+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6kio | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
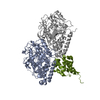
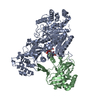
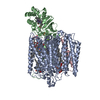
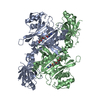
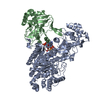
| Title | Complex of yeast cytoplasmic dynein MTBD-High and MT without DTT | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN/STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / MOTOR PROTEIN-STRUCTURAL PROTEIN COMPLEX | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationkaryogamy / nuclear migration along microtubule / astral microtubule / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / spindle pole body / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / motile cilium / nuclear migration ...karyogamy / nuclear migration along microtubule / astral microtubule / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / spindle pole body / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / motile cilium / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / Neutrophil degranulation / mitotic spindle organization / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / neuron migration / mitotic cell cycle / cell cortex / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / hydrolase activity / GTPase activity / GTP binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.94 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Komori, Y. / Nishida, N. / Shimada, I. / Kikkawa, M. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 2items Japan, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis for two-way communication between dynein and microtubules. Authors: Noritaka Nishida / Yuta Komori / Osamu Takarada / Atsushi Watanabe / Satoko Tamura / Satoshi Kubo / Ichio Shimada / Masahide Kikkawa /  Abstract: The movements of cytoplasmic dynein on microtubule (MT) tracks is achieved by two-way communication between the microtubule-binding domain (MTBD) and the ATPase domain via a coiled-coil stalk, but ...The movements of cytoplasmic dynein on microtubule (MT) tracks is achieved by two-way communication between the microtubule-binding domain (MTBD) and the ATPase domain via a coiled-coil stalk, but the structural basis of this communication remains elusive. Here, we regulate MTBD either in high-affinity or low-affinity states by introducing a disulfide bond to the stalk and analyze the resulting structures by NMR and cryo-EM. In the MT-unbound state, the affinity changes of MTBD are achieved by sliding of the stalk α-helix by a half-turn, which suggests that structural changes propagate from the ATPase-domain to MTBD. In addition, MT binding induces further sliding of the stalk α-helix even without the disulfide bond, suggesting how the MT-induced conformational changes propagate toward the ATPase domain. Based on differences in the MT-binding surface between the high- and low-affinity states, we propose a potential mechanism for the directional bias of dynein movement on MT tracks. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6kio.cif.gz 6kio.cif.gz | 328.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6kio.ent.gz pdb6kio.ent.gz | 257.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6kio.json.gz 6kio.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ki/6kio https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ki/6kio ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ki/6kio ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ki/6kio | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9996MC  9997C  6kiqC  6kjnC  6kjoC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10657 (Title: Complex of yeast cytoplasmic dynein MTBD-High and MT without DTT EMPIAR-10657 (Title: Complex of yeast cytoplasmic dynein MTBD-High and MT without DTTData size: 360.5 Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs of the complex of yeast cytoplasmic dynein MTBD-High and MT without DTT [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 47809.746 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 15264.564 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 45959.980 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: MTBD-High/MT complex without DTT / Type: CELL / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER/RHODIUM / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3250 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1000 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: OTHER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Electron dose: 54 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 1820 |
| Image scans | Width: 3838 / Height: 3710 / Movie frames/image: 40 / Used frames/image: 1-40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: -25.7561 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 9.20776 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 76377 / Details: particles were collected using PyFilamentPicker | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.94 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 58999 / Details: FSCtrue was calculated to validate the resolution. / Symmetry type: HELICAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj












