[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-60009: Structure of the RBM3 ring of Salmonella flagellar MS-ring protei... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the RBM3 ring of Salmonella flagellar MS-ring protein FliF with C34 symmetry applied | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Bacterial flagellum / flagellar assembly / electron Cryomicroscopy / MS-ring / type III secretion system / Salmonella / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbacterial-type flagellum basal body, MS ring / cytoskeletal motor activity / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) / Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) /  Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium (bacteria) Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.5 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kinoshita M / Makino F / Miyata T / Imada K / Minamino T / Namba K | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 10 items Japan, 10 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2025Title: Structural basis for assembly and function of the Salmonella flagellar MS-ring with three different symmetries. Authors: Miki Kinoshita / Fumiaki Makino / Tomoko Miyata / Katsumi Imada / Keiichi Namba / Tohru Minamino /  Abstract: The flagellar MS-ring is the initial template for flagellar assembly and houses the flagellar protein export complex. The MS-ring has three parts of different symmetries within the ring structure by ...The flagellar MS-ring is the initial template for flagellar assembly and houses the flagellar protein export complex. The MS-ring has three parts of different symmetries within the ring structure by assembly of FliF subunits in two different conformations with distinct arrangements of three ring-building motifs, RBM1, RBM2, and RBM3. However, it remains unknown how these symmetries are generated. A combination of cryoEM structure and structure-based mutational analyses demonstrates that the well-conserved DQxGxxL motif in the RBM2-RBM3 hinge loop allows RBM2 to take two different orientations relative to RBM3. Of 34 FliF subunits of the MS-ring in the basal body, 23 RBM2 domains form an inner ring with a central pore that accommodates the flagellar protein export complex, and the remaining 11 RBM2 domains form 11 cog-like structures together with RBM1 domains just outside the inner RBM2-ring. We propose that a dimer of FliF with two different conformations initiates MS-ring assembly. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_60009.map.gz emd_60009.map.gz | 227.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-60009-v30.xml emd-60009-v30.xml emd-60009.xml emd-60009.xml | 22.9 KB 22.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_60009_fsc.xml emd_60009_fsc.xml | 14.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_60009.png emd_60009.png | 64.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-60009.cif.gz emd-60009.cif.gz | 6.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_60009_half_map_1.map.gz emd_60009_half_map_1.map.gz emd_60009_half_map_2.map.gz emd_60009_half_map_2.map.gz | 189.9 MB 189.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60009 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60009 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60009 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60009 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8zduMC  8zdsC  8zdtC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_60009.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_60009.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
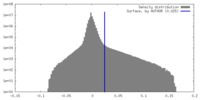
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_60009_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_60009_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Structure of the RBM3 ring of Salmonella flagellar MS-ring protei...
| Entire | Name: Structure of the RBM3 ring of Salmonella flagellar MS-ring protein FliF with C34 symmetry applied |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Structure of the RBM3 ring of Salmonella flagellar MS-ring protei...
| Supramolecule | Name: Structure of the RBM3 ring of Salmonella flagellar MS-ring protein FliF with C34 symmetry applied type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Flagellar M-ring protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Flagellar M-ring protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 34 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium (bacteria) Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 61.295645 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium (bacteria) Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MSATASTATQ PKPLEWLNRL RANPRIPLIV AGSAAVAIVV AMVLWAKTPD YRTLFSNLSD QDGGAIVAQL TQMNIPYRFA NGSGAIEVP ADKVHELRLR LAQQGLPKGG AVGFELLDQE KFGISQFSEQ VNYQRALEGE LARTIETLGP VKSARVHLAM P KPSLFVRE ...String: MSATASTATQ PKPLEWLNRL RANPRIPLIV AGSAAVAIVV AMVLWAKTPD YRTLFSNLSD QDGGAIVAQL TQMNIPYRFA NGSGAIEVP ADKVHELRLR LAQQGLPKGG AVGFELLDQE KFGISQFSEQ VNYQRALEGE LARTIETLGP VKSARVHLAM P KPSLFVRE QKSPSASVTV TLEPGRALDE GQISAVVHLV SSAVAGLPPG NVTLVDQSGH LLTQSNTSGR DLNDAQLKFA ND VESRIQR RIEAILSPIV GNGNVHAQVT AQLDFANKEQ TEEHYSPNGD ASKATLRSRQ LNISEQVGAG YPGGVPGALS NQP APPNEA PIATPPTNQQ NAQNTPQTST STNSNSAGPR STQRNETSNY EVDRTIRHTK MNVGDIERLS VAVVVNYKTL ADGK PLPLT ADQMKQIEDL TREAMGFSDK RGDTLNVVNS PFSAVDNTGG ELPFWQQQSF IDQLLAAGRW LLVLVVAWIL WRKAV RPQL TRRVEEAKAA QEQAQVRQET EEAVEVRLSK DEQLQQRRAN QRLGAEVMSQ RIREMSDNDP RVVALVIRQW MSNDHE UniProtKB: Flagellar M-ring protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R0.6/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 10 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL CRYO ARM 300 |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: In-column Omega Filter / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Number real images: 4885 / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: JEOL CRYOSPECPORTER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model |
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | |||||||||
| Output model |  PDB-8zdu: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)