[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
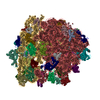
Yorodumi- PDB-7ood: Mycoplasma pneumoniae 50S subunit of ribosomes in chloramphenicol... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ood | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Mycoplasma pneumoniae 50S subunit of ribosomes in chloramphenicol-treated cells | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / In-cell cryo-electron tomography chloramphenicol-treated sub-tomogram analysis | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationlarge ribosomal subunit / transferase activity / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding ...large ribosomal subunit / transferase activity / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / response to antibiotic / mRNA binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Mycoplasma pneumoniae (Filterable agent of primary atypical pneumonia) Mycoplasma pneumoniae (Filterable agent of primary atypical pneumonia) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Xue, L. / Lenz, S. / Rappsilber, J. / Mahamid, J. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, Germany,  United Kingdom, 3items United Kingdom, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Visualizing translation dynamics at atomic detail inside a bacterial cell. Authors: Liang Xue / Swantje Lenz / Maria Zimmermann-Kogadeeva / Dimitry Tegunov / Patrick Cramer / Peer Bork / Juri Rappsilber / Julia Mahamid /    Abstract: Translation is the fundamental process of protein synthesis and is catalysed by the ribosome in all living cells. Here we use advances in cryo-electron tomography and sub-tomogram analysis to ...Translation is the fundamental process of protein synthesis and is catalysed by the ribosome in all living cells. Here we use advances in cryo-electron tomography and sub-tomogram analysis to visualize the structural dynamics of translation inside the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae. To interpret the functional states in detail, we first obtain a high-resolution in-cell average map of all translating ribosomes and build an atomic model for the M. pneumoniae ribosome that reveals distinct extensions of ribosomal proteins. Classification then resolves 13 ribosome states that differ in their conformation and composition. These recapitulate major states that were previously resolved in vitro, and reflect intermediates during active translation. On the basis of these states, we animate translation elongation inside native cells and show how antibiotics reshape the cellular translation landscapes. During translation elongation, ribosomes often assemble in defined three-dimensional arrangements to form polysomes. By mapping the intracellular organization of translating ribosomes, we show that their association into polysomes involves a local coordination mechanism that is mediated by the ribosomal protein L9. We propose that an extended conformation of L9 within polysomes mitigates collisions to facilitate translation fidelity. Our work thus demonstrates the feasibility of visualizing molecular processes at atomic detail inside cells. #1:  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Visualizing translation dynamics at atomic detail inside a bacterial cell. Authors: Liang Xue / Swantje Lenz / Maria Zimmermann-Kogadeeva / Dimitry Tegunov / Patrick Cramer / Peer Bork / Juri Rappsilber / Julia Mahamid /    Abstract: Translation is the fundamental process of protein synthesis and is catalysed by the ribosome in all living cells. Here we use advances in cryo-electron tomography and sub-tomogram analysis to ...Translation is the fundamental process of protein synthesis and is catalysed by the ribosome in all living cells. Here we use advances in cryo-electron tomography and sub-tomogram analysis to visualize the structural dynamics of translation inside the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae. To interpret the functional states in detail, we first obtain a high-resolution in-cell average map of all translating ribosomes and build an atomic model for the M. pneumoniae ribosome that reveals distinct extensions of ribosomal proteins. Classification then resolves 13 ribosome states that differ in their conformation and composition. These recapitulate major states that were previously resolved in vitro, and reflect intermediates during active translation. On the basis of these states, we animate translation elongation inside native cells and show how antibiotics reshape the cellular translation landscapes. During translation elongation, ribosomes often assemble in defined three-dimensional arrangements to form polysomes. By mapping the intracellular organization of translating ribosomes, we show that their association into polysomes involves a local coordination mechanism that is mediated by the ribosomal protein L9. We propose that an extended conformation of L9 within polysomes mitigates collisions to facilitate translation fidelity. Our work thus demonstrates the feasibility of visualizing molecular processes at atomic detail inside cells. #2:  Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2021 Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2021Title: Visualizing translation dynamics at atomic detail inside a bacterial cell Authors: Xue, L. / Lenz, S. / Zimmermann-Kogadeeva, M. / Tegunov, D. / Cramer, P. / Bork, P. / Rappsilber, J. / Mahamid, J. