[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
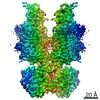
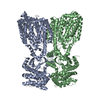
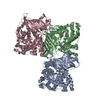
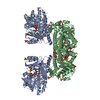
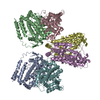
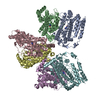
Yorodumi- PDB-7nj0: CryoEM structure of the human Separase-Cdk1-cyclin B1-Cks1 complex -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7nj0 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM structure of the human Separase-Cdk1-cyclin B1-Cks1 complex | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / autoinhibition phosphate-binding pocket pseudosubstrate Scc1 | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of Schwann cell differentiation / cyclin A1-CDK1 complex / regulation of attachment of mitotic spindle microtubules to kinetochore / pronuclear fusion / response to DDT / negative regulation of sister chromatid cohesion / cyclin B1-CDK1 complex / separase / positive regulation of mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport / regulation of chromosome condensation ...regulation of Schwann cell differentiation / cyclin A1-CDK1 complex / regulation of attachment of mitotic spindle microtubules to kinetochore / pronuclear fusion / response to DDT / negative regulation of sister chromatid cohesion / cyclin B1-CDK1 complex / separase / positive regulation of mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport / regulation of chromosome condensation / Mitotic Prophase / positive regulation of mitotic sister chromatid segregation / histone kinase activity / meiotic chromosome separation / Golgi disassembly / E2F-enabled inhibition of pre-replication complex formation / G2/M DNA replication checkpoint / microtubule cytoskeleton organization involved in mitosis / ventricular cardiac muscle cell development / Depolymerization of the Nuclear Lamina / MASTL Facilitates Mitotic Progression / positive regulation of mRNA 3'-end processing / regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint / positive regulation of attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochore / mitotic sister chromatid separation / Activation of NIMA Kinases NEK9, NEK6, NEK7 / mitotic nuclear membrane disassembly / : / patched binding / homologous chromosome segregation / cyclin A2-CDK1 complex / Phosphorylation of Emi1 / Transcriptional regulation by RUNX2 / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / tissue regeneration / Phosphorylation of the APC/C / Nuclear Pore Complex (NPC) Disassembly / meiotic spindle organization / outer kinetochore / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / protein localization to kinetochore / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by p107 (RBL1) and p130 (RBL2) in complex with HDAC1 / Polo-like kinase mediated events / Initiation of Nuclear Envelope (NE) Reformation / cellular response to fatty acid / Golgi Cisternae Pericentriolar Stack Reorganization / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / chromosome condensation / digestive tract development / [RNA-polymerase]-subunit kinase / oocyte maturation / centrosome cycle / Condensation of Prometaphase Chromosomes / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / SCF ubiquitin ligase complex / response to copper ion / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity / response to amine / MAPK3 (ERK1) activation / G1/S-Specific Transcription / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / microtubule organizing center / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / mitotic cytokinesis / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / regulation of embryonic development / catalytic activity / peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / protein deubiquitination / positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / chromosome organization / cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / cyclin-dependent kinase / response to cadmium ion / response to mechanical stimulus / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / response to axon injury / Chk1/Chk2(Cds1) mediated inactivation of Cyclin B:Cdk1 complex / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in cell cycle and proliferation / positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation / Cyclin A/B1/B2 associated events during G2/M transition / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / epithelial cell differentiation / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / RNA polymerase II CTD heptapeptide repeat kinase activity / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / cysteine-type peptidase activity / Hsp70 protein binding / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G2 Cell Cycle Arrest / molecular function activator activity Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yu, J. / Raia, P. / Ghent, C.M. / Raisch, T. / Sadian, Y. / Barford, D. / Raunser, S. / Morgan, D.O. / Boland, A. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, Switzerland,  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Structural basis of human separase regulation by securin and CDK1-cyclin B1. Authors: Jun Yu / Pierre Raia / Chloe M Ghent / Tobias Raisch / Yashar Sadian / Simone Cavadini / Pramod M Sabale / David Barford / Stefan Raunser / David O Morgan / Andreas Boland /     Abstract: In early mitosis, the duplicated chromosomes are held together by the ring-shaped cohesin complex. Separation of chromosomes during anaphase is triggered by separase-a large cysteine endopeptidase ...In early mitosis, the duplicated chromosomes are held together by the ring-shaped cohesin complex. Separation of chromosomes during anaphase is triggered by separase-a large cysteine endopeptidase that cleaves the cohesin subunit SCC1 (also known as RAD21). Separase is activated by degradation of its inhibitors, securin and cyclin B, but the molecular mechanisms of separase regulation are not clear. Here we used cryogenic electron microscopy to determine the structures of human separase in complex with either securin or CDK1-cyclin B1-CKS1. In both complexes, separase is inhibited by pseudosubstrate motifs that block substrate binding at the catalytic site and at nearby docking sites. As in Caenorhabditis elegans and yeast, human securin contains its own pseudosubstrate motifs. By contrast, CDK1-cyclin B1 inhibits separase by deploying pseudosubstrate motifs from intrinsically disordered loops in separase itself. One autoinhibitory loop is oriented by CDK1-cyclin B1 to block the catalytic sites of both separase and CDK1. Another autoinhibitory loop blocks substrate docking in a cleft adjacent to the separase catalytic site. A third separase loop contains a phosphoserine that promotes complex assembly by binding to a conserved phosphate-binding pocket in cyclin B1. Our study reveals the diverse array of mechanisms by which securin and CDK1-cyclin B1 bind and inhibit separase, providing the molecular basis for the robust control of chromosome segregation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7nj0.cif.gz 7nj0.cif.gz | 358.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7nj0.ent.gz pdb7nj0.ent.gz | 267.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7nj0.json.gz 7nj0.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nj/7nj0 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nj/7nj0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nj/7nj0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nj/7nj0 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  12368MC  7nj1C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 244677.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PTTG1, EAP1, PTTG, TUTR1, ESPL1, ESP1, KIAA0165 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PTTG1, EAP1, PTTG, TUTR1, ESPL1, ESP1, KIAA0165 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 36667.098 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDK1, CDC2, CDC28A, CDKN1, P34CDC2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDK1, CDC2, CDC28A, CDKN1, P34CDC2 / Production host:  References: UniProt: P06493, cyclin-dependent kinase, [RNA-polymerase]-subunit kinase |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 52625.723 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CCNB1, CCNB / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CCNB1, CCNB / Production host:  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 9679.211 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CKS1B, CKS1, PNAS-143, PNAS-16 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CKS1B, CKS1, PNAS-143, PNAS-16 / Production host:  |
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-PO4 / |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Mutual inhibitory complex of human separase-Cdk1-cyclin B1-Cks1 (CCC) complex. Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.05 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: The sample was monodisperse. We use graphene oxide-coated EM grids. |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1300 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1300 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2500 nm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 3 sec. / Electron dose: 78 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 5 / Num. of real images: 13640 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18rc5_3822: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 312836 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj