+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6nd1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
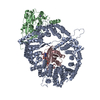
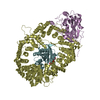
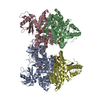
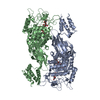
| Title | CryoEM structure of the Sec Complex from yeast | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN TRANSPORT / Sec61 / post-translational translocation / yeast / Sec63 / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmisfolded protein transport / Sec62/Sec63 complex / translocon complex / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane / cytosol to endoplasmic reticulum transport / Ssh1 translocon complex / Sec61 translocon complex / protein-transporting ATPase activity / post-translational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane ...misfolded protein transport / Sec62/Sec63 complex / translocon complex / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane / cytosol to endoplasmic reticulum transport / Ssh1 translocon complex / Sec61 translocon complex / protein-transporting ATPase activity / post-translational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / filamentous growth / signal sequence binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / post-translational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / peptide transmembrane transporter activity / nuclear inner membrane / retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol / transmembrane protein transporter activity / ERAD pathway / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / cell periphery / ribosome binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / structural molecule activity / endoplasmic reticulum / mitochondrion / membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Wu, X. / Cabanos, C. / Rapoport, T.A. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2019 Journal: Nature / Year: 2019Title: Structure of the post-translational protein translocation machinery of the ER membrane. Authors: Xudong Wu / Cerrone Cabanos / Tom A Rapoport /  Abstract: Many proteins must translocate through the protein-conducting Sec61 channel in the eukaryotic endoplasmic reticulum membrane or the SecY channel in the prokaryotic plasma membrane. Proteins with ...Many proteins must translocate through the protein-conducting Sec61 channel in the eukaryotic endoplasmic reticulum membrane or the SecY channel in the prokaryotic plasma membrane. Proteins with highly hydrophobic signal sequences are first recognized by the signal recognition particle (SRP) and then moved co-translationally through the Sec61 or SecY channel by the associated translating ribosome. Substrates with less hydrophobic signal sequences bypass the SRP and are moved through the channel post-translationally. In eukaryotic cells, post-translational translocation is mediated by the association of the Sec61 channel with another membrane protein complex, the Sec62-Sec63 complex, and substrates are moved through the channel by the luminal BiP ATPase. How the Sec62-Sec63 complex activates the Sec61 channel for post-translational translocation is not known. Here we report the electron cryo-microscopy structure of the Sec complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, consisting of the Sec61 channel and the Sec62, Sec63, Sec71 and Sec72 proteins. Sec63 causes wide opening of the lateral gate of the Sec61 channel, priming it for the passage of low-hydrophobicity signal sequences into the lipid phase, without displacing the channel's plug domain. Lateral channel opening is triggered by Sec63 interacting both with cytosolic loops in the C-terminal half of Sec61 and transmembrane segments in the N-terminal half of the Sec61 channel. The cytosolic Brl domain of Sec63 blocks ribosome binding to the channel and recruits Sec71 and Sec72, positioning them for the capture of polypeptides associated with cytosolic Hsp70. Our structure shows how the Sec61 channel is activated for post-translational protein translocation. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6nd1.cif.gz 6nd1.cif.gz | 225.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6nd1.ent.gz pdb6nd1.ent.gz | 172.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6nd1.json.gz 6nd1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nd/6nd1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nd/6nd1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nd/6nd1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nd/6nd1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  0440MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 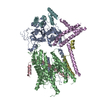
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein transport protein ... , 3 types, 3 molecules BCD
| #1: Protein | Mass: 52978.148 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 8958.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Production host:  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 8723.155 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules A
| #2: Protein | Mass: 76831.602 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Production host:  |
|---|
-Translocation protein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules EF
| #5: Protein | Mass: 24263.939 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 21631.090 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: The yeast Sec Complex involved in post-translational protein translocation Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: This sample was monodisperse | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3 / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K / Details: blot for 2.5 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: OTHER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 54.8 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 91218 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 4.1 Å |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj