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ood.cif.gz 7ood.cif.gz | 2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ood.ent.gz pdb7ood.ent.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ood.json.gz 7ood.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/7ood https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/7ood ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/7ood ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/7ood | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7oocC  7p6zC  7pahC  7paiC  7pajC  7pakC  7palC  7pamC  7panC  7paoC  7paqC  7parC  7pasC  7patC  7pauC  7ph9C  7phaC  7phbC  7phcC  7pi8C  7pi9C  7piaC  7pibC  7picC  7pioC 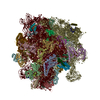 7pipC  7piqC  7pirC  7pisC 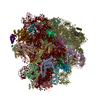 7pitC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10499 (Title: Tilt series of native M. pneumoniae cells treated with chloramphenicol EMPIAR-10499 (Title: Tilt series of native M. pneumoniae cells treated with chloramphenicolData size: 83.8 Data #1: Unaligned tilt movies of M. pneumoniae [tilt series])  EMPIAR-10731 (Title: Locating Macromolecular Assemblies in Cells by 2D Template Matching with cisTEM EMPIAR-10731 (Title: Locating Macromolecular Assemblies in Cells by 2D Template Matching with cisTEMData size: 67.8 Data #1: 50S templates of Mycoplasma pneumoniae used for 2D and 3D template matching [reconstructed volumes] Data #2: Single-exposure micrographs of untilted Mycoplasma pneumoniae cells [micrographs - single frame] Data #3: Tomographic tilt series of Mycoplasma pneumoniae cells [tilt series] Data #4: Tomographic reconstructions of Mycoplasma pneumoniae cells [reconstructed volumes]) |
| Experimental dataset #1 | Data reference:  10.6019/EMPIAR-10499 / Data set type: EMPIAR 10.6019/EMPIAR-10499 / Data set type: EMPIAR |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules 34
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 940911.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycoplasma pneumoniae (strain ATCC 29342 / M129) (bacteria) Mycoplasma pneumoniae (strain ATCC 29342 / M129) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 29342 / M129 |
|---|---|
| #2: RNA chain | Mass: 34796.676 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycoplasma pneumoniae (strain ATCC 29342 / M129) (bacteria) Mycoplasma pneumoniae (strain ATCC 29342 / M129) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 29342 / M129 |
+50S ribosomal protein ... , 29 types, 29 molecules wacekimquy021osvxzdblpjntrfhg
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 30 molecules 

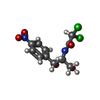




| #32: Chemical | ChemComp-K / | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #33: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #34: Chemical | ChemComp-CLM / | #35: Chemical | |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: CELL / 3D reconstruction method: subtomogram averaging |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: cryo-electron tomograms of chloramphenicol-treated Mycoplasma pneumoniae cells Type: RIBOSOME Details: ribosome sub-tomograms extracted in silico from cellular tomograms, focused refinement on 50S Entity ID: #1-#31 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycoplasma pneumoniae (strain ATCC 29342 / M129) (bacteria) Mycoplasma pneumoniae (strain ATCC 29342 / M129) (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Mycoplasma pneumoniae M129 cells grown on gold Quantifoil grids at 37 degrees Celsius before plunge freezing. |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE Details: ack-side blotting for 2-3 second before plunging using a manual plunger without an environmental chamber |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3750 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 3.2 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 17890 Details: Map generated by focused refinement on the 50S subunit in M Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM volume selection | Num. of tomograms: 65 / Num. of volumes extracted: 17890 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 83.32 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








































 PDBj
PDBj