+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6znl | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
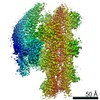
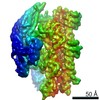
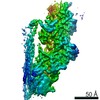
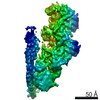
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the dynactin complex | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Dynactin / Complex / Scaffold / Cytoskeleton | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / retrograde axonal transport of mitochondrion / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / Adherens junctions interactions / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / MAP2K and MAPK activation ...: / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / retrograde axonal transport of mitochondrion / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / Adherens junctions interactions / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / MAP2K and MAPK activation / UCH proteinases / Gap junction degradation / Formation of annular gap junctions / RHOF GTPase cycle / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / dynactin complex / centriolar subdistal appendage / positive regulation of neuromuscular junction development / centriole-centriole cohesion / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / microtubule anchoring at centrosome / F-actin capping protein complex / WASH complex / ventral spinal cord development / retromer complex / cytoskeleton-dependent cytokinesis / microtubule plus-end / nuclear membrane disassembly / cellular response to cytochalasin B / positive regulation of microtubule nucleation / regulation of transepithelial transport / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / melanosome transport / barbed-end actin filament capping / protein localization to adherens junction / dense body / Tat protein binding / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Neutrophil degranulation / coronary vasculature development / non-motile cilium assembly / regulation of cell morphogenesis / dynein complex / retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi / adherens junction assembly / apical protein localization / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / MHC class II antigen presentation / tight junction / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / microtubule associated complex / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / ventricular septum development / aorta development / nuclear migration / apical junction complex / neuromuscular process / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / nitric-oxide synthase binding / neuromuscular junction development / transporter regulator activity / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / motor behavior / cell leading edge / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / cortical cytoskeleton / cleavage furrow / dynein complex binding / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / brush border / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / kinesin binding / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / intercellular bridge / stress fiber / neuron projection maintenance / axon cytoplasm / cytoskeleton organization / axonogenesis / calyx of Held / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / sarcomere / mitotic spindle organization / centriole / adherens junction / actin filament / cell motility / neuron cellular homeostasis / kinetochore Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lau, C.K. / Lacey, S.E. / Carter, A.P. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2021 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-EM reveals the complex architecture of dynactin's shoulder region and pointed end. Authors: Clinton K Lau / Francis J O'Reilly / Balaji Santhanam / Samuel E Lacey / Juri Rappsilber / Andrew P Carter /   Abstract: Dynactin is a 1.1 MDa complex that activates the molecular motor dynein for ultra-processive transport along microtubules. In order to do this, it forms a tripartite complex with dynein and a coiled- ...Dynactin is a 1.1 MDa complex that activates the molecular motor dynein for ultra-processive transport along microtubules. In order to do this, it forms a tripartite complex with dynein and a coiled-coil adaptor. Dynactin consists of an actin-related filament whose length is defined by its flexible shoulder domain. Despite previous cryo-EM structures, the molecular architecture of the shoulder and pointed end of the filament is still poorly understood due to the lack of high-resolution information in these regions. Here we combine multiple cryo-EM datasets and define precise masking strategies for particle signal subtraction and 3D classification. This overcomes domain flexibility and results in high-resolution maps into which we can build the shoulder and pointed end. The unique architecture of the shoulder securely houses the p150 subunit and positions the four identical p50 subunits in different conformations to bind dynactin's filament. The pointed end map allows us to build the first structure of p62 and reveals the molecular basis for cargo adaptor binding to different sites at the pointed end. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6znl.cif.gz 6znl.cif.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6znl.ent.gz pdb6znl.ent.gz | 974.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6znl.json.gz 6znl.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zn/6znl https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zn/6znl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zn/6znl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zn/6znl | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 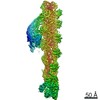 11313MC  6znmC  6znnC  6znoC  6zo4C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 6 types, 13 molecules ABCDEFGIHJKLU
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42670.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | | Mass: 41782.660 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | | Mass: 46250.785 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Protein | | Mass: 33059.848 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | | Mass: 30669.768 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #8: Protein | | Mass: 20703.910 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Dynactin subunit ... , 5 types, 10 molecules MNmnOoVYZz
| #6: Protein | Mass: 44704.414 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #7: Protein | Mass: 21192.477 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #9: Protein | | Mass: 20150.533 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #10: Protein | | Mass: 52920.434 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #11: Protein | Mass: 142547.156 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 13 molecules 




| #12: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #13: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / | #14: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Dynactin complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#11 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 52 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image processing | Details: All 4 image detectors used for reconstruction | |||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 336972 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj








