[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8axl: Outer membrane secretin pore of the type 3 secretion system of Sh... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8axl | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
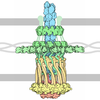
| Title | Outer membrane secretin pore of the type 3 secretion system of Shigella flexneri | ||||||
 Components Components | Outer membrane protein MxiD | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN TRANSPORT / type 3 secretion / secretin / outer membrane ring / shigella / infection | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtype III protein secretion system complex / type II protein secretion system complex / protein secretion by the type III secretion system / cell outer membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Shigella flexneri (bacteria) Shigella flexneri (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.42 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lunelli, M. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Protein Sci / Year: 2023 Journal: Protein Sci / Year: 2023Title: Integrative structural analysis of the type III secretion system needle complex from Shigella flexneri. Authors: Lara Flacht / Michele Lunelli / Karol Kaszuba / Zhuo Angel Chen / Francis J O' Reilly / Juri Rappsilber / Jan Kosinski / Michael Kolbe /   Abstract: The type III secretion system (T3SS) is a large, transmembrane protein machinery used by various pathogenic gram-negative bacteria to transport virulence factors into the host cell during infection. ...The type III secretion system (T3SS) is a large, transmembrane protein machinery used by various pathogenic gram-negative bacteria to transport virulence factors into the host cell during infection. Understanding the structure of T3SSs is crucial for future developments of therapeutics that could target this system. However, much of the knowledge about the structure of T3SS is available only for Salmonella, and it is unclear how this large assembly is conserved across species. Here, we combined cryo-electron microscopy, cross-linking mass spectrometry, and integrative modeling to determine the structure of the T3SS needle complex from Shigella flexneri. We show that the Shigella T3SS exhibits unique features distinguishing it from other structurally characterized T3SSs. The secretin pore complex adopts a new fold of its C-terminal S domain and the pilotin MxiM[SctG] locates around the outer surface of the pore. The export apparatus structure exhibits a conserved pseudohelical arrangement but includes the N-terminal domain of the SpaS[SctU] subunit, which was not present in any of the previously published virulence-related T3SS structures. Similar to other T3SSs, however, the apparatus is anchored within the needle complex by a network of flexible linkers that either adjust conformation to connect to equivalent patches on the secretin oligomer or bind distinct surface patches at the same height of the export apparatus. The conserved and unique features delineated by our analysis highlight the necessity to analyze T3SS in a species-specific manner, in order to fully understand the underlying molecular mechanisms of these systems. The structure of the type III secretion system from Shigella flexneri delineates conserved and unique features, which could be used for the development of broad-range therapeutics. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8axl.cif.gz 8axl.cif.gz | 844.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8axl.ent.gz pdb8axl.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8axl.json.gz 8axl.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ax/8axl https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ax/8axl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ax/8axl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ax/8axl | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  15701MC  8axkC  8axnC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 63230.414 Da / Num. of mol.: 15 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Shigella flexneri (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q04641 Shigella flexneri (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q04641Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 101179 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1.5 sec. / Electron dose: 25 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 5238 |
| Image scans | Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 / Movie frames/image: 7 / Used frames/image: 1-6 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18.2_3874: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C15 (15 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.42 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 69589 Details: Focused reconstruction obtained after partial signal subtraction. Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 72.8 / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj