[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
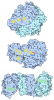
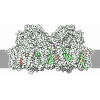
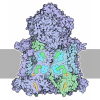
Yorodumi- PDB-6tjv: Structure of the NDH-1MS complex from Thermosynechococcus elongatus -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6tjv | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the NDH-1MS complex from Thermosynechococcus elongatus | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / carbon concentrating photosynthetic complex I / proton pump | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTranslocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions / NADH dehydrogenase complex / transmembrane transporter complex / photosynthetic electron transport chain / oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, quinone or similar compound as acceptor / plasma membrane-derived thylakoid membrane / photosynthesis, light reaction / ubiquinone binding / electron transport coupled proton transport / NADH dehydrogenase activity ...Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions / NADH dehydrogenase complex / transmembrane transporter complex / photosynthetic electron transport chain / oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, quinone or similar compound as acceptor / plasma membrane-derived thylakoid membrane / photosynthesis, light reaction / ubiquinone binding / electron transport coupled proton transport / NADH dehydrogenase activity / respiratory chain complex I / NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity / quinone binding / ATP synthesis coupled electron transport / endomembrane system / aerobic respiration / NAD binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / iron ion binding / extracellular space / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Schuller, J.M. / Saura, P. / Thiemann, J. / Schuller, S.K. / Gamiz-Hernandez, A.P. / Kurisu, G. / Nowaczyk, M.M. / Kaila, V.R.I. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 4items Germany, 4items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Redox-coupled proton pumping drives carbon concentration in the photosynthetic complex I. Authors: Jan M Schuller / Patricia Saura / Jacqueline Thiemann / Sandra K Schuller / Ana P Gamiz-Hernandez / Genji Kurisu / Marc M Nowaczyk / Ville R I Kaila /    Abstract: Photosynthetic organisms capture light energy to drive their energy metabolism, and employ the chemical reducing power to convert carbon dioxide (CO) into organic molecules. Photorespiration, ...Photosynthetic organisms capture light energy to drive their energy metabolism, and employ the chemical reducing power to convert carbon dioxide (CO) into organic molecules. Photorespiration, however, significantly reduces the photosynthetic yields. To survive under low CO concentrations, cyanobacteria evolved unique carbon-concentration mechanisms that enhance the efficiency of photosynthetic CO fixation, for which the molecular principles have remained unknown. We show here how modular adaptations enabled the cyanobacterial photosynthetic complex I to concentrate CO using a redox-driven proton-pumping machinery. Our cryo-electron microscopy structure at 3.2 Å resolution shows a catalytic carbonic anhydrase module that harbours a Zn active site, with connectivity to proton-pumping subunits that are activated by electron transfer from photosystem I. Our findings illustrate molecular principles in the photosynthetic complex I machinery that enabled cyanobacteria to survive in drastically changing CO conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6tjv.cif.gz 6tjv.cif.gz | 761.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6tjv.ent.gz pdb6tjv.ent.gz | 612.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6tjv.json.gz 6tjv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tj/6tjv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tj/6tjv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tj/6tjv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tj/6tjv | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  10513MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase subunit ... , 12 types, 12 molecules ABCEHIJKLMNO
| #1: Protein | Mass: 40565.984 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DL32, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 55168.543 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DMR6, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 15013.919 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DJ02, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 11140.265 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DL29, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 45271.184 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DJD9, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 22444.801 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DL31, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 19363.789 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DJ01, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 25766.998 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DKZ4, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 8575.137 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DKZ3, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 12584.056 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DLN5, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #14: Protein | Mass: 16656.182 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DJU2, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #15: Protein | Mass: 7877.076 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DMU4, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
-NADH dehydrogenase subunit ... , 3 types, 3 molecules DFG
| #4: Protein | Mass: 53908.137 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DKF4 |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 66283.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DKF5 |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 21580.568 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DL30, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules PQS
| #16: Protein | Mass: 51003.430 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DKF3 |
|---|---|
| #17: Protein | Mass: 15785.082 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DMA1 |
| #18: Protein | Mass: 12462.559 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)References: UniProt: Q8DL61 |
-Sugars , 1 types, 2 molecules 
| #19: Sugar |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 7 types, 14 molecules 







| #20: Chemical | | #21: Chemical | ChemComp-SQD / #22: Chemical | ChemComp-BCR / | #23: Chemical | ChemComp-CLA / | #24: Chemical | #25: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / | #26: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: NDH-1MS / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#18 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermosynechococcus elongatus BP-1 (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus BP-1 (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40.2 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.15.2_3472: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 170151 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj