+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7rl6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
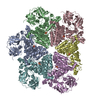
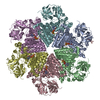
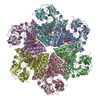
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of human p97-R155H mutant bound to ADP. | ||||||
 Components Components | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / p97 / VCP / TERA / Inhibitor / CB-5083 | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / flavin adenine dinucleotide catabolic process / VCP-NSFL1C complex / endosome to lysosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway / endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced pre-emptive quality control / BAT3 complex binding / cellular response to arsenite ion / protein-DNA covalent cross-linking repair / Derlin-1 retrotranslocation complex / positive regulation of protein K63-linked deubiquitination ...: / flavin adenine dinucleotide catabolic process / VCP-NSFL1C complex / endosome to lysosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway / endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced pre-emptive quality control / BAT3 complex binding / cellular response to arsenite ion / protein-DNA covalent cross-linking repair / Derlin-1 retrotranslocation complex / positive regulation of protein K63-linked deubiquitination / cytoplasm protein quality control / : / positive regulation of oxidative phosphorylation / aggresome assembly / deubiquitinase activator activity / mitotic spindle disassembly / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity / regulation of protein localization to chromatin / VCP-NPL4-UFD1 AAA ATPase complex / cellular response to misfolded protein / positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / vesicle-fusing ATPase / K48-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / regulation of aerobic respiration / retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol / stress granule disassembly / ATPase complex / regulation of synapse organization / ubiquitin-specific protease binding / positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process / MHC class I protein binding / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / RHOH GTPase cycle / polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / autophagosome maturation / endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / negative regulation of hippo signaling / HSF1 activation / translesion synthesis / negative regulation of protein localization to chromatin / interstrand cross-link repair / ATP metabolic process / endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / proteasomal protein catabolic process / Protein methylation / Attachment and Entry / ERAD pathway / lipid droplet / proteasome complex / viral genome replication / Josephin domain DUBs / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / macroautophagy / establishment of protein localization / Hh mutants are degraded by ERAD / positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / ADP binding / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / autophagy / cytoplasmic stress granule / Aggrephagy / azurophil granule lumen / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / Ovarian tumor domain proteases / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / double-strand break repair / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / cellular response to heat / site of double-strand break / Neddylation / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / secretory granule lumen / protein phosphatase binding / regulation of apoptotic process / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Attachment and Entry / protein ubiquitination / ciliary basal body / protein domain specific binding / DNA repair / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / DNA damage response / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / lipid binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / glutamatergic synapse / endoplasmic reticulum / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein-containing complex / RNA binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Caffrey, B. / Zhu, X. / Berezuk, A. / Tuttle, K. / Chittori, S. / Subramaniam, S. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2021 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2021Title: AAA+ ATPase p97/VCP mutants and inhibitor binding disrupt inter-domain coupling and subsequent allosteric activation. Authors: Brian Caffrey / Xing Zhu / Alison Berezuk / Katharine Tuttle / Sagar Chittori / Sriram Subramaniam /  Abstract: The human AAA+ ATPase p97, also known as valosin-containing protein, a potential target for cancer therapeutics, plays a vital role in the clearing of misfolded proteins. p97 dysfunction is also ...The human AAA+ ATPase p97, also known as valosin-containing protein, a potential target for cancer therapeutics, plays a vital role in the clearing of misfolded proteins. p97 dysfunction is also known to play a crucial role in several neurodegenerative disorders, such as MultiSystem Proteinopathy 1 (MSP-1) and Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). However, the structural basis of its role in such diseases remains elusive. Here, we present cryo-EM structural analyses of four disease mutants p97, p97, p97, p97, as well as p97, implicated in resistance to the drug CB-5083, a potent p97 inhibitor. Our cryo-EM structures demonstrate that these mutations affect nucleotide-driven allosteric activation across the three principal p97 domains (N, D1, and D2) by predominantly interfering with either (1) the coupling between the D1 and N-terminal domains (p97 and p97), (2) the interprotomer interactions (p97), or (3) the coupling between D1 and D2 nucleotide domains (p97, p97). We also show that binding of the competitive inhibitor, CB-5083, to the D2 domain prevents conformational changes similar to those seen for mutations that affect coupling between the D1 and D2 domains. Our studies enable tracing of the path of allosteric activation across p97 and establish a common mechanistic link between active site inhibition and defects in allosteric activation by disease-causing mutations and have potential implications for the design of novel allosteric compounds that can modulate p97 function. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7rl6.cif.gz 7rl6.cif.gz | 749.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7rl6.ent.gz pdb7rl6.ent.gz | 627.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7rl6.json.gz 7rl6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rl/7rl6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rl/7rl6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rl/7rl6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rl/7rl6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 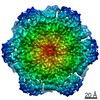 24518MC 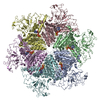 7rl7C  7rl9C  7rlaC  7rlbC  7rlcC  7rldC  7rlfC  7rlgC  7rlhC  7rliC  7rljC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 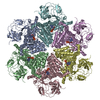
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 91472.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Mutation: R155H Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: VCP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: VCP / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / Has ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: 2D ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Full-length Hexameric p97-R155H mutant / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.540 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 / Details: Protein Storage Buffer with ADP. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 4410 |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 629745 |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C6 (6 fold cyclic) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 146973 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 PDBj
PDBj















