[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
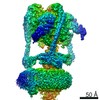
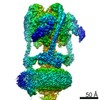
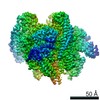
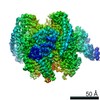
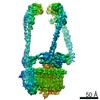
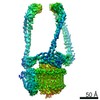
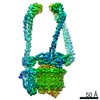
Yorodumi- PDB-6vq7: Mammalian V-ATPase from rat brain - composite model of rotational... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vq7 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Mammalian V-ATPase from rat brain - composite model of rotational state 2 bound to ADP and SidK (built from focused refinement models) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTON TRANSPORT / membrane protein complex / rotary atpase | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMetabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / Ion channel transport / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / symbiont-mediated suppression of host phagosome acidification / negative regulation of autophagic cell death / Insulin receptor recycling / RHOA GTPase cycle / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation ...Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / Ion channel transport / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / symbiont-mediated suppression of host phagosome acidification / negative regulation of autophagic cell death / Insulin receptor recycling / RHOA GTPase cycle / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / endosome to plasma membrane protein transport / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / lysosomal lumen acidification / endosomal lumen acidification / NURF complex / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / head morphogenesis / protein localization to cilium / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / osteoclast development / vacuolar acidification / regulation of cellular pH / dendritic spine membrane / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Neutrophil degranulation / ATPase complex / microvillus / ATPase activator activity / regulation of MAPK cascade / MLL1 complex / autophagosome membrane / cilium assembly / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / regulation of macroautophagy / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / transporter activator activity / ATP metabolic process / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / angiotensin maturation / ruffle / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / axon terminus / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / RNA endonuclease activity / proton transmembrane transport / receptor-mediated endocytosis / secretory granule / transmembrane transport / small GTPase binding / terminal bouton / apical part of cell / synaptic vesicle / synaptic vesicle membrane / melanosome / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / signaling receptor activity / ATPase binding / cell body / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / postsynaptic membrane / early endosome / lysosome / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / endosome / endosome membrane / cilium / apical plasma membrane / axon / external side of plasma membrane / lysosomal membrane / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / centrosome / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein-containing complex / extracellular space / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila (bacteria) Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Abbas, Y.M. / Rubinstein, J.L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1items Canada, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2020 Journal: Science / Year: 2020Title: Structure of V-ATPase from the mammalian brain. Authors: Yazan M Abbas / Di Wu / Stephanie A Bueler / Carol V Robinson / John L Rubinstein /   Abstract: In neurons, the loading of neurotransmitters into synaptic vesicles uses energy from proton-pumping vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases). These membrane protein complexes ...In neurons, the loading of neurotransmitters into synaptic vesicles uses energy from proton-pumping vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases). These membrane protein complexes possess numerous subunit isoforms, which complicates their analysis. We isolated homogeneous rat brain V-ATPase through its interaction with SidK, a effector protein. Cryo-electron microscopy allowed the construction of an atomic model, defining the enzyme's ATP:proton ratio as 3:10 and revealing a homolog of yeast subunit f in the membrane region, which we tentatively identify as RNAseK. The c ring encloses the transmembrane anchors for cleaved ATP6AP1/Ac45 and ATP6AP2/PRR, the latter of which is the (pro)renin receptor that, in other contexts, is involved in both Wnt signaling and the renin-angiotensin system that regulates blood pressure. This structure shows how ATP6AP1/Ac45 and ATP6AP2/PRR enable assembly of the enzyme's catalytic and membrane regions. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vq7.cif.gz 6vq7.cif.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vq7.ent.gz pdb6vq7.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vq7.json.gz 6vq7.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vq/6vq7 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vq/6vq7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vq/6vq7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vq/6vq7 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 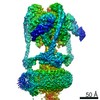 21318MC 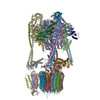 6vq6C 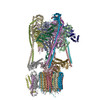 6vq8C 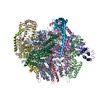 6vq9C  6vqaC  6vqbC  6vqcC  6vqgC  6vqhC  6vqiC  6vqjC  6vqkC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATPase H+-transporting V1 subunit ... , 2 types, 4 molecules ABCH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 68341.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Protein | | Mass: 28359.020 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-V-type proton ATPase ... , 10 types, 24 molecules DEFGIJKLMNOacdeghijklmno
| #2: Protein | Mass: 56611.570 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | | Mass: 43958.453 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | Mass: 26167.453 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #6: Protein | | Mass: 13389.262 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #7: Protein | Mass: 13690.476 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #9: Protein | | Mass: 96429.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #11: Protein | | Mass: 51160.359 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #12: Protein | | Mass: 40341.934 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #13: Protein | | Mass: 9203.020 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #15: Protein | Mass: 15815.833 Da / Num. of mol.: 9 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Protein , 4 types, 6 molecules QRSbfp
| #8: Protein | Mass: 34693.605 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Fragment: N-terminal fragment with 3x FLAG tag Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila (strain Philadelphia 1 / ATCC 33152 / DSM 7513) (bacteria) Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila (strain Philadelphia 1 / ATCC 33152 / DSM 7513) (bacteria)Strain: Philadelphia 1 / ATCC 33152 / DSM 7513 / Gene: lpg0968 / Production host:  #10: Protein | | Mass: 21618.553 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #14: Protein | | Mass: 11000.004 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #16: Protein | | Mass: 39118.578 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 2 molecules 


| #17: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / |
|---|---|
| #18: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Rat brain V-ATPase complex bound to the Legionella pneumophila effector protein SidK Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#16 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 43 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 74789 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Details: Final composite model was built from focused refinement models that were built into their corresponding focused refinement maps and subsequently aligned against the overall map before ...Details: Final composite model was built from focused refinement models that were built into their corresponding focused refinement maps and subsequently aligned against the overall map before combining into the composite model. The composite model was not refined against the data. |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj











