+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5yfp | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM Structure of the Exocyst Complex | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components | (Exocyst complex component ...) x 8 | |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | EXOCYTOSIS / exocyst / coiled-coil | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationvesicle tethering involved in exocytosis / exocyst assembly / exocyst localization / negative regulation of SNARE complex assembly / endoplasmic reticulum inheritance / exocyst / prospore membrane / incipient cellular bud site / cellular bud tip / Golgi inheritance ...vesicle tethering involved in exocytosis / exocyst assembly / exocyst localization / negative regulation of SNARE complex assembly / endoplasmic reticulum inheritance / exocyst / prospore membrane / incipient cellular bud site / cellular bud tip / Golgi inheritance / Golgi to plasma membrane transport / cellular bud neck / mating projection tip / vesicle docking involved in exocytosis / spliceosomal complex assembly / exocytosis / transport vesicle / Rho protein signal transduction / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / SNARE binding / cell periphery / intracellular protein transport / small GTPase binding / intracellular protein localization / protein transport / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.4 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mei, K. / Li, Y. / Wang, S. / Shao, G. / Wang, J. / Ding, Y. / Luo, G. / Yue, P. / Liu, J.J. / Wang, X. ...Mei, K. / Li, Y. / Wang, S. / Shao, G. / Wang, J. / Ding, Y. / Luo, G. / Yue, P. / Liu, J.J. / Wang, X. / Dong, M.Q. / Guo, W. / Wang, H.W. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, China,  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2018Title: Cryo-EM structure of the exocyst complex. Authors: Kunrong Mei / Yan Li / Shaoxiao Wang / Guangcan Shao / Jia Wang / Yuehe Ding / Guangzuo Luo / Peng Yue / Jun-Jie Liu / Xinquan Wang / Meng-Qiu Dong / Hong-Wei Wang / Wei Guo /   Abstract: The exocyst is an evolutionarily conserved octameric protein complex that mediates the tethering of post-Golgi secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane during exocytosis and is implicated in many ...The exocyst is an evolutionarily conserved octameric protein complex that mediates the tethering of post-Golgi secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane during exocytosis and is implicated in many cellular processes such as cell polarization, cytokinesis, ciliogenesis and tumor invasion. Using cryo-EM and chemical cross-linking MS (CXMS), we solved the structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae exocyst complex at an average resolution of 4.4 Å. Our model revealed the architecture of the exocyst and led to the identification of the helical bundles that mediate the assembly of the complex at its core. Sequence analysis suggests that these regions are evolutionarily conserved across eukaryotic systems. Additional cell biological data suggest a mechanism for exocyst assembly that leads to vesicle tethering at the plasma membrane. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5yfp.cif.gz 5yfp.cif.gz | 919.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5yfp.ent.gz pdb5yfp.ent.gz | 636.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5yfp.json.gz 5yfp.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yf/5yfp https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yf/5yfp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yf/5yfp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yf/5yfp | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6827MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10206 (Title: Cryo electron microscopy micrographs of yeast Exocyst complex EMPIAR-10206 (Title: Cryo electron microscopy micrographs of yeast Exocyst complexData size: 10.0 TB Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs of Yeast Exocyst complex [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 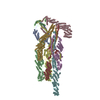
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Exocyst complex component ... , 8 types, 8 molecules ABCDEFGH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 154889.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 112236.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 93539.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 122367.109 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 100459.578 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 105166.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 71382.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 85649.672 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Cryo-EM map of the Yeast Exocyst complex overall structure at 5.5A resolution Type: COMPLEX / Details: overall map of Yeast Exocyst complex / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.844 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 Details: Solutions were freshly prepared from stock and filtered with 0.22um membrane to avoid microbial contamination. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: This sample was mono-disperse. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Purchased Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 gold grid was directly glow discharged 60 seconds before use. Before glow discharge, the sample chamber was vacuumed by an air bump for 2 minutes. Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 301 K Details: Protein sample was applied onto a Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 golden grid and hold for 60 seconds, then blot for 2.5 seconds before plunging. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 22500 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1800 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 3200 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 123 K / Temperature (min): 113 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 8 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 11 / Num. of real images: 6466 |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 5 µm / Width: 3838 / Height: 3710 / Movie frames/image: 32 / Used frames/image: 0-31 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.11.1_2575: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj