[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
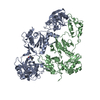
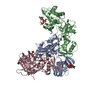
Yorodumi- PDB-6vwh: Leg region of the open conformation of the human type 1 insulin-l... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vwh | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
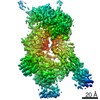
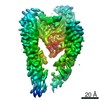
| Title | Leg region of the open conformation of the human type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor ectodomain in complex with human insulin-like growth factor II. | |||||||||
 Components Components | Leucine-zippered human type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor ectodomain | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor / Insulin-like growth factor II / ectodomain receptor / tyrosine kinase | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationinsulin-like growth factor receptor activity / protein kinase complex / insulin-like growth factor binding / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / protein transporter activity / FCERI mediated MAPK activation / protein localization to nuclear periphery / Activation of the AP-1 family of transcription factors / transcytosis ...insulin-like growth factor receptor activity / protein kinase complex / insulin-like growth factor binding / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / protein transporter activity / FCERI mediated MAPK activation / protein localization to nuclear periphery / Activation of the AP-1 family of transcription factors / transcytosis / response to amino acid starvation / negative regulation of ribosomal protein gene transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of cellular response to amino acid starvation / mediator complex binding / insulin receptor complex / insulin-like growth factor I binding / insulin receptor activity / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / alphav-beta3 integrin-IGF-1-IGF1R complex / peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation / dendritic spine maintenance / regulation of JNK cascade / insulin binding / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / amino acid biosynthetic process / amyloid-beta clearance / Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) attachment and entry / insulin receptor substrate binding / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / SHC-related events triggered by IGF1R / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / negative regulation of MAPK cascade / cellular response to nutrient levels / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / cellular response to amino acid starvation / insulin receptor binding / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / cellular response to glucose stimulus / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex / cellular response to amyloid-beta / insulin receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / protein autophosphorylation / DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / protein tyrosine kinase activity / transcription regulator complex / sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / signaling receptor complex / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / intracellular signal transduction / cilium / positive regulation of cell migration / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / immune response / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / axon / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / chromatin binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process / nucleolus / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / signal transduction / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / ATP binding / membrane / identical protein binding / nucleus / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.26 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Xu, Y. / Kirk, N.S. / Lawrence, M.C. / Croll, T.I. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, Australia,  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2020 Journal: Structure / Year: 2020Title: How IGF-II Binds to the Human Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor. Authors: Yibin Xu / Nicholas S Kirk / Hariprasad Venugopal / Mai B Margetts / Tristan I Croll / Jarrod J Sandow / Andrew I Webb / Carlie A Delaine / Briony E Forbes / Michael C Lawrence /   Abstract: Human type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) signals chiefly in response to the binding of insulin-like growth factor I. Relatively little is known about the role of insulin-like growth ...Human type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) signals chiefly in response to the binding of insulin-like growth factor I. Relatively little is known about the role of insulin-like growth factor II signaling via IGF-1R, despite the affinity of insulin-like growth factor II for IGF-1R being within an order of magnitude of that of insulin-like growth factor I. Here, we describe the cryoelectron microscopy structure of insulin-like growth factor II bound to a leucine-zipper-stabilized IGF-1R ectodomain, determined in two conformations to a maximum average resolution of 3.2 Å. The two conformations differ in the relative separation of their respective points of membrane entry, and comparison with the structure of insulin-like growth factor I bound to IGF-1R reveals long-suspected differences in the way in which the critical C domain of the respective growth factors interact with IGF-1R. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vwh.cif.gz 6vwh.cif.gz | 212.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vwh.ent.gz pdb6vwh.ent.gz | 157.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vwh.json.gz 6vwh.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vwh https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vwh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vwh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vwh | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21416MC  6vwgC  6vwiC  6vwjC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 108937.242 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human), (gene. exp.) Homo sapiens (human), (gene. exp.)  Gene: IGF1R, GCN4, AAS3, ARG9, YEL009C / Plasmid: pEE14 / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Cell line (production host): CHO-K1 / Production host:  References: UniProt: P08069, UniProt: P03069, receptor protein-tyrosine kinase Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: leg region of the open-leg conformation of the human type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor ectodomain in complex with human insulin-like growth factor II. Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.25 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: IGFII:IGF-1R molar ratio 1.5:1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: 15mA current / Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil, UltrAuFoil, R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 4585 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 50 / Used frames/image: 1-50 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.16_3549: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2057701 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.26 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 205471 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL Details: UCSF Chimera was used for the initial fitting and ISOLDE v 1.03b was using for flexible fitting. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 5U8R Accession code: 5U8R / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj