[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
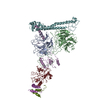
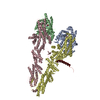
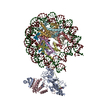
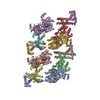
Yorodumi- PDB-6d8c: Cryo-EM structure of FLNaABD E254K bound to phalloidin-stabilized... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6d8c | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
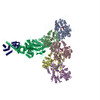
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of FLNaABD E254K bound to phalloidin-stabilized F-actin | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Actin-binding domain / Actin crosslinker | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / establishment of Sertoli cell barrier / Myb complex / glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting dopamine receptor signaling pathway / formation of radial glial scaffolds / positive regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway / actin crosslink formation / blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway ...regulation of membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / establishment of Sertoli cell barrier / Myb complex / glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting dopamine receptor signaling pathway / formation of radial glial scaffolds / positive regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway / actin crosslink formation / blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway / tubulin deacetylation / OAS antiviral response / Striated Muscle Contraction / positive regulation of actin filament bundle assembly / positive regulation of neuron migration / protein localization to bicellular tight junction / Fc-gamma receptor I complex binding / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / apical dendrite / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / positive regulation of platelet activation / positive regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation / protein localization to cell surface / wound healing, spreading of cells / podosome / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / megakaryocyte development / GP1b-IX-V activation signalling / SMAD binding / receptor clustering / cortical cytoskeleton / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / cilium assembly / mitotic spindle assembly / potassium channel regulator activity / : / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / protein sequestering activity / regulation of cell migration / dendritic shaft / protein localization to plasma membrane / actin filament / establishment of protein localization / mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II / G protein-coupled receptor binding / cerebral cortex development / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / positive regulation of protein import into nucleus / small GTPase binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / platelet aggregation / kinase binding / Z disc / cell-cell junction / actin filament binding / Platelet degranulation / actin cytoskeleton / toxin activity / growth cone / actin cytoskeleton organization / GTPase binding / perikaryon / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / transmembrane transporter binding / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / postsynapse / protein stabilization / hydrolase activity / cadherin binding / focal adhesion / negative regulation of apoptotic process / nucleolus / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / glutamatergic synapse / protein homodimerization activity / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / ATP binding / nucleus / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  Amanita phalloides (death cap) Amanita phalloides (death cap) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.54 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Iwamoto, D.V. / Huehn, A.R. / Simon, B. / Huet-Calderwood, C. / Baldassarre, M. / Sindelar, C.V. / Calderwood, D.A. | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2018Title: Structural basis of the filamin A actin-binding domain interaction with F-actin. Authors: Daniel V Iwamoto / Andrew Huehn / Bertrand Simon / Clotilde Huet-Calderwood / Massimiliano Baldassarre / Charles V Sindelar / David A Calderwood /   Abstract: Actin-cross-linking proteins assemble actin filaments into higher-order structures essential for orchestrating cell shape, adhesion, and motility. Missense mutations in the tandem calponin homology ...Actin-cross-linking proteins assemble actin filaments into higher-order structures essential for orchestrating cell shape, adhesion, and motility. Missense mutations in the tandem calponin homology domains of their actin-binding domains (ABDs) underlie numerous genetic diseases, but a molecular understanding of these pathologies is hampered by the lack of high-resolution structures of any actin-cross-linking protein bound to F-actin. Here, taking advantage of a high-affinity, disease-associated mutant of the human filamin A (FLNa) ABD, we combine cryo-electron microscopy and functional studies to reveal at near-atomic resolution how the first calponin homology domain (CH1) and residues immediately N-terminal to it engage actin. We further show that reorientation of CH2 relative to CH1 is required to avoid clashes with actin and to expose F-actin-binding residues on CH1. Our data explain localization of disease-associated loss-of-function mutations to FLNaCH1 and gain-of-function mutations to the regulatory FLNaCH2. Sequence conservation argues that this provides a general model for ABD-F-actin binding. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6d8c.cif.gz 6d8c.cif.gz | 854.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6d8c.ent.gz pdb6d8c.ent.gz | 711.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6d8c.json.gz 6d8c.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d8/6d8c https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d8/6d8c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d8/6d8c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d8/6d8c | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7831MC  7832C  7833C  8918C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 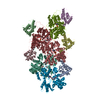
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 34476.250 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Fragment: UNP residues 1-278 / Mutation: E254K Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FLNA, FLN, FLN1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FLNA, FLN, FLN1 / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 41862.613 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein/peptide | #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Helical complex of FLNaABD E254K bound to phalloidin-stabilized F-actin Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Calibrated magnification: 37500 X / Nominal defocus max: 2900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 12 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 2140 Details: Micrographs from only one of the grids were used in the reconstruction. From that grid, only micrographs where Gctf detected signal at resolutions better than 4A were used in the reconstruction (~15%). |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 / Used frames/image: 1-40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: -166.73 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 27.54 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 67000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.54 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 67000 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj