[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6p5i: Structure of a mammalian 80S ribosome in complex with the Israeli... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6p5i | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
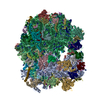
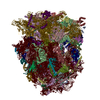
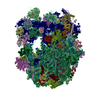
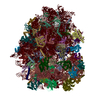
| Title | Structure of a mammalian 80S ribosome in complex with the Israeli Acute Paralysis Virus IRES (Class 1) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / Israeli Acute Paralysis Virus / Internal Ribosome Entry Site / IRES / Small Ribosomal Subunit / 40S / Large Ribosomal Subunit / 60S / 80S | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationribosomal subunit / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / 90S preribosome / phagocytic cup / rough endoplasmic reticulum / translation regulator activity / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / gastrulation / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding ...ribosomal subunit / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / 90S preribosome / phagocytic cup / rough endoplasmic reticulum / translation regulator activity / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / gastrulation / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / cytosolic ribosome / class I DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity / DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase / ribosomal large subunit biogenesis / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA / small-subunit processome / spindle / rRNA processing / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / rhythmic process / heparin binding / regulation of translation / large ribosomal subunit / ribosome binding / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / ribosomal large subunit assembly / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / perikaryon / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / killing of cells of another organism / cytoplasmic translation / cell differentiation / tRNA binding / mitochondrial inner membrane / postsynaptic density / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / cell division / DNA repair / mRNA binding / apoptotic process / synapse / dendrite / centrosome / nucleolus / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Israeli acute paralysis virus Israeli acute paralysis virus | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Acosta-Reyes, F.J. / Neupane, R. / Frank, J. / Fernandez, I.S. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2019 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2019Title: The Israeli acute paralysis virus IRES captures host ribosomes by mimicking a ribosomal state with hybrid tRNAs. Authors: Francisco Acosta-Reyes / Ritam Neupane / Joachim Frank / Israel S Fernández /  Abstract: Colony collapse disorder (CCD) is a multi-faceted syndrome decimating bee populations worldwide, and a group of viruses of the widely distributed Dicistroviridae family have been identified as a ...Colony collapse disorder (CCD) is a multi-faceted syndrome decimating bee populations worldwide, and a group of viruses of the widely distributed Dicistroviridae family have been identified as a causing agent of CCD. This family of viruses employs non-coding RNA sequences, called internal ribosomal entry sites (IRESs), to precisely exploit the host machinery for viral protein production. Using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), we have characterized how the IRES of Israeli acute paralysis virus (IAPV) intergenic region captures and redirects translating ribosomes toward viral RNA messages. We reconstituted two in vitro reactions targeting a pre-translocation and a post-translocation state of the IAPV-IRES in the ribosome, allowing us to identify six structures using image processing classification methods. From these, we reconstructed the trajectory of IAPV-IRES from the early small subunit recruitment to the final post-translocated state in the ribosome. An early commitment of IRES/ribosome complexes for global pre-translocation mimicry explains the high efficiency observed for this IRES. Efforts directed toward fighting CCD by targeting the IAPV-IRES using RNA-interference technology are underway, and the structural framework presented here may assist in further refining these approaches. | ||||||
| History |
|
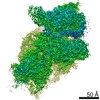
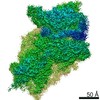
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6p5i.cif.gz 6p5i.cif.gz | 5.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6p5i.ent.gz pdb6p5i.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6p5i.json.gz 6p5i.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p5/6p5i https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p5/6p5i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p5/6p5i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p5/6p5i | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  20255MC  6p4gC  6p4hC  6p5jC  6p5kC  6p5nC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 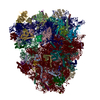
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 5 types, 5 molecules 21578
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 602776.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #35: RNA chain | Mass: 81572.078 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Cell Free Synthesis. The RNA molecule was made in vitro Source: (gene. exp.)  Israeli acute paralysis virus / Production host: Synthetic construct (others) Israeli acute paralysis virus / Production host: Synthetic construct (others) |
| #36: RNA chain | Mass: 1164741.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #37: RNA chain | Mass: 38385.750 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #38: RNA chain | Mass: 50143.648 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
+Protein , 75 types, 75 molecules BCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcde...
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules An
| #77: Protein/peptide | Mass: 3473.451 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Structure of a mammalian 80S ribosome in complex with the Israeli Acute Paralysis Virus IRES (Class 1) Type: RIBOSOME / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Ribosomal complexes for the pre-translocated state were assembled at 240-390 nM concentration and applied to plasma treated holey carbon. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Plasma cleaning for both holey carbon and holey gold grids was done on a Gatan Solarus with Hydrogen (6.4 sccm gas flow) and Oxygen (27.5 sccm gas flow) and 10 W cleaning power. Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K Details: Blot force = 3s Wait time = 15s Drain time = 0s Blot time = 2.5 to 3 s |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F30 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F30 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 31000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.26 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 8 sec. / Electron dose: 42.09 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 11234 |
| Image scans | Width: 3710 / Height: 3838 / Movie frames/image: 40 / Used frames/image: 1-40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1240275 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 120176 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj






























