[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7n3i: Crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain in co... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7n3i | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
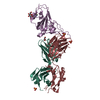
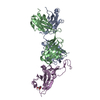
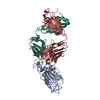
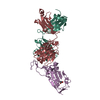
| Title | Crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain in complex with the human neutralizing antibody Fab fragment C098 | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM/VIRAL PROTEIN / severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 / spike protein / neutralizing antibodies / IMMUNE SYSTEM / IMMUNE SYSTEM-VIRAL PROTEIN complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / viral translation / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion ...symbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / viral translation / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / Attachment and Entry / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / receptor ligand activity / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.03 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.03 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Flyak, A.I. / Bjorkman, P.J. / Barnes, C.O. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Immunity / Year: 2021 Journal: Immunity / Year: 2021Title: Affinity maturation of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies confers potency, breadth, and resilience to viral escape mutations. Authors: Frauke Muecksch / Yiska Weisblum / Christopher O Barnes / Fabian Schmidt / Dennis Schaefer-Babajew / Zijun Wang / Julio C C Lorenzi / Andrew I Flyak / Andrew T DeLaitsch / Kathryn E Huey- ...Authors: Frauke Muecksch / Yiska Weisblum / Christopher O Barnes / Fabian Schmidt / Dennis Schaefer-Babajew / Zijun Wang / Julio C C Lorenzi / Andrew I Flyak / Andrew T DeLaitsch / Kathryn E Huey-Tubman / Shurong Hou / Celia A Schiffer / Christian Gaebler / Justin Da Silva / Daniel Poston / Shlomo Finkin / Alice Cho / Melissa Cipolla / Thiago Y Oliveira / Katrina G Millard / Victor Ramos / Anna Gazumyan / Magdalena Rutkowska / Marina Caskey / Michel C Nussenzweig / Pamela J Bjorkman / Theodora Hatziioannou / Paul D Bieniasz /  Abstract: Antibodies elicited by infection accumulate somatic mutations in germinal centers that can increase affinity for cognate antigens. We analyzed 6 independent groups of clonally related severe acute ...Antibodies elicited by infection accumulate somatic mutations in germinal centers that can increase affinity for cognate antigens. We analyzed 6 independent groups of clonally related severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) Spike receptor-binding domain (RBD)-specific antibodies from 5 individuals shortly after infection and later in convalescence to determine the impact of maturation over months. In addition to increased affinity and neutralization potency, antibody evolution changed the mutational pathways for the acquisition of viral resistance and restricted neutralization escape options. For some antibodies, maturation imposed a requirement for multiple substitutions to enable escape. For certain antibodies, affinity maturation enabled the neutralization of circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and heterologous sarbecoviruses. Antibody-antigen structures revealed that these properties resulted from substitutions that allowed additional variability at the interface with the RBD. These findings suggest that increasing antibody diversity through prolonged or repeated antigen exposure may improve protection against diversifying SARS-CoV-2 populations, and perhaps against other pandemic threat coronaviruses. #1: Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2021 Title: Development of potency, breadth and resilience to viral escape mutations in SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Authors: Frauke Muecksch / Yiska Weisblum / Christopher O Barnes / Fabian Schmidt / Dennis Schaefer-Babajew / Julio C C Lorenzi / Andrew I Flyak / Andrew T DeLaitsch / Kathryn E Huey-Tubman / Shurong ...Authors: Frauke Muecksch / Yiska Weisblum / Christopher O Barnes / Fabian Schmidt / Dennis Schaefer-Babajew / Julio C C Lorenzi / Andrew I Flyak / Andrew T DeLaitsch / Kathryn E Huey-Tubman / Shurong Hou / Celia A Schiffer / Christian Gaebler / Zijun Wang / Justin Da Silva / Daniel Poston / Shlomo Finkin / Alice Cho / Melissa Cipolla / Thiago Y Oliveira / Katrina G Millard / Victor Ramos / Anna Gazumyan / Magdalena Rutkowska / Marina Caskey / Michel C Nussenzweig / Pamela J Bjorkman / Theodora Hatziioannou / Paul D Bieniasz /  Abstract: Antibodies elicited in response to infection undergo somatic mutation in germinal centers that can result in higher affinity for the cognate antigen. To determine the effects of somatic mutation on ...Antibodies elicited in response to infection undergo somatic mutation in germinal centers that can result in higher affinity for the cognate antigen. To determine the effects of somatic mutation on the properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD)-specific antibodies, we analyzed six independent antibody lineages. As well as increased neutralization potency, antibody evolution changed pathways for acquisition of resistance and, in some cases, restricted the range of neutralization escape options. For some antibodies, maturation apparently imposed a requirement for multiple spike mutations to enable escape. For certain antibody lineages, maturation enabled neutralization of circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and heterologous sarbecoviruses. Antibody-antigen structures revealed that these properties resulted from substitutions that allowed additional variability at the interface with the RBD. These findings suggest that increasing antibody diversity through prolonged or repeated antigen exposure may improve protection against diversifying SARS-CoV-2 populations, and perhaps against other pandemic threat coronaviruses. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7n3i.cif.gz 7n3i.cif.gz | 266.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7n3i.ent.gz pdb7n3i.ent.gz | 211.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7n3i.json.gz 7n3i.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n3/7n3i https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n3/7n3i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n3/7n3i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n3/7n3i | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7n3eC  7n3fC  7n3gC  7n3hC  7r8lC  7r8mC  7r8nC  7r8oC  7bz5S S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 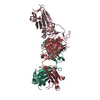
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 24004.926 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: Receptor Binding Domain Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: S, 2 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / Strain (production host): Expi293F / References: UniProt: P0DTC2 Homo sapiens (human) / Strain (production host): Expi293F / References: UniProt: P0DTC2 |
|---|---|
| #2: Antibody | Mass: 24452.252 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / Strain (production host): Expi293F Homo sapiens (human) / Strain (production host): Expi293F |
| #3: Antibody | Mass: 23317.795 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / Strain (production host): Expi293F Homo sapiens (human) / Strain (production host): Expi293F |
| #4: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / |
| #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
| Has ligand of interest | N |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.28 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 62.47 % / Mosaicity: 0.44 ° |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 298 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop Details: 0.05 M citric acid, 0.05M BIS-TRIS propane pH 5.0, 14% PEG 3350 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SSRL SSRL  / Beamline: BL12-2 / Wavelength: 0.98 Å / Beamline: BL12-2 / Wavelength: 0.98 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Feb 10, 2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.98 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.03→94.27 Å / Num. obs: 57277 / % possible obs: 96 % / Redundancy: 3 % / CC1/2: 0.994 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.097 / Rpim(I) all: 0.065 / Rrim(I) all: 0.117 / Net I/σ(I): 6.8 / Num. measured all: 173101 / Scaling rejects: 50 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 7BZ5 Resolution: 2.03→44.32 Å / SU ML: 0.21 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.33 / Phase error: 22.55 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 108.18 Å2 / Biso mean: 40.5783 Å2 / Biso min: 20.67 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 2.03→44.32 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 21
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj








