+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8812 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the PulG pseudopilus | ||||||||||||
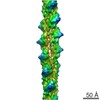
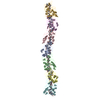
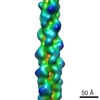
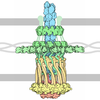
 Map data Map data | map of PulG filament | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | helical polymer / bacterial secretion / cryo-EM / PROTEIN TRANSPORT | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationprotein secretion by the type II secretion system / type II protein secretion system complex / membrane => GO:0016020 / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Klebsiella oxytoca (bacteria) Klebsiella oxytoca (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.0 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lopez-Castilla A / Thomassin JL | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  France, European Union, 3 items France, European Union, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2017 Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2017Title: Structure of the calcium-dependent type 2 secretion pseudopilus. Authors: Aracelys López-Castilla / Jenny-Lee Thomassin / Benjamin Bardiaux / Weili Zheng / Mangayarkarasi Nivaskumar / Xiong Yu / Michael Nilges / Edward H Egelman / Nadia Izadi-Pruneyre / Olivera Francetic /   Abstract: Many Gram-negative bacteria use type 2 secretion systems (T2SSs) to secrete proteins involved in virulence and adaptation. Transport of folded proteins via T2SS nanomachines requires the assembly of ...Many Gram-negative bacteria use type 2 secretion systems (T2SSs) to secrete proteins involved in virulence and adaptation. Transport of folded proteins via T2SS nanomachines requires the assembly of inner membrane-anchored fibres called pseudopili. Although efficient pseudopilus assembly is essential for protein secretion, structure-based functional analyses are required to unravel the mechanistic link between these processes. Here, we report an atomic model for a T2SS pseudopilus from Klebsiella oxytoca, obtained by fitting the NMR structure of its calcium-bound subunit PulG into the ~5-Å-resolution cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of assembled fibres. This structure reveals the comprehensive network of inter-subunit contacts and unexpected features, including a disordered central region of the PulG helical stem, and highly flexible C-terminal residues on the fibre surface. NMR, mutagenesis and functional analyses highlight the key role of calcium in PulG folding and stability. Fibre disassembly in the absence of calcium provides a basis for pseudopilus length control, essential for protein secretion, and supports the Archimedes screw model for the type 2 secretion mechanism. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8812.map.gz emd_8812.map.gz | 4.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8812-v30.xml emd-8812-v30.xml emd-8812.xml emd-8812.xml | 15.9 KB 15.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8812.png emd_8812.png | 110.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8812.cif.gz emd-8812.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8812 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8812 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8812 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8812 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5wdaMC  5o2yC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8812.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8812.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | map of PulG filament | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : PulG pseudopilus
| Entire | Name: PulG pseudopilus |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: PulG pseudopilus
| Supramolecule | Name: PulG pseudopilus / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Klebsiella oxytoca (bacteria) Klebsiella oxytoca (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: General secretion pathway protein G
| Macromolecule | Name: General secretion pathway protein G / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 25 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Klebsiella oxytoca (bacteria) Klebsiella oxytoca (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.525482 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: (MEA)TLLEIMVVI VILGVLASLV VPNLMGNKEK ADRQKVVSDL VALEGALDMY KLDNSRYPTT EQGLQALVSA PSAEPH ARN YPEGGYIRRL PQDPWGSDYQ LLSPGQCGQV DIFSLGPDGV PESNDDIGNC TIGKK UniProtKB: Type II secretion system core protein G |
-Macromolecule #2: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 25 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 1819 / Average electron dose: 20.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 10.2 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 83.2 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 5.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: IHRSR / Number images used: 85619 |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Software - Name: CTFFIND3 / Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER / Details: solid cylinder |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















