, H3FD, HIST1H3F, H3FI, HIST1H3G, H3FH, HIST1H3H, H3FK, HIST1H3I, H3FF, HIST1H3J, H3FJ Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 11676.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, ...Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, H4FE, HIST1H4K, H4/D, H4FD, HIST1H4L, H4/K, H4FK, HIST2H4A, H4/N, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, HIST2H4B, H4/O, H4FO, HIST4H4 Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 14447.825 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AB, H2AFM, HIST1H2AE, H2AFA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AB, H2AFM, HIST1H2AE, H2AFA / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 14088.336 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BJ, H2BFR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BJ, H2BFR / Production host:  #7: Protein | | Mass: 59814.410 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: GFP, POU5F1, OCT3, OCT4, OTF3 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P42212, UniProt: Q01860 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P42212, UniProt: Q01860#8: Protein | | Mass: 11501.192 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MYC, BHLHE39 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MYC, BHLHE39 / Production host:  #9: Protein | | Mass: 9780.037 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MAX, BHLHD4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MAX, BHLHD4 / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 39092.895 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 39298.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 8 molecules 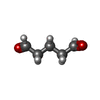
| #10: Chemical | ChemComp-PTD / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 102411 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj