+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6tb9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
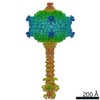
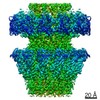
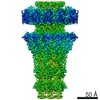
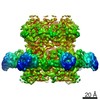
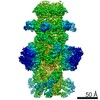
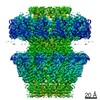
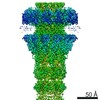
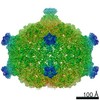
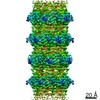
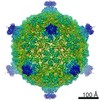
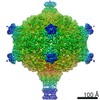
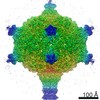
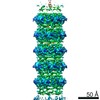
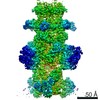
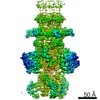
| Title | Capsid of native GTA particle computed with C5 symmetry | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRUS / "capsid" / "gene transfer agent" / "bacteriophage" / "HK97" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology | : / Phage capsid / Phage capsid family / : / : / Phage major capsid protein, HK97 family Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Rhodobacter capsulatus (bacteria) Rhodobacter capsulatus (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.56 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bardy, P. / Fuzik, T. / Hrebik, D. / Pantucek, R. / Beatty, J.T. / Plevka, P. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Czech Republic, 7items Czech Republic, 7items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Structure and mechanism of DNA delivery of a gene transfer agent. Authors: Pavol Bárdy / Tibor Füzik / Dominik Hrebík / Roman Pantůček / J Thomas Beatty / Pavel Plevka /   Abstract: Alphaproteobacteria, which are the most abundant microorganisms of temperate oceans, produce phage-like particles called gene transfer agents (GTAs) that mediate lateral gene exchange. However, the ...Alphaproteobacteria, which are the most abundant microorganisms of temperate oceans, produce phage-like particles called gene transfer agents (GTAs) that mediate lateral gene exchange. However, the mechanism by which GTAs deliver DNA into cells is unknown. Here we present the structure of the GTA of Rhodobacter capsulatus (RcGTA) and describe the conformational changes required for its DNA ejection. The structure of RcGTA resembles that of a tailed phage, but it has an oblate head shortened in the direction of the tail axis, which limits its packaging capacity to less than 4,500 base pairs of linear double-stranded DNA. The tail channel of RcGTA contains a trimer of proteins that possess features of both tape measure proteins of long-tailed phages from the family Siphoviridae and tail needle proteins of short-tailed phages from the family Podoviridae. The opening of a constriction within the RcGTA baseplate enables the ejection of DNA into bacterial periplasm. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6tb9.cif.gz 6tb9.cif.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6tb9.ent.gz pdb6tb9.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6tb9.json.gz 6tb9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tb/6tb9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tb/6tb9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tb/6tb9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tb/6tb9 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 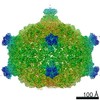 10442MC  6tbaC  6te8C  6te9C  6teaC  6tebC  6tehC  6to8C  6toaC  6tsuC  6tsvC 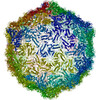 6tswC  6tuiC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 5
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 40982.066 Da / Num. of mol.: 29 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Rhodobacter capsulatus (bacteria) / References: UniProt: D5ATZ3 Rhodobacter capsulatus (bacteria) / References: UniProt: D5ATZ3#2: Protein | Mass: 9104.348 Da / Num. of mol.: 11 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Rhodobacter capsulatus (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A507Z9H3 Rhodobacter capsulatus (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A507Z9H3#3: Protein | Mass: 32996.828 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Rhodobacter capsulatus (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A507Z6Q1 Rhodobacter capsulatus (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A507Z6Q1 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details of virus |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural host |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Virus shell |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.8 / Details: G-buffer, doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90508-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 20 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: -3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: -1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1 sec. / Electron dose: 42.75 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 3114 |
| Image scans | Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 53432 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C5 (5 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.56 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 39403 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 2 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj