[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
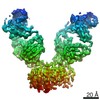
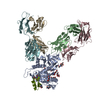
Yorodumi- PDB-7bwa: Cryo-EM Structure for the Ectodomain of the Full-length Human Ins... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7bwa | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM Structure for the Ectodomain of the Full-length Human Insulin Receptor in Complex with 2 Insulin | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / Human Insulin Receptor / Full-length / Ectodomain / Insulin / Conformation. | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcellular response to oxygen-containing compound / regulation of female gonad development / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / insulin-like growth factor II binding / positive regulation of developmental growth / male sex determination / insulin receptor complex / insulin-like growth factor I binding / insulin receptor activity / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly ...cellular response to oxygen-containing compound / regulation of female gonad development / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / insulin-like growth factor II binding / positive regulation of developmental growth / male sex determination / insulin receptor complex / insulin-like growth factor I binding / insulin receptor activity / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly / exocrine pancreas development / dendritic spine maintenance / cargo receptor activity / insulin binding / adrenal gland development / negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / PTB domain binding / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / Signaling by Insulin receptor / negative regulation of feeding behavior / IRS activation / Insulin processing / regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / neuronal cell body membrane / positive regulation of respiratory burst / Regulation of gene expression in beta cells / negative regulation of acute inflammatory response / amyloid-beta clearance / alpha-beta T cell activation / insulin receptor substrate binding / regulation of embryonic development / positive regulation of receptor internalization / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / epidermis development / negative regulation of protein secretion / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / fatty acid homeostasis / Signal attenuation / protein kinase activator activity / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / negative regulation of lipid catabolic process / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / transport across blood-brain barrier / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / heart morphogenesis / transport vesicle / nitric oxide-cGMP-mediated signaling / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Insulin receptor recycling / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / neuron projection maintenance / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / dendrite membrane / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / receptor-mediated endocytosis / positive regulation of glycolytic process / endosome lumen / positive regulation of cytokine production / acute-phase response / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / positive regulation of D-glucose import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of protein secretion / learning / insulin receptor binding / positive regulation of cell differentiation / Regulation of insulin secretion / wound healing / positive regulation of neuron projection development / hormone activity / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / regulation of synaptic plasticity / receptor internalization / caveola / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / Golgi lumen / cellular response to growth factor stimulus / male gonad development / vasodilation / cognition / memory / glucose metabolic process / cellular response to insulin stimulus / positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / insulin receptor signaling pathway / late endosome / cell-cell signaling Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Yu, D. / Zhang, X. / Sun, J. / Li, X. / Wu, Z. / Han, X. / Fan, C. / Ma, Y. / Ouyang, Q. / Wang, T. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: To Be Published Journal: To Be PublishedTitle: Insulin Binding Induced the Ectodomain Conformational Dynamics in the Full-length Human Insulin Receptor Authors: Yu, D. / Zhang, X. / Sun, J. / Li, X. / Wu, Z. / Han, X. / Fan, C. / Ma, Y. / Ouyang, Q. / Wang, T. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7bwa.cif.gz 7bwa.cif.gz | 294.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7bwa.ent.gz pdb7bwa.ent.gz | 220.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7bwa.json.gz 7bwa.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bw/7bwa https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bw/7bwa ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bw/7bwa ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bw/7bwa | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  30231MC  7bw7C  7bw8C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
| 2 | 
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 154114.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: UNP residues 28-1382 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INSR / Cell line (production host): HEK293 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INSR / Cell line (production host): HEK293 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P06213, receptor protein-tyrosine kinase #2: Protein | Mass: 8380.529 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Fragment: UNP residues 25-53, UNP residues 54-77, UNP residues 90-110 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INS / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INS / Production host:  Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.13 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: The sample was prepared using the gradient fixation method. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 4 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Calibrated magnification: 43796 X / Nominal defocus max: 2700 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 700 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2700 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 5 / Num. of real images: 17122 Details: Images were collected in movie mode with 40 frames per 10 seconds. |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18_3845: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Image processing | Details: The movie stacks were motion corrected for further analysis. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2069212 Details: Particle picking was done using EMAN2. 2D classifications were done in Relion 2.1 and good classes were selected. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 368511 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 255 / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Accession code: 6PXV / Initial refinement model-ID: 1 / PDB-ID: 6PXV / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj






















