+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7li3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
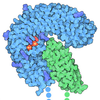
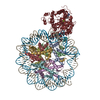
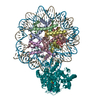
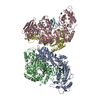
| Title | Structure of the LRRK2 G2019S mutant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / HYDROLASE / Parkinson's disease / microtubule / kinase / cryo-EM / NEUROPEPTIDE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcaveola neck / : / beta-catenin destruction complex binding / regulation of branching morphogenesis of a nerve / Wnt signalosome assembly / regulation of kidney size / regulation of cell projection organization / tangential migration from the subventricular zone to the olfactory bulb / GTP-dependent protein kinase activity / regulation of SNARE complex assembly ...caveola neck / : / beta-catenin destruction complex binding / regulation of branching morphogenesis of a nerve / Wnt signalosome assembly / regulation of kidney size / regulation of cell projection organization / tangential migration from the subventricular zone to the olfactory bulb / GTP-dependent protein kinase activity / regulation of SNARE complex assembly / regulation of neuroblast proliferation / regulation of ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum exit site / peroxidase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of late endosome to lysosome transport / regulation of mitochondrial depolarization / : / positive regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway / amphisome / regulation of synaptic vesicle transport / : / regulation of CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade / co-receptor binding / negative regulation of GTPase activity / regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of microglial cell activation / regulation of retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi / regulation of neuron maturation / positive regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / cytoplasmic side of mitochondrial outer membrane / negative regulation of autophagosome assembly / olfactory bulb development / JUN kinase kinase kinase activity / regulation of cAMP/PKA signal transduction / multivesicular body, internal vesicle / neuron projection arborization / negative regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / striatum development / regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis / mitochondrion localization / protein localization to mitochondrion / cellular response to dopamine / positive regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway / endoplasmic reticulum organization / positive regulation of protein autoubiquitination / negative regulation of protein processing / Wnt signalosome / positive regulation of programmed cell death / GTP metabolic process / regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / syntaxin-1 binding / regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process / Golgi-associated vesicle / lysosome organization / clathrin binding / PTK6 promotes HIF1A stabilization / negative regulation of macroautophagy / regulation of mitochondrial fission / regulation of locomotion / intracellular distribution of mitochondria / protein kinase A binding / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / neuromuscular junction development / Golgi organization / microvillus / exploration behavior / endoplasmic reticulum exit site / autolysosome / locomotory exploration behavior / negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway / canonical Wnt signaling pathway / MAP kinase kinase kinase activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / Rho protein signal transduction / presynaptic cytosol / neuron projection morphogenesis / phagocytic vesicle / cellular response to manganese ion / JNK cascade / positive regulation of autophagy / dendrite cytoplasm / GTPase activator activity / cellular response to starvation / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / determination of adult lifespan / SNARE binding / regulation of autophagy / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / mitochondrion organization / excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of membrane potential / tubulin binding / trans-Golgi network / calcium-mediated signaling / regulation of protein stability / autophagy / mitochondrial membrane / small GTPase binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Myasnikov, A. / Zhu, H. / Hixson, P. / Xie, B. / Yu, K. / Pitre, A. / Peng, J. / Sun, J. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Cell / Year: 2021Title: Structural analysis of the full-length human LRRK2. Authors: Alexander Myasnikov / Hanwen Zhu / Patricia Hixson / Boer Xie / Kaiwen Yu / Aaron Pitre / Junmin Peng / Ji Sun /  Abstract: Mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) are commonly implicated in the pathogenesis of both familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease (PD). LRRK2 regulates critical cellular processes at ...Mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) are commonly implicated in the pathogenesis of both familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease (PD). LRRK2 regulates critical cellular processes at membranous organelles and forms microtubule-based pathogenic filaments, yet the molecular basis underlying these biological roles of LRRK2 remains largely enigmatic. Here, we determined high-resolution structures of full-length human LRRK2, revealing its architecture and key interdomain scaffolding elements for rationalizing disease-causing mutations. The kinase domain of LRRK2 is captured in an inactive state, a conformation also adopted by the most common PD-associated mutation, LRRK2. This conformation serves as a framework for structure-guided design of conformational specific inhibitors. We further determined the structure of COR-mediated LRRK2 dimers and found that single-point mutations at the dimer interface abolished pathogenic filamentation in cells. Overall, our study provides mechanistic insights into physiological and pathological roles of LRRK2 and establishes a structural template for future therapeutic intervention in PD. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7li3.cif.gz 7li3.cif.gz | 340.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7li3.ent.gz pdb7li3.ent.gz | 261.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7li3.json.gz 7li3.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/li/7li3 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/li/7li3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/li/7li3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/li/7li3 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  23359MC  7lhtC  7lhwC  7li4C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 286457.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: G2019S variant Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LRRK2, PARK8 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LRRK2, PARK8 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: Q5S007, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-GDP / |
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: LRRK2 G2019S mutant / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 81 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.17.1_3660: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 81046 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj