[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-4toi: Crystal structure of E.coli ribosomal protein S2 in complex with ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 4toi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of E.coli ribosomal protein S2 in complex with N-terminal domain of S1 | ||||||
 Components Components | 30S ribosomal protein S2,Ribosomal protein S1 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN / complex / translation | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationribosomal small subunit assembly / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / structural constituent of ribosome / translation / zinc ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /  molecular replacement / Resolution: 2.3 Å molecular replacement / Resolution: 2.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Grishkovskaya, I. / Byrgazov, K. / Moll, I. / Djinovic-Carugo, K. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2015 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2015Title: Structural basis for the interaction of protein S1 with the Escherichia coli ribosome. Authors: Konstantin Byrgazov / Irina Grishkovskaya / Stefan Arenz / Nicolas Coudevylle / Hannes Temmel / Daniel N Wilson / Kristina Djinovic-Carugo / Isabella Moll /    Abstract: In Gram-negative bacteria, the multi-domain protein S1 is essential for translation initiation, as it recruits the mRNA and facilitates its localization in the decoding centre. In sharp contrast to ...In Gram-negative bacteria, the multi-domain protein S1 is essential for translation initiation, as it recruits the mRNA and facilitates its localization in the decoding centre. In sharp contrast to its functional importance, S1 is still lacking from the high-resolution structures available for Escherichia coli and Thermus thermophilus ribosomes and thus the molecular mechanism governing the S1-ribosome interaction has still remained elusive. Here, we present the structure of the N-terminal S1 domain D1 when bound to the ribosome at atomic resolution by using a combination of NMR, X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy. Together with biochemical assays, the structure reveals that S1 is anchored to the ribosome primarily via a stabilizing π-stacking interaction within the short but conserved N-terminal segment that is flexibly connected to domain D1. This interaction is further stabilized by salt bridges involving the zinc binding pocket of protein S2. Overall, this work provides one hitherto enigmatic piece in the 'ribosome puzzle', namely the detailed molecular insight into the topology of the S1-ribosome interface. Moreover, our data suggest novel mechanisms that have the potential to modulate protein synthesis in response to environmental cues by changing the affinity of S1 for the ribosome. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  4toi.cif.gz 4toi.cif.gz | 80.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb4toi.ent.gz pdb4toi.ent.gz | 57.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  4toi.json.gz 4toi.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  4toi_validation.pdf.gz 4toi_validation.pdf.gz | 429.2 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  4toi_full_validation.pdf.gz 4toi_full_validation.pdf.gz | 430.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  4toi_validation.xml.gz 4toi_validation.xml.gz | 14.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  4toi_validation.cif.gz 4toi_validation.cif.gz | 20.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/to/4toi https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/to/4toi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/to/4toi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/to/4toi | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6211C  2oceS  2qbf S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 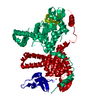
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 35924.781 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: 1-236,3-84 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Gene: rpsB, BU34_07500, ECs0171, LF82_1969, ECKG_00790 / Production host:  References: UniProt: C3TPN2, UniProt: F4TQ64, UniProt: P0A7V0*PLUS |
|---|---|
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
| #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.03 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 59.46 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 295.15 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 7.4 Details: 0.1 M HEPES-KOH, pH 7.4, 3 mM MgCl2, 7.5% w/v PEG 6000, 3% w/v 2-methyl-pentanediol-2,4, 100 mM KCl |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Diamond Diamond  / Beamline: I04 / Wavelength: 0.98 Å / Beamline: I04 / Wavelength: 0.98 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 6M-F / Detector: PIXEL / Date: May 20, 2012 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Monochromator: Diamond / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.98 Å / Relative weight: 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.3→37.79 Å / Num. obs: 18726 / % possible obs: 99 % / Redundancy: 8.1 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 32.2 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.993 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.175 / Rpim(I) all: 0.063 / Net I/σ(I): 7.4 / Num. measured all: 151502 / Scaling rejects: 437 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1 / Rejects: _
|
-Phasing
| Phasing | Method:  molecular replacement molecular replacement |
|---|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: PDB entries 2qbf and 2oce Resolution: 2.3→37.79 Å / SU ML: 0.26 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.33 / Phase error: 22.59 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 133.24 Å2 / Biso mean: 42.5864 Å2 / Biso min: 14.98 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 2.3→37.79 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Total num. of bins used: 7
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj





