+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6s1k | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | E. coli Core Signaling Unit, carrying QQQQ receptor mutation | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / chemotaxis / methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein / histidine kinase | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / negative regulation of protein modification process / detection of chemical stimulus / methyl accepting chemotaxis protein complex / positive regulation of post-translational protein modification / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent swimming motility / protein trimerization / aerotaxis / regulation of bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / protein histidine kinase activity ...: / negative regulation of protein modification process / detection of chemical stimulus / methyl accepting chemotaxis protein complex / positive regulation of post-translational protein modification / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent swimming motility / protein trimerization / aerotaxis / regulation of bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / protein histidine kinase activity / cell tip / thermotaxis / regulation of chemotaxis / signal complex assembly / phosphorelay sensor kinase activity / receptor clustering / histidine kinase / phosphorelay signal transduction system / establishment of localization in cell / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / cell motility / protein homooligomerization / chemotaxis / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / protein domain specific binding / signal transduction / ATP binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 8.38 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cassidy, C.K. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2020Title: Structure and dynamics of the E. coli chemotaxis core signaling complex by cryo-electron tomography and molecular simulations. Authors: C Keith Cassidy / Benjamin A Himes / Dapeng Sun / Jun Ma / Gongpu Zhao / John S Parkinson / Phillip J Stansfeld / Zaida Luthey-Schulten / Peijun Zhang /   Abstract: To enable the processing of chemical gradients, chemotactic bacteria possess large arrays of transmembrane chemoreceptors, the histidine kinase CheA, and the adaptor protein CheW, organized as ...To enable the processing of chemical gradients, chemotactic bacteria possess large arrays of transmembrane chemoreceptors, the histidine kinase CheA, and the adaptor protein CheW, organized as coupled core-signaling units (CSU). Despite decades of study, important questions surrounding the molecular mechanisms of sensory signal transduction remain unresolved, owing especially to the lack of a high-resolution CSU structure. Here, we use cryo-electron tomography and sub-tomogram averaging to determine a structure of the Escherichia coli CSU at sub-nanometer resolution. Based on our experimental data, we use molecular simulations to construct an atomistic model of the CSU, enabling a detailed characterization of CheA conformational dynamics in its native structural context. We identify multiple, distinct conformations of the critical P4 domain as well as asymmetries in the localization of the P3 bundle, offering several novel insights into the CheA signaling mechanism. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
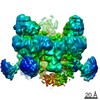
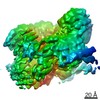
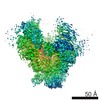
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6s1k.cif.gz 6s1k.cif.gz | 433.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6s1k.ent.gz pdb6s1k.ent.gz | 308.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6s1k.json.gz 6s1k.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s1/6s1k https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s1/6s1k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s1/6s1k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s1/6s1k | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  10050MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 71454.180 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: cheA, b1888, JW1877 Production host:  References: UniProt: P07363, histidine kinase #2: Protein | Mass: 18095.693 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Production host:  References: UniProt: P0A964*PLUS #3: Protein | Mass: 59495.758 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: tsr, cheD, b4355, JW4318 Production host:  References: UniProt: P02942 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: 2D ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: subtomogram averaging |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: core signaling complex of bacterial chemotaxis / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 1.3 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: MDFF / Category: model refinement / Details: implemented in NAMD |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 8.38 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 91636 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| EM volume selection | Num. of tomograms: 24 / Num. of volumes extracted: 91636 |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: global correlation coefficeint Details: MDFF was used to flexible fit atomic models of E. coli chemosensory proteins |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj