+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7d9z | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
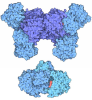
| Title | Crystal structure of anti-basigin Fab fragment | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / Fab / antibody / basigin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology | Immunoglobulins / Immunoglobulin-like / Sandwich / Mainly Beta / CITRATE ANION Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.123 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.123 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sakuragi, T. / Kanai, R. / Narita, H. / Onishi, E. / Miyazaki, T. / Baba, T. / Nakagawa, A. / Toyoshima, C. / Nagata, S. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 6items Japan, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2021Title: The tertiary structure of the human Xkr8-Basigin complex that scrambles phospholipids at plasma membranes. Authors: Takaharu Sakuragi / Ryuta Kanai / Akihisa Tsutsumi / Hirotaka Narita / Eriko Onishi / Kohei Nishino / Takuya Miyazaki / Takeshi Baba / Hidetaka Kosako / Atsushi Nakagawa / Masahide Kikkawa / ...Authors: Takaharu Sakuragi / Ryuta Kanai / Akihisa Tsutsumi / Hirotaka Narita / Eriko Onishi / Kohei Nishino / Takuya Miyazaki / Takeshi Baba / Hidetaka Kosako / Atsushi Nakagawa / Masahide Kikkawa / Chikashi Toyoshima / Shigekazu Nagata /  Abstract: Xkr8-Basigin is a plasma membrane phospholipid scramblase activated by kinases or caspases. We combined cryo-EM and X-ray crystallography to investigate its structure at an overall resolution of 3. ...Xkr8-Basigin is a plasma membrane phospholipid scramblase activated by kinases or caspases. We combined cryo-EM and X-ray crystallography to investigate its structure at an overall resolution of 3.8 Å. Its membrane-spanning region carrying 22 charged amino acids adopts a cuboid-like structure stabilized by salt bridges between hydrophilic residues in transmembrane helices. Phosphatidylcholine binding was observed in a hydrophobic cleft on the surface exposed to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane. Six charged residues placed from top to bottom inside the molecule were essential for scrambling phospholipids in inward and outward directions, apparently providing a pathway for their translocation. A tryptophan residue was present between the head group of phosphatidylcholine and the extracellular end of the path. Its mutation to alanine made the Xkr8-Basigin complex constitutively active, indicating that it plays a vital role in regulating its scramblase activity. The structure of Xkr8-Basigin provides insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying phospholipid scrambling. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7d9z.cif.gz 7d9z.cif.gz | 344.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7d9z.ent.gz pdb7d9z.ent.gz | 236.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7d9z.json.gz 7d9z.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d9/7d9z https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d9/7d9z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d9/7d9z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d9/7d9z | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7daaC  7dceC  4ma3S S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
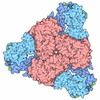
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Antibody | Mass: 23319.902 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Antibody | Mass: 22786.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||
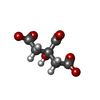
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-EDO / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-FLC / | #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.47 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 50.12 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293.15 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop Details: 0.1% n-Octyl-beta-D-glucoside, 0.1M sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate, 22% PEG 3350 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SPring-8 SPring-8  / Beamline: BL32XU / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: BL32XU / Wavelength: 1 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 9M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Jun 9, 2018 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.123→78.924 Å / Num. obs: 139276 / % possible obs: 81.6 % / Redundancy: 4.8 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 13.35 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.999 / Net I/σ(I): 13.5 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.123→1.194 Å / Num. unique obs: 6905 / CC1/2: 0.575 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 4ma3 Resolution: 1.123→36.4 Å / SU ML: 0.0836 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.37 / Phase error: 15.0715 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 19.68 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.123→36.4 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 PDBj
PDBj