[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6f0x: Cryo-EM structure of TRIP13 in complex with ATP gamma S, p31comet... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6f0x | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of TRIP13 in complex with ATP gamma S, p31comet, C-Mad2 and Cdc20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / AAA+ ATPase / remodeller / spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) / mitosis / chromosome segregation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdeactivation of mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint / mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint MAD1-MAD2 complex / metaphase/anaphase transition of cell cycle / metaphase/anaphase transition of meiosis I / Inhibition of the proteolytic activity of APC/C required for the onset of anaphase by mitotic spindle checkpoint components / mitotic checkpoint complex / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / meiotic recombination checkpoint signaling / positive regulation of synapse maturation / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint ...deactivation of mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint / mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint MAD1-MAD2 complex / metaphase/anaphase transition of cell cycle / metaphase/anaphase transition of meiosis I / Inhibition of the proteolytic activity of APC/C required for the onset of anaphase by mitotic spindle checkpoint components / mitotic checkpoint complex / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / meiotic recombination checkpoint signaling / positive regulation of synapse maturation / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint / regulation of meiotic nuclear division / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / establishment of centrosome localization / Inactivation of APC/C via direct inhibition of the APC/C complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins / regulation of dendrite development / synaptonemal complex assembly / positive regulation of synaptic plasticity / anaphase-promoting complex / Phosphorylation of Emi1 / regulation of meiotic cell cycle / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / anaphase-promoting complex binding / regulation of exit from mitosis / nuclear pore nuclear basket / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / ubiquitin ligase activator activity / negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle / oocyte maturation / reciprocal meiotic recombination / female meiosis I / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / oogenesis / mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling / negative regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / male meiosis I / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / mitotic spindle assembly / spermatid development / ubiquitin-like ligase-substrate adaptor activity / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Mitotic Prometaphase / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / male germ cell nucleus / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / transcription coregulator activity / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / kinetochore / spindle / histone deacetylase binding / spindle pole / mitotic spindle / Separation of Sister Chromatids / nervous system development / double-strand break repair / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / chromosome / spermatogenesis / nuclear membrane / transcription by RNA polymerase II / cell differentiation / Ub-specific processing proteases / protein ubiquitination / cell division / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / centrosome / nucleolus / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / protein homodimerization activity / ATP hydrolysis activity / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.6 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Alfieri, C. / Chang, L. / Barford, D. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2018 Journal: Nature / Year: 2018Title: Mechanism for remodelling of the cell cycle checkpoint protein MAD2 by the ATPase TRIP13. Authors: Claudio Alfieri / Leifu Chang / David Barford /   Abstract: The maintenance of genome stability during mitosis is coordinated by the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) through its effector the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC), an inhibitor of the anaphase- ...The maintenance of genome stability during mitosis is coordinated by the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) through its effector the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC), an inhibitor of the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C, also known as the cyclosome). Unattached kinetochores control MCC assembly by catalysing a change in the topology of the β-sheet of MAD2 (an MCC subunit), thereby generating the active closed MAD2 (C-MAD2) conformer. Disassembly of free MCC, which is required for SAC inactivation and chromosome segregation, is an ATP-dependent process driven by the AAA+ ATPase TRIP13. In combination with p31, an SAC antagonist, TRIP13 remodels C-MAD2 into inactive open MAD2 (O-MAD2). Here, we present a mechanism that explains how TRIP13-p31 disassembles the MCC. Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the TRIP13-p31-C-MAD2-CDC20 complex reveal that p31 recruits C-MAD2 to a defined site on the TRIP13 hexameric ring, positioning the N terminus of C-MAD2 (MAD2) to insert into the axial pore of TRIP13 and distorting the TRIP13 ring to initiate remodelling. Molecular modelling suggests that by gripping MAD2 within its axial pore, TRIP13 couples sequential ATP-driven translocation of its hexameric ring along MAD2 to push upwards on, and simultaneously rotate, the globular domains of the p31-C-MAD2 complex. This unwinds a region of the αA helix of C-MAD2 that is required to stabilize the C-MAD2 β-sheet, thus destabilizing C-MAD2 in favour of O-MAD2 and dissociating MAD2 from p31. Our study provides insights into how specific substrates are recruited to AAA+ ATPases through adaptor proteins and suggests a model of how translocation through the axial pore of AAA+ ATPases is coupled to protein remodelling. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6f0x.cif.gz 6f0x.cif.gz | 470.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6f0x.ent.gz pdb6f0x.ent.gz | 377.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6f0x.json.gz 6f0x.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f0/6f0x https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f0/6f0x ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f0/6f0x ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f0/6f0x | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4166MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 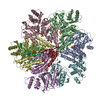
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 48606.664 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TRIP13, PCH2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TRIP13, PCH2 / Production host:  #2: Protein | | Mass: 31086.646 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  #3: Protein | | Mass: 54796.508 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC20 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC20 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q12834 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q12834#4: Protein | | Mass: 23533.883 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MAD2L1, MAD2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MAD2L1, MAD2 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13257 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13257#5: Chemical | ChemComp-AGS / Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 400 kDa/nm / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: dev_2919: / Classification: refinement |
|---|---|
| EM software | Name: RELION / Version: 2.1-beta-1 / Category: 3D reconstruction |
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 354157 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj














