+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5w3f | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
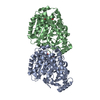
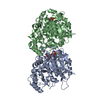
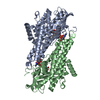
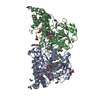
| Title | Yeast tubulin polymerized with GTP in vitro | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / Cytoskeleton / tubulin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnuclear migration by microtubule mediated pushing forces / nuclear division / mitotic spindle elongation / Platelet degranulation / homologous chromosome segregation / nuclear migration along microtubule / positive regulation of intracellular protein transport / tubulin complex / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / mitotic spindle assembly ...nuclear migration by microtubule mediated pushing forces / nuclear division / mitotic spindle elongation / Platelet degranulation / homologous chromosome segregation / nuclear migration along microtubule / positive regulation of intracellular protein transport / tubulin complex / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / mitotic spindle assembly / microtubule-based process / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / cytoskeleton organization / nuclear periphery / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / spindle / mitotic cell cycle / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / hydrolase activity / response to antibiotic / GTPase activity / GTP binding / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Howes, S.C. / Geyer, E.A. / LaFrance, B. / Zhang, R. / Kellogg, E.H. / Westermann, S. / Rice, L.M. / Nogales, E. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 7items United States, 7items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Cell Biol / Year: 2017 Journal: J Cell Biol / Year: 2017Title: Structural differences between yeast and mammalian microtubules revealed by cryo-EM. Authors: Stuart C Howes / Elisabeth A Geyer / Benjamin LaFrance / Rui Zhang / Elizabeth H Kellogg / Stefan Westermann / Luke M Rice / Eva Nogales /   Abstract: Microtubules are polymers of αβ-tubulin heterodimers essential for all eukaryotes. Despite sequence conservation, there are significant structural differences between microtubules assembled in ...Microtubules are polymers of αβ-tubulin heterodimers essential for all eukaryotes. Despite sequence conservation, there are significant structural differences between microtubules assembled in vitro from mammalian or budding yeast tubulin. Yeast MTs were not observed to undergo compaction at the interdimer interface as seen for mammalian microtubules upon GTP hydrolysis. Lack of compaction might reflect slower GTP hydrolysis or a different degree of allosteric coupling in the lattice. The microtubule plus end-tracking protein Bim1 binds yeast microtubules both between αβ-tubulin heterodimers, as seen for other organisms, and within tubulin dimers, but binds mammalian tubulin only at interdimer contacts. At the concentrations used in cryo-electron microscopy, Bim1 causes the compaction of yeast microtubules and induces their rapid disassembly. Our studies demonstrate structural differences between yeast and mammalian microtubules that likely underlie their differing polymerization dynamics. These differences may reflect adaptations to the demands of different cell size or range of physiological growth temperatures. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5w3f.cif.gz 5w3f.cif.gz | 323.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5w3f.ent.gz pdb5w3f.ent.gz | 265.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5w3f.json.gz 5w3f.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w3/5w3f https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w3/5w3f ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w3/5w3f ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w3/5w3f | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8755MC  8756C  8757C  8758C  8759C  5w3hC  5w3jC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 49853.867 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P09733 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 50967.457 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P02557 |
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-GTP / |
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-GDP / |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: HELICAL ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Dynamic microtubule lattice / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.9 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 303 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 28 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 20 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: -29.85 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 10.4 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 42871 / Symmetry type: HELICAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj









