[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-5jqi: Crystal structure of FimH A62S from E. coli UTI89 bound to FimG N... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5jqi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of FimH A62S from E. coli UTI89 bound to FimG N-terminal extension | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SUGAR BINDING PROTEIN / lectin / immunoglobulin fold / carbohydrate binding protein / donor strand exchange | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcell adhesion involved in single-species biofilm formation / pilus / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.962 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.962 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kalas, V. / Hultgren, S.J. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2017 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2017Title: Evolutionary fine-tuning of conformational ensembles in FimH during host-pathogen interactions. Authors: Vasilios Kalas / Jerome S Pinkner / Thomas J Hannan / Michael E Hibbing / Karen W Dodson / Alex S Holehouse / Hao Zhang / Niraj H Tolia / Michael L Gross / Rohit V Pappu / James Janetka / Scott J Hultgren /  Abstract: Positive selection in the two-domain type 1 pilus adhesin FimH enhances fitness in urinary tract infection (UTI). We report a comprehensive atomic-level view of FimH in two-state conformational ...Positive selection in the two-domain type 1 pilus adhesin FimH enhances fitness in urinary tract infection (UTI). We report a comprehensive atomic-level view of FimH in two-state conformational ensembles in solution, composed of one low-affinity tense (T) and multiple high-affinity relaxed (R) conformations. Positively selected residues allosterically modulate the equilibrium between these two conformational states, each of which engages mannose through distinct binding orientations. A FimH variant that only adopts the R state is severely attenuated early in a mouse model of uncomplicated UTI but is proficient at colonizing catheterized bladders in vivo or bladder transitional-like epithelial cells in vitro. Thus, the bladder habitat has barrier(s) to R state-mediated colonization possibly conferred by the terminally differentiated bladder epithelium and/or decoy receptors in urine. Together, our studies reveal the conformational landscape in solution, binding mechanisms, and adhesive strength of an allosteric two-domain adhesin that evolved "moderate" affinity to optimize persistence in the bladder during UTI. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5jqi.cif.gz 5jqi.cif.gz | 240.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5jqi.ent.gz pdb5jqi.ent.gz | 193.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5jqi.json.gz 5jqi.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jq/5jqi https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jq/5jqi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jq/5jqi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jq/5jqi | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5jr4C  3jwnS C: citing same article ( S: Starting model for refinement |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
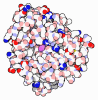
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 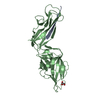
| ||||||||
| 3 | 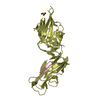
| ||||||||
| 4 | 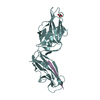
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1513.776 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  #2: Protein | Mass: 29053.260 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: UNP residues 22-300 / Mutation: A62S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: UTI89 / UPEC / Gene: fimH, UTI89_C5017 / Production host:  #3: Chemical | ChemComp-GOL / #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.36 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 47.94 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop Details: 0.2 M Calcium Acetate, 0.1 M HEPES 7.5, 10% PEG 8000 PH range: 5-8 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  ROTATING ANODE / Type: RIGAKU MICROMAX-007 / Wavelength: 1.54179 Å ROTATING ANODE / Type: RIGAKU MICROMAX-007 / Wavelength: 1.54179 Å |
| Detector | Type: MAR scanner 345 mm plate / Detector: IMAGE PLATE / Date: Feb 21, 2016 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.54179 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.96→48.67 Å / Num. obs: 75411 / % possible obs: 94.2 % / Redundancy: 3.9 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.141 / Net I/σ(I): 8.5 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.96→2.03 Å / Redundancy: 3.8 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.706 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 2 / % possible all: 90.4 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 3JWN Resolution: 1.962→48.666 Å / SU ML: 0.25 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.96 / Phase error: 25.08
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.962→48.666 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj