+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7pkd | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | C-reactive protein decamer at pH 7.5 with phosphocholine ligand | ||||||
 Components Components | C-reactive protein | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / C-reactive protein / CRP / innate immunity | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of interleukin-8 production / opsonization / complement component C1q complex binding / low-density lipoprotein particle binding / vasoconstriction / choline binding / negative regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation / Classical antibody-mediated complement activation / low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding / negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation ...regulation of interleukin-8 production / opsonization / complement component C1q complex binding / low-density lipoprotein particle binding / vasoconstriction / choline binding / negative regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation / Classical antibody-mediated complement activation / low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding / negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / negative regulation of lipid storage / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / acute-phase response / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / inflammatory response / innate immune response / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / extracellular space / extracellular region / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Noone, D.P. / Sharp, T.H. | ||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Front Immunol / Year: 2021 Journal: Front Immunol / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-Electron Microscopy and Biochemical Analysis Offer Insights Into the Effects of Acidic pH, Such as Occur During Acidosis, on the Complement Binding Properties of C-Reactive Protein. Authors: Dylan P Noone / Tijn T van der Velden / Thomas H Sharp /  Abstract: The pentraxin family of proteins includes C-reactive protein (CRP), a canonical marker for the acute phase inflammatory response. As compared to normal physiological conditions in human serum, under ...The pentraxin family of proteins includes C-reactive protein (CRP), a canonical marker for the acute phase inflammatory response. As compared to normal physiological conditions in human serum, under conditions associated with damage and inflammation, such as acidosis and the oxidative burst, CRP exhibits modulated biochemical properties that may have a structural basis. Here, we explore how pH and ligand binding affect the structure and biochemical properties of CRP. Cryo-electron microscopy was used to solve structures of CRP at pH 7.5 or pH 5 and in the presence or absence of the ligand phosphocholine (PCh), which yielded 7 new high-resolution structures of CRP, including pentameric and decameric complexes. Structures previously derived from crystallography were imperfect pentagons, as shown by the variable angles between each subunit, whereas pentameric CRP derived from cryoEM was found to have C5 symmetry, with subunits forming a regular pentagon with equal angles. This discrepancy indicates flexibility at the interfaces of monomers that may relate to activation of the complement system by the C1 complex. CRP also appears to readily decamerise in solution into dimers of pentamers, which obscures the postulated binding sites for C1. Subtle structural rearrangements were observed between the conditions tested, including a putative change in histidine protonation that may prime the disulphide bridges for reduction and enhanced ability to activate the immune system. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays showed that CRP had markedly increased association to the C1 complex and immunoglobulins under conditions associated with acidosis, whilst a reduction in the Ca concentration lowered this pH-sensitivity for C1q, but not immunoglobulins, suggesting different modes of binding. These data suggest a model whereby a change in the ionic nature of CRP and immunological proteins can make it more adhesive to potential ligands without large structural rearrangements. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7pkd.cif.gz 7pkd.cif.gz | 666 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7pkd.ent.gz pdb7pkd.ent.gz | 562.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7pkd.json.gz 7pkd.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pk/7pkd https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pk/7pkd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pk/7pkd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pk/7pkd | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  13468MC  7pk9C  7pkbC  7pkeC  7pkfC  7pkgC  7pkhC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 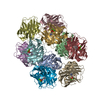
|
|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
| 2 | 
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 23068.039 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CRP, PTX1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CRP, PTX1 / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-PC / #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: C-reactive protein decamer with phosphocholine ligand / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.230 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 65 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.25 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 4599 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Details: Gatan BioQuantum K3 / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18.2_3874: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 932224 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 167957 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 1B09 Accession code: 1B09 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 PDBj
PDBj