[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-4mkq: Crystal structure of the Pore-Forming Toxin Monalysin mutant dele... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 4mkq | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of the Pore-Forming Toxin Monalysin mutant deleted of the membrane-spanning domain | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TOXIN / Pore-Forming Toxin | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhemolysis in another organism / porin activity / pore complex / monoatomic ion transport / protein homooligomerization / toxin activity / host cell plasma membrane / extracellular region Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Pseudomonas entomophila (bacteria) Pseudomonas entomophila (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.65 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.65 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Leone, P. / Roussel, A. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2015 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2015Title: X-ray and Cryo-electron Microscopy Structures of Monalysin Pore-forming Toxin Reveal Multimerization of the Pro-form. Authors: Philippe Leone / Cecilia Bebeacua / Onya Opota / Christine Kellenberger / Bruno Klaholz / Igor Orlov / Christian Cambillau / Bruno Lemaitre / Alain Roussel /   Abstract: β-Barrel pore-forming toxins (β-PFT), a large family of bacterial toxins, are generally secreted as water-soluble monomers and can form oligomeric pores in membranes following proteolytic cleavage ...β-Barrel pore-forming toxins (β-PFT), a large family of bacterial toxins, are generally secreted as water-soluble monomers and can form oligomeric pores in membranes following proteolytic cleavage and interaction with cell surface receptors. Monalysin has been recently identified as a β-PFT that contributes to the virulence of Pseudomonas entomophila against Drosophila. It is secreted as a pro-protein that becomes active upon cleavage. Here we report the crystal and cryo-electron microscopy structure of the pro-form of Monalysin as well as the crystal structures of the cleaved form and of an inactive mutant lacking the membrane-spanning region. The overall structure of Monalysin displays an elongated shape, which resembles those of β-pore-forming toxins, such as Aerolysin, but is devoid of a receptor-binding domain. X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy, and light-scattering studies show that pro-Monalysin forms a stable doughnut-like 18-mer complex composed of two disk-shaped nonamers held together by N-terminal swapping of the pro-peptides. This observation is in contrast with the monomeric pro-form of the other β-PFTs that are receptor-dependent for membrane interaction. The membrane-spanning region of pro-Monalysin is fully buried in the center of the doughnut, suggesting that upon cleavage of pro-peptides, the two disk-shaped nonamers can, and have to, dissociate to leave the transmembrane segments free to deploy and lead to pore formation. In contrast with other toxins, the delivery of 18 subunits at once, nearby the cell surface, may be used to bypass the requirement of receptor-dependent concentration to reach the threshold for oligomerization into the pore-forming complex. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  4mkq.cif.gz 4mkq.cif.gz | 89.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb4mkq.ent.gz pdb4mkq.ent.gz | 67.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  4mkq.json.gz 4mkq.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  4mkq_validation.pdf.gz 4mkq_validation.pdf.gz | 437.4 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  4mkq_full_validation.pdf.gz 4mkq_full_validation.pdf.gz | 438.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  4mkq_validation.xml.gz 4mkq_validation.xml.gz | 17.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  4mkq_validation.cif.gz 4mkq_validation.cif.gz | 25.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mk/4mkq https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mk/4mkq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mk/4mkq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mk/4mkq | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2698C  4mjtSC  4mkoC S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 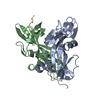
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 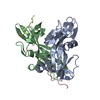
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 19108.105 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: see remark 999 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Pseudomonas entomophila (bacteria) / Strain: L48 / Gene: PSEEN3174 / Production host: Pseudomonas entomophila (bacteria) / Strain: L48 / Gene: PSEEN3174 / Production host:  #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2886.110 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: see remark 999 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Pseudomonas entomophila (bacteria) / Strain: L48 / Gene: PSEEN3174 / Production host: Pseudomonas entomophila (bacteria) / Strain: L48 / Gene: PSEEN3174 / Production host:  #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Compound details | AUTHORS STATE THAT PEPTIDE CHAINS (C AND D) AND PROTEIN CHAINS (A AND B) BELONG TO A SAME SINGLE ...AUTHORS STATE THAT PEPTIDE CHAINS (C AND D) AND PROTEIN CHAINS (A AND B) BELONG TO A SAME SINGLE CHAIN WITHOUT BEEN CLEAVED BETWEEN RESIDUES 35 AND 36. AUTHORS HAVE STRONG EVIDENCE OF THE DOMAIN SWAPPING BUT NO EXPERIMENT | Sequence details | THE SEQUENCE OF CHAIN C AND D MATCHES UNIPROT ENTRY Q1I8U1 BETWEEN RESIDUES 9 AND 35. THE SEQUENCE ...THE SEQUENCE OF CHAIN C AND D MATCHES UNIPROT ENTRY Q1I8U1 BETWEEN RESIDUES 9 AND 35. THE SEQUENCE OF CHAIN A AND B MATCHES UNIPROT ENTRY Q1I8U1 BETWEEN RESIDUES 36 AND 271, WITH A DELETION OF MEMBRANE SPANNING DOMAIN (RESIDUES 102-170), THAT IS REPLACED BY A GLY501-SER502 DIPEPTIDE LINKER. SEE REMARK 400 FOR CHAIN ID ASSIGNMENT | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 4.34 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 71.65 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / pH: 6.5 Details: 0.1M sodium cacodylate, 0.2M calcium acetate, 18% PEG8000, pH 6.5, VAPOR DIFFUSION, SITTING DROP, temperature 293K |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  ESRF ESRF  / Beamline: ID29 / Wavelength: 0.97887 Å / Beamline: ID29 / Wavelength: 0.97887 Å |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.97887 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.65→30 Å / Num. all: 21936 / Num. obs: 21936 / % possible obs: 100 % / Observed criterion σ(F): 0 / Observed criterion σ(I): 0 / Redundancy: 3.4 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 53.13 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.132 / Net I/σ(I): 7.8 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.65→2.79 Å / Redundancy: 3.4 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.534 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 2 / Num. unique all: 3186 / % possible all: 100 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: PDB entry 4MJT Resolution: 2.65→29.94 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.8983 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.8748 / SU R Cruickshank DPI: 0.288 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 38.36 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine analyze | Luzzati coordinate error obs: 0.296 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.65→29.94 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 2.65→2.78 Å / Total num. of bins used: 11
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj
