+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6xja | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
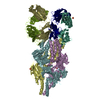
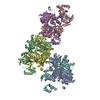
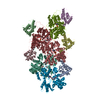
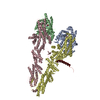
| Title | Streptococcus Pneumoniae IgA1 Protease with IgA1 substrate | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / IgA1 / Complex / Protease / metalloprotease | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationIgA-specific metalloendopeptidase / secretory dimeric IgA immunoglobulin complex / monomeric IgA immunoglobulin complex / secretory IgA immunoglobulin complex / IgA immunoglobulin complex / glomerular filtration / IgG immunoglobulin complex / immunoglobulin complex, circulating / positive regulation of respiratory burst / complement activation, classical pathway ...IgA-specific metalloendopeptidase / secretory dimeric IgA immunoglobulin complex / monomeric IgA immunoglobulin complex / secretory IgA immunoglobulin complex / IgA immunoglobulin complex / glomerular filtration / IgG immunoglobulin complex / immunoglobulin complex, circulating / positive regulation of respiratory burst / complement activation, classical pathway / Scavenging of heme from plasma / antigen binding / Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall / B cell receptor signaling pathway / metalloendopeptidase activity / antibacterial humoral response / blood microparticle / adaptive immune response / immune response / proteolysis / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / zinc ion binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Eisenmesser, E.Z. / Zheng, H. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Mechanism and inhibition of Streptococcus pneumoniae IgA1 protease. Authors: Zhiming Wang / Jeremy Rahkola / Jasmina S Redzic / Ying-Chih Chi / Norman Tran / Todd Holyoak / Hongjin Zheng / Edward Janoff / Elan Eisenmesser /   Abstract: Opportunistic pathogens such as Streptococcus pneumoniae secrete a giant metalloprotease virulence factor responsible for cleaving host IgA1, yet the molecular mechanism has remained unknown since ...Opportunistic pathogens such as Streptococcus pneumoniae secrete a giant metalloprotease virulence factor responsible for cleaving host IgA1, yet the molecular mechanism has remained unknown since their discovery nearly 30 years ago despite the potential for developing vaccines that target these enzymes to block infection. Here we show through a series of cryo-electron microscopy single particle reconstructions how the Streptococcus pneumoniae IgA1 protease facilitates IgA1 substrate recognition and how this can be inhibited. Specifically, the Streptococcus pneumoniae IgA1 protease subscribes to an active-site-gated mechanism where a domain undergoes a 10.0 Å movement to facilitate cleavage. Monoclonal antibody binding inhibits this conformational change, providing a direct means to block infection at the host interface. These structural studies explain decades of biological and biochemical studies and provides a general strategy to block Streptococcus pneumoniae IgA1 protease activity to potentially prevent infection. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6xja.cif.gz 6xja.cif.gz | 380.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6xja.ent.gz pdb6xja.ent.gz | 299.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6xja.json.gz 6xja.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xj/6xja https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xj/6xja ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xj/6xja ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xj/6xja | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  22204MC  6xjbC  7jgjC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 145926.625 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: E1605A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Streptococcus pneumoniae (strain ATCC BAA-255 / R6) (bacteria) Streptococcus pneumoniae (strain ATCC BAA-255 / R6) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC BAA-255 / R6 / Gene: iga, spr1042 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q59947, IgA-specific metalloendopeptidase | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 22887.988 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P01876 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P01876#3: Antibody | | Mass: 21947.256 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)#4: Antibody | | Mass: 21930.480 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Has protein modification | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.3 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 / Details: 20 mM Hepes, pH 7 150 mM NaCl | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 30 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: dev_3758: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 3 SIGMA CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 100000 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj