[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
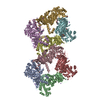
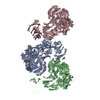
Yorodumi- PDB-6x5z: Bovine Cardiac Myosin in Complex with Chicken Skeletal Actin and ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6x5z | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Bovine Cardiac Myosin in Complex with Chicken Skeletal Actin and Human Cardiac Tropomyosin in the Rigor State | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CONTRACTILE PROTEIN / myosin / tropomyosin / actin / cardiac | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / Striated Muscle Contraction / regulation of muscle contraction / bleb / myosin filament / adult heart development / ruffle organization / Striated Muscle Contraction / muscle filament sliding ...positive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / Striated Muscle Contraction / regulation of muscle contraction / bleb / myosin filament / adult heart development / ruffle organization / Striated Muscle Contraction / muscle filament sliding / myosin II complex / sarcomere organization / structural constituent of muscle / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / microfilament motor activity / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / regulation of heart contraction / myofibril / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / Smooth Muscle Contraction / skeletal muscle fiber development / cardiac muscle contraction / stress fiber / cytoskeletal protein binding / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / cytoskeleton organization / positive regulation of cell adhesion / negative regulation of cell migration / actin filament organization / sarcomere / actin filament / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / wound healing / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / ruffle membrane / actin filament binding / regulation of cell shape / actin cytoskeleton / actin binding / cytoskeleton / calmodulin binding / hydrolase activity / protein heterodimerization activity / protein homodimerization activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.24 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Doran, M.H. / Lehman, W. / Rynkiewicz, M.J. / Bullitt, E. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, European Union, 7items United States, European Union, 7items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Biophys J / Year: 2020 Journal: Biophys J / Year: 2020Title: Cryo-EM and Molecular Docking Shows Myosin Loop 4 Contacts Actin and Tropomyosin on Thin Filaments. Authors: Matthew H Doran / Elumalai Pavadai / Michael J Rynkiewicz / Jonathan Walklate / Esther Bullitt / Jeffrey R Moore / Michael Regnier / Michael A Geeves / William Lehman /   Abstract: The motor protein myosin drives muscle and nonmuscle motility by binding to and moving along actin of thin filaments. Myosin binding to actin also modulates interactions of the regulatory protein, ...The motor protein myosin drives muscle and nonmuscle motility by binding to and moving along actin of thin filaments. Myosin binding to actin also modulates interactions of the regulatory protein, tropomyosin, on thin filaments, and conversely tropomyosin affects myosin binding to actin. Insight into this reciprocity will facilitate a molecular level elucidation of tropomyosin regulation of myosin interaction with actin in muscle contraction, and in turn, promote better understanding of nonmuscle cell motility. Indeed, experimental approaches such as fiber diffraction, cryoelectron microscopy, and three-dimensional reconstruction have long been used to define regulatory interaction of tropomyosin and myosin on actin at a structural level. However, their limited resolution has not proven sufficient to determine tropomyosin and myosin contacts at an atomic-level and thus to fully substantiate possible functional contributions. To overcome this deficiency, we have followed a hybrid approach by performing new cryogenic electron microscopy reconstruction of myosin-S1-decorated F-actin-tropomyosin together with atomic scale protein-protein docking of tropomyosin to the EM models. Here, cryo-EM data were derived from filaments reconstituted with α1-actin, cardiac αα-tropomyosin, and masseter muscle β-myosin complexes; masseter myosin, which shares sequence identity with β-cardiac myosin-heavy chain, was used because of its stability in vitro. The data were used to build an atomic model of the tropomyosin cable that fits onto the actin filament between the tip of the myosin head and a cleft on the innermost edge of actin subunits. The docking and atomic scale fitting showed multiple discrete interactions of myosin loop 4 and acidic residues on successive 39-42 residue-long tropomyosin pseudorepeats. The contacts between S1 and tropomyosin on actin appear to compete with and displace ones normally found between actin and tropomyosin on myosin-free thin filaments in relaxed muscle, thus restructuring the filament during myosin-induced activation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6x5z.cif.gz 6x5z.cif.gz | 634.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6x5z.ent.gz pdb6x5z.ent.gz | 510.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6x5z.json.gz 6x5z.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x5/6x5z https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x5/6x5z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x5/6x5z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x5/6x5z | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  22067MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
| Symmetry | Helical symmetry: (Circular symmetry: 1 / Dyad axis: no / N subunits divisor: 1 / Num. of operations: 2 / Rise per n subunits: 27.5 Å / Rotation per n subunits: -166.4 °) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42096.953 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: Residues 1-9 and 377 were disordered and were not modeled. Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 32763.621 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Only the central section (residues 45-210) was modeled. Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TPM1, C15orf13, TMSA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TPM1, C15orf13, TMSA / Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 97446.898 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Fragment: S1 fragment (UNP residues 1-850) / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: Residues 1-35, 200-216, 624-641, and 777-850 were disordered and not modeled. Source: (natural)  #4: Chemical | #5: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: HELICAL ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.40322 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.525 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Glow discharged using a PELCO easiGlow station / Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K Details: Thin filaments were reconstituted by first mixing F-actin and tropomyosin to final concentrations of 10 uM actin and 7 uM tropomyosin. Just before applying 1.5 uL actin-tropomyosin to a ...Details: Thin filaments were reconstituted by first mixing F-actin and tropomyosin to final concentrations of 10 uM actin and 7 uM tropomyosin. Just before applying 1.5 uL actin-tropomyosin to a freshly glow discharged holey-carbon grid, the surfactant octyl B-D-glucopyranoside was added to the protein solution to a concentration of 12 nM. The grid sample was manually blotted for 1 second and a 1.5 uL drop of 7.5 uM myosin-S1 sub-fragment was then applied to the blotted grid sample. The sample was immediately blotted for 4 seconds and plunge-frozen in liquid ethane. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Calibrated magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 7 sec. / Electron dose: 53 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 2496 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: In-column Omega Filter / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Width: 3838 / Height: 3710 / Movie frames/image: 35 / Used frames/image: 1-35 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: -166.4 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 27.5 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 45040 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.24 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 32158 / Details: Performed in the Relion post-processing step / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj
















