+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6a70 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
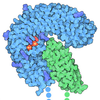
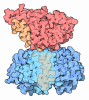
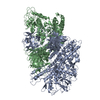
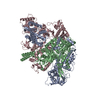
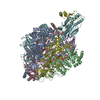
| Title | Structure of the human PKD1/PKD2 complex | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Asymmetric complex / polycystic kidney disease | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmetanephric distal tubule morphogenesis / nitrogen cycle metabolic process / detection of nodal flow / metanephric smooth muscle tissue development / metanephric cortex development / metanephric cortical collecting duct development / metanephric distal tubule development / polycystin complex / mesonephric tubule development / mesonephric duct development ...metanephric distal tubule morphogenesis / nitrogen cycle metabolic process / detection of nodal flow / metanephric smooth muscle tissue development / metanephric cortex development / metanephric cortical collecting duct development / metanephric distal tubule development / polycystin complex / mesonephric tubule development / mesonephric duct development / metanephric part of ureteric bud development / renal tubule morphogenesis / determination of liver left/right asymmetry / lung epithelium development / metanephric ascending thin limb development / lymph vessel morphogenesis / metanephric mesenchyme development / metanephric S-shaped body morphogenesis / basal cortex / renal artery morphogenesis / mitocytosis / metanephric proximal tubule development / HLH domain binding / calcium-induced calcium release activity / calcium-independent cell-matrix adhesion / Wnt receptor activity / VxPx cargo-targeting to cilium / cilium organization / genitalia development / migrasome / muscle alpha-actinin binding / detection of mechanical stimulus / regulation of calcium ion import / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / placenta blood vessel development / cellular response to hydrostatic pressure / Golgi-associated vesicle membrane / response to fluid shear stress / metanephric collecting duct development / cellular response to fluid shear stress / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / non-motile cilium / cation channel complex / cartilage development / cellular response to osmotic stress / determination of left/right symmetry / actinin binding / digestive tract development / : / neural tube development / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / motile cilium / aorta development / ciliary membrane / branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis / cartilage condensation / skin development / branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube / negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / protein heterotetramerization / spinal cord development / positive regulation of phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / heart looping / cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane / establishment of cell polarity / homophilic cell-cell adhesion / centrosome duplication / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / lateral plasma membrane / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / cell surface receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / anatomical structure morphogenesis / potassium channel activity / embryonic placenta development / regulation of cell adhesion / transcription regulator inhibitor activity / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / monoatomic cation channel activity / cytoskeletal protein binding / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / potassium ion transmembrane transport / calcium channel complex / cellular response to calcium ion / protein export from nucleus / basal plasma membrane / cellular response to cAMP / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / sodium ion transmembrane transport / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / cell-matrix adhesion / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / establishment of localization in cell / lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein tetramerization / kidney development / phosphoprotein binding / liver development / calcium ion transmembrane transport Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Su, Q. / Hu, F. / Ge, X. / Lei, J. / Yu, S. / Wang, T. / Zhou, Q. / Mei, C. / Shi, Y. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 3items China, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2018 Journal: Science / Year: 2018Title: Structure of the human PKD1-PKD2 complex. Authors: Qiang Su / Feizhuo Hu / Xiaofei Ge / Jianlin Lei / Shengqiang Yu / Tingliang Wang / Qiang Zhou / Changlin Mei / Yigong Shi /  Abstract: Mutations in two genes, and , account for most cases of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, one of the most common monogenetic disorders. Here we report the 3.6-angstrom cryo-electron ...Mutations in two genes, and , account for most cases of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, one of the most common monogenetic disorders. Here we report the 3.6-angstrom cryo-electron microscopy structure of truncated human PKD1-PKD2 complex assembled in a 1:3 ratio. PKD1 contains a voltage-gated ion channel (VGIC) fold that interacts with PKD2 to form the domain-swapped, yet noncanonical, transient receptor potential (TRP) channel architecture. The S6 helix in PKD1 is broken in the middle, with the extracellular half, S6a, resembling pore helix 1 in a typical TRP channel. Three positively charged, cavity-facing residues on S6b may block cation permeation. In addition to the VGIC, a five-transmembrane helix domain and a cytosolic PLAT domain were resolved in PKD1. The PKD1-PKD2 complex structure establishes a framework for dissecting the function and disease mechanisms of the PKD proteins. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6a70.cif.gz 6a70.cif.gz | 374.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6a70.ent.gz pdb6a70.ent.gz | 281.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6a70.json.gz 6a70.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a7/6a70 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a7/6a70 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a7/6a70 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a7/6a70 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6991MC  6992C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10262 (Title: Structure of the human PKD1-PKD2 complex / Data size: 209.8 EMPIAR-10262 (Title: Structure of the human PKD1-PKD2 complex / Data size: 209.8 Data #1: Autopicked particles of PKD1/PKD2 complex [picked particles - multiframe - unprocessed]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 66623.406 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PKD2, TRPP2 / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PKD2, TRPP2 / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host:  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q13563 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q13563#2: Protein | | Mass: 127024.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PKD1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PKD1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host:  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: P98161 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: P98161 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: the structure of an asymmetric complex / Type: COMPLEX Details: Samples were obtained by co-expression in 293F cells. A complex contains one PKD1 subunit and three PKD2 subunits. Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.31 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell: HEK293F HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell: HEK293F | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 10 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: This sample was monodisperse. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: DARK FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.13_2998: / Classification: refinement |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 27296 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj