+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
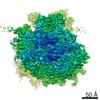
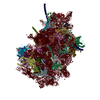
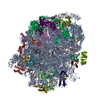
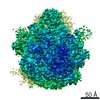
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6swa | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Mus musculus brain neocortex ribosome 60S bound to Ebp1 | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / 60S / EBP1 / neurodevelopment / neocortex / 80S / peptide tunnel exit | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationProtein hydroxylation / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / embryonic brain development / eukaryotic 80S initiation complex ...Protein hydroxylation / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / embryonic brain development / eukaryotic 80S initiation complex / negative regulation of protein neddylation / negative regulation of formation of translation preinitiation complex / regulation of G1 to G0 transition / axial mesoderm development / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / regulation of translation involved in cellular response to UV / protein-DNA complex disassembly / 90S preribosome assembly / translation at postsynapse / GAIT complex / TORC2 complex binding / alpha-beta T cell differentiation / G1 to G0 transition / middle ear morphogenesis / exit from mitosis / translation at presynapse / optic nerve development / retinal ganglion cell axon guidance / homeostatic process / response to aldosterone / cell-substrate adhesion / macrophage chemotaxis / lung morphogenesis / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / blastocyst development / cellular response to actinomycin D / negative regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / protein localization to nucleus / protein targeting / rough endoplasmic reticulum / translation regulator activity / negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / cytosolic ribosome / Neutrophil degranulation / cellular response to interleukin-4 / ossification / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / ribosomal large subunit biogenesis / liver regeneration / positive regulation of translation / skeletal system development / positive regulation of cell differentiation / sensory perception of sound / transcription coactivator binding / cellular response to gamma radiation / bone development / multicellular organism growth / cellular response to type II interferon / mRNA 5'-UTR binding / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / rRNA processing / transcription corepressor activity / regulation of translation / ribosome biogenesis / heparin binding / presynapse / cell body / retina development in camera-type eye / 5S rRNA binding / ribosomal large subunit assembly / fibroblast proliferation / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / killing of cells of another organism / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / response to lipopolysaccharide / nucleic acid binding / cytoplasmic translation / postsynapse / postsynaptic density / negative regulation of translation / protein stabilization / rRNA binding / nuclear body / ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / mRNA binding / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / synapse / dendrite / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / positive regulation of gene expression / negative regulation of apoptotic process / nucleolus / glutamatergic synapse Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kraushar, M.L. / Sprink, T. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 4items Germany, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021Title: Protein Synthesis in the Developing Neocortex at Near-Atomic Resolution Reveals Ebp1-Mediated Neuronal Proteostasis at the 60S Tunnel Exit. Authors: Matthew L Kraushar / Ferdinand Krupp / Dermot Harnett / Paul Turko / Mateusz C Ambrozkiewicz / Thiemo Sprink / Koshi Imami / Manuel Günnigmann / Ulrike Zinnall / Carlos H Vieira-Vieira / ...Authors: Matthew L Kraushar / Ferdinand Krupp / Dermot Harnett / Paul Turko / Mateusz C Ambrozkiewicz / Thiemo Sprink / Koshi Imami / Manuel Günnigmann / Ulrike Zinnall / Carlos H Vieira-Vieira / Theres Schaub / Agnieszka Münster-Wandowski / Jörg Bürger / Ekaterina Borisova / Hiroshi Yamamoto / Mladen-Roko Rasin / Uwe Ohler / Dieter Beule / Thorsten Mielke / Victor Tarabykin / Markus Landthaler / Günter Kramer / Imre Vida / Matthias Selbach / Christian M T Spahn /    Abstract: Protein synthesis must be finely tuned in the developing nervous system as the final essential step of gene expression. This study investigates the architecture of ribosomes from the neocortex during ...Protein synthesis must be finely tuned in the developing nervous system as the final essential step of gene expression. This study investigates the architecture of ribosomes from the neocortex during neurogenesis, revealing Ebp1 as a high-occupancy 60S peptide tunnel exit (TE) factor during protein synthesis at near-atomic resolution by cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM). Ribosome profiling demonstrated Ebp1-60S binding is highest during start codon initiation and N-terminal peptide elongation, regulating ribosome occupancy of these codons. Membrane-targeting domains emerging from the 60S tunnel, which recruit SRP/Sec61 to the shared binding site, displace Ebp1. Ebp1 is particularly abundant in the early-born neural stem cell (NSC) lineage and regulates neuronal morphology. Ebp1 especially impacts the synthesis of membrane-targeted cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), measured by pulsed stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (pSILAC)/bioorthogonal noncanonical amino acid tagging (BONCAT) mass spectrometry (MS). Therefore, Ebp1 is a central component of protein synthesis, and the ribosome TE is a focal point of gene expression control in the molecular specification of neuronal morphology during development. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6swa.cif.gz 6swa.cif.gz | 3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6swa.ent.gz pdb6swa.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6swa.json.gz 6swa.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sw/6swa https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sw/6swa ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sw/6swa ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sw/6swa | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  10321MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
+60S ribosomal protein ... , 38 types, 38 molecules ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVXYZabcde...
-Ribosomal protein ... , 4 types, 4 molecules Wjmn
| #23: Protein | Mass: 15161.899 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #36: Protein/peptide | Mass: 6295.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #39: Protein | Mass: 12345.776 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #40: Protein | Mass: 10168.153 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-RNA chain , 3 types, 3 molecules qrs
| #43: RNA chain | Mass: 1170200.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: We used the Oryctolagus cuniculus sequence to model the Mus musculus 28S ribosomal RNA Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #44: RNA chain | Mass: 50449.812 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: We used the Oryctolagus cuniculus sequence to model the Mus musculus 5.8S ribosomal RNA Source: (natural)  |
| #45: RNA chain | Mass: 38385.750 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: We used the Oryctolagus cuniculus sequence to model the Mus musculus 5S ribosomal RNA Source: (natural)  |
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules t
| #46: Protein | Mass: 39388.098 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 250 molecules 


| #47: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #48: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Mus musculus postnatal day 0 brain neocortex 80S ribosome bound to Ebp1 Type: RIBOSOME / Entity ID: #1-#46 / Source: NATURAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 3.2 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 100 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R3/3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 31000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 20 sec. / Electron dose: 31.78 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 5379 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 208206 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 208206 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj







































