[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-3jap: Structure of a partial yeast 48S preinitiation complex in closed ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3jap | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
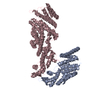
| Title | Structure of a partial yeast 48S preinitiation complex in closed conformation | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSLATION / Eukaryotic translation initiation / 48S / small ribosome subunit / 40S / 43S | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationformation of translation initiation ternary complex / Recycling of eIF2:GDP / Cellular response to mitochondrial stress / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / methionyl-initiator methionine tRNA binding / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex, eIF3e / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex, eIF3m / incipient cellular bud site / translation reinitiation / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 complex ...formation of translation initiation ternary complex / Recycling of eIF2:GDP / Cellular response to mitochondrial stress / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / methionyl-initiator methionine tRNA binding / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex, eIF3e / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex, eIF3m / incipient cellular bud site / translation reinitiation / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 complex / formation of cytoplasmic translation initiation complex / multi-eIF complex / cytoplasmic translational initiation / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex / eukaryotic 43S preinitiation complex / formation of translation preinitiation complex / eukaryotic 48S preinitiation complex / positive regulation of translational fidelity / protein-synthesizing GTPase / GDP-dissociation inhibitor activity / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / Translation initiation complex formation / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / ribosomal small subunit binding / 90S preribosome / ribosomal subunit export from nucleus / regulation of translational fidelity / endonucleolytic cleavage in ITS1 to separate SSU-rRNA from 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / translation regulator activity / translation initiation factor binding / translation initiation factor activity / cellular response to amino acid starvation / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA / translational initiation / small-subunit processome / maintenance of translational fidelity / cytoplasmic stress granule / rRNA processing / double-stranded RNA binding / regulation of translation / ribosome binding / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / ribonucleoprotein complex / GTPase activity / mRNA binding / protein kinase binding / GTP binding / nucleolus / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Kluyveromyces lactis (yeast) Kluyveromyces lactis (yeast)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Llacer, J.L. / Hussain, T. / Ramakrishnan, V. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2015 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2015Title: Conformational Differences between Open and Closed States of the Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Complex. Authors: Jose L Llácer / Tanweer Hussain / Laura Marler / Colin Echeverría Aitken / Anil Thakur / Jon R Lorsch / Alan G Hinnebusch / V Ramakrishnan /   Abstract: Translation initiation in eukaryotes begins with the formation of a pre-initiation complex (PIC) containing the 40S ribosomal subunit, eIF1, eIF1A, eIF3, ternary complex (eIF2-GTP-Met-tRNAi), and ...Translation initiation in eukaryotes begins with the formation of a pre-initiation complex (PIC) containing the 40S ribosomal subunit, eIF1, eIF1A, eIF3, ternary complex (eIF2-GTP-Met-tRNAi), and eIF5. The PIC, in an open conformation, attaches to the 5' end of the mRNA and scans to locate the start codon, whereupon it closes to arrest scanning. We present single particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) reconstructions of 48S PICs from yeast in these open and closed states, at 6.0 Å and 4.9 Å, respectively. These reconstructions show eIF2β as well as a configuration of eIF3 that appears to encircle the 40S, occupying part of the subunit interface. Comparison of the complexes reveals a large conformational change in the 40S head from an open mRNA latch conformation to a closed one that constricts the mRNA entry channel and narrows the P site to enclose tRNAi, thus elucidating key events in start codon recognition. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3jap.cif.gz 3jap.cif.gz | 2.1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3jap.ent.gz pdb3jap.ent.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3jap.json.gz 3jap.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/3jap https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/3jap ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/3jap ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/3jap | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 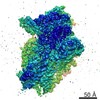 3048MC  3047C 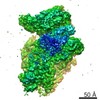 3049C  3050C  3jamC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 3 types, 3 molecules 123
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 24223.482 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Kluyveromyces lactis (yeast) Kluyveromyces lactis (yeast) |
|---|---|
| #2: RNA chain | Mass: 573814.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Kluyveromyces lactis (yeast) Kluyveromyces lactis (yeast) |
| #3: RNA chain | Mass: 7786.572 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
+Protein , 42 types, 42 molecules ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcd...
-Protein/peptide , 2 types, 2 molecules hr
| #37: Protein/peptide | Mass: 3354.243 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Kluyveromyces lactis (yeast) / References: UniProt: P0CX86 Kluyveromyces lactis (yeast) / References: UniProt: P0CX86 |
|---|---|
| #46: Protein/peptide | Mass: 3963.560 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Production host:  |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 87 molecules 

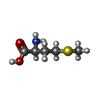
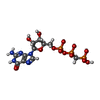



| #48: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #49: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #50: Chemical | ChemComp-MET / | #51: Chemical | ChemComp-GCP / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 20 mM MES-KOH, 40 mM potassium acetate, 10 mM ammonium acetate, 8 mM magnesium acetate, 2 mM DTT pH: 6.5 Details: 20 mM MES-KOH, 40 mM potassium acetate, 10 mM ammonium acetate, 8 mM magnesium acetate, 2 mM DTT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.17 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Quantifoil R2/2 400 mesh copper grids with 4-5 nm thin carbon on top | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Temp: 120 K / Humidity: 100 % Details: Blot for 2.5 to 3 seconds before plunging into liquid ethane (FEI VITROBOT MARK I). Method: Blot for 2.5 to 3 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS / Date: Jul 4, 2014 Details: Complete dataset was collected over two non-consecutive days. |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 59000 X / Calibrated magnification: 104478 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder type: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 27 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 5500 |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: REFMAC / Version: 5.8.0124 2015/06/03 / Classification: refinement / Contact author: Garib N. Murshudov / Contact author email: garib[at]mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk Description: (un)restrained refinement or idealisation of macromolecular structures | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Details: Each particle | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 21401 / Nominal pixel size: 1.34 Å / Actual pixel size: 1.34 Å / Details: gold-standard / Refinement type: HALF-MAPS REFINED INDEPENDENTLY / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: RECIPROCAL / Target criteria: R-factor, FSC / Details: METHOD--Local refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Details: Hydrogens have been added in their riding positions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj