[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6rza: Cryo-EM structure of the human inner arm dynein DNAH7 microtubule... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6rza | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
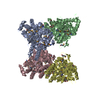
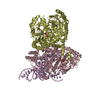
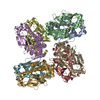
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human inner arm dynein DNAH7 microtubule binding domain bound to microtubules | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / filament / complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationinner dynein arm / axonemal dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / cilium-dependent cell motility / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / inner dynein arm assembly / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Aggrephagy / 9+2 motile cilium ...inner dynein arm / axonemal dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / cilium-dependent cell motility / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / inner dynein arm assembly / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Aggrephagy / 9+2 motile cilium / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / cilium movement involved in cell motility / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / cilium movement / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / positive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / positive regulation of spindle assembly / MHC class II antigen presentation / establishment of spindle localization / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Hedgehog 'off' state / Cilium Assembly / Intraflagellar transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Mitotic Prometaphase / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / RHOH GTPase cycle / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Kinesins / PKR-mediated signaling / Separation of Sister Chromatids / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / Aggrephagy / dynein complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / P-body assembly / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / microtubule motor activity / MHC class II antigen presentation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / dynein intermediate chain binding / Neutrophil degranulation / stress granule assembly / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / filopodium / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / neuron migration / mitotic cell cycle / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / microtubule cytoskeleton / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / cilium / cell division / GTPase activity / calcium ion binding / centrosome / GTP binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lacey, S.E. / He, S. / Scheres, S.H.W. / Carter, A.P. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2019 Journal: Elife / Year: 2019Title: Cryo-EM of dynein microtubule-binding domains shows how an axonemal dynein distorts the microtubule. Authors: Samuel E Lacey / Shaoda He / Sjors Hw Scheres / Andrew P Carter /  Abstract: Dyneins are motor proteins responsible for transport in the cytoplasm and the beating of axonemes in cilia and flagella. They bind and release microtubules via a compact microtubule-binding domain ...Dyneins are motor proteins responsible for transport in the cytoplasm and the beating of axonemes in cilia and flagella. They bind and release microtubules via a compact microtubule-binding domain (MTBD) at the end of a coiled-coil stalk. We address how cytoplasmic and axonemal dynein MTBDs bind microtubules at near atomic resolution. We decorated microtubules with MTBDs of cytoplasmic dynein-1 and axonemal dynein DNAH7 and determined their cryo-EM structures using helical Relion. The majority of the MTBD is rigid upon binding, with the transition to the high-affinity state controlled by the movement of a single helix at the MTBD interface. DNAH7 contains an 18-residue insertion, found in many axonemal dyneins, that contacts the adjacent protofilament. Unexpectedly, we observe that DNAH7, but not dynein-1, induces large distortions in the microtubule cross-sectional curvature. This raises the possibility that dynein coordination in axonemes is mediated via conformational changes in the microtubule. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6rza.cif.gz 6rza.cif.gz | 389.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6rza.ent.gz pdb6rza.ent.gz | 312 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6rza.json.gz 6rza.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rz/6rza https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rz/6rza ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rz/6rza ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rz/6rza | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 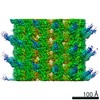 10060MC  6rzbC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 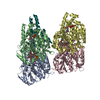
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments: Component-ID: _ / Beg auth comp-ID: MET / Beg label comp-ID: MET / Refine code: _
NCS ensembles :
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 5 molecules XACBD
| #1: Protein | Mass: 18133.164 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again ...Details: Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end,Fusion between two proteins. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence from position 1 to 15 DNAH7 sequence from proline at position 16 to proline at position 154 Cytoplasmic dynein 1 sequence again from from 155 to end Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: Dync1h1, Dhc1, Dnch1, Dnchc1, Dyhc, DNAH7, KIAA0944 / Production host:  | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 48679.051 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | Mass: 47825.859 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 8 molecules 






| #4: Chemical | | #5: Chemical | #6: Chemical | #7: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: HELICAL ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 67.5 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: REFMAC / Version: 5.8.0247 / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 41984 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Resolution: 4.5→4.5 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.582 / SU B: 243.237 / SU ML: 2.563 / ESU R: 2.187 Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD WITH PHASES
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Solvent model: PARAMETERS FOR MASK CACLULATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 206.247 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: 1 / Resolution: 5.402→195.3 Å / Total: 14908 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj














