+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Single particle cryo-EM structure of the multidrug efflux pump MdtF from Escherichia coli | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | ||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | multidrug / pump / anaerobic / lipid / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報xenobiotic transmembrane transport / bile acid transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transport / bile acid and bile salt transport / efflux transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / response to toxic substance / response to antibiotic / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  | |||||||||
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3.56 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Lawrence R / Adams C / Sousa JS / Ahdash Z / Reading E | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  英国, 1件 英国, 1件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: bioRxiv / 年: 2025 ジャーナル: bioRxiv / 年: 2025タイトル: Molecular basis for multidrug efflux by an anaerobic RND transporter. 著者: Ryan Lawrence / Mohd Athar / Muhammad R Uddin / Christopher Adams / Joana S Sousa / Oliver Durrant / Sophie Lellman / Lucy Sutton / C William Keevil / Nisha Patel / Christine Prosser / David ...著者: Ryan Lawrence / Mohd Athar / Muhammad R Uddin / Christopher Adams / Joana S Sousa / Oliver Durrant / Sophie Lellman / Lucy Sutton / C William Keevil / Nisha Patel / Christine Prosser / David McMillan / Helen I Zgurskaya / Attilio V Vargiu / Zainab Ahdash / Eamonn Reading 要旨: Bacteria can resist antibiotics and toxic substances within demanding ecological settings, such as low oxygen, extreme acid, and during nutrient starvation. MdtEF, a proton motive force-driven efflux ...Bacteria can resist antibiotics and toxic substances within demanding ecological settings, such as low oxygen, extreme acid, and during nutrient starvation. MdtEF, a proton motive force-driven efflux pump from the resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND) superfamily, is upregulated in these conditions but its molecular mechanism is unknown. Here, we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of Escherichia coli multidrug transporter MdtF within native-lipid nanodiscs, including a single-point mutant with an altered multidrug phenotype and associated substrate-bound form. We reveal that drug binding domain and channel conformational plasticity likely governs promiscuous substrate specificity, analogous to its closely related, constitutively expressed counterpart, AcrB. Whereas we discover distinct transmembrane state transitions within MdtF, which create a more engaged proton relay network, altered drug transport allostery and an acid-responsive increase in efflux efficiency. Physiologically, this provides means of xenobiotic and metabolite disposal within remodelled cell membranes that presage encounters with acid stresses, as endured in the gastrointestinal tract. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
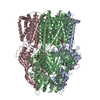
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_53281.map.gz emd_53281.map.gz | 62.7 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-53281-v30.xml emd-53281-v30.xml emd-53281.xml emd-53281.xml | 18.2 KB 18.2 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| FSC (解像度算出) |  emd_53281_fsc.xml emd_53281_fsc.xml | 9.3 KB | 表示 |  FSCデータファイル FSCデータファイル |
| 画像 |  emd_53281.png emd_53281.png | 100.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-53281.cif.gz emd-53281.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_53281_half_map_1.map.gz emd_53281_half_map_1.map.gz emd_53281_half_map_2.map.gz emd_53281_half_map_2.map.gz | 51.9 MB 51.9 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-53281 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-53281 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-53281 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-53281 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_53281_validation.pdf.gz emd_53281_validation.pdf.gz | 888 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_53281_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_53281_full_validation.pdf.gz | 887.5 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_53281_validation.xml.gz emd_53281_validation.xml.gz | 16.2 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_53281_validation.cif.gz emd_53281_validation.cif.gz | 21.2 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-53281 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-53281 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-53281 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-53281 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_53281.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 67 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_53281.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 67 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 0.946 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
-ハーフマップ: #2
| ファイル | emd_53281_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: #1
| ファイル | emd_53281_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : Homotrimer of WT multidrug resistance protein MdtF in SMALP nanodisc
| 全体 | 名称: Homotrimer of WT multidrug resistance protein MdtF in SMALP nanodisc |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: Homotrimer of WT multidrug resistance protein MdtF in SMALP nanodisc
| 超分子 | 名称: Homotrimer of WT multidrug resistance protein MdtF in SMALP nanodisc タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: #1 |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 334.551 KDa |
-分子 #1: Multidrug resistance protein MdtF
| 分子 | 名称: Multidrug resistance protein MdtF / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 詳細: MdtF protein with a C-terminal 6x His (hexahistidine) tag, separated by a linker sequence including a TEV cleavage site コピー数: 3 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 113.759867 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  |
| 配列 | 文字列: MANYFIDRPV FAWVLAIIMM LAGGLAIMNL PVAQYPQIAP PTITVSATYP GADAQTVEDS VTQVIEQNMN GLDGLMYMSS TSDAAGNAS ITLTFETGTS PDIAQVQVQN KLQLAMPSLP EAVQQQGISV DKSSSNILMV AAFISDNGSL NQYDIADYVA S NIKDPLSR ...文字列: MANYFIDRPV FAWVLAIIMM LAGGLAIMNL PVAQYPQIAP PTITVSATYP GADAQTVEDS VTQVIEQNMN GLDGLMYMSS TSDAAGNAS ITLTFETGTS PDIAQVQVQN KLQLAMPSLP EAVQQQGISV DKSSSNILMV AAFISDNGSL NQYDIADYVA S NIKDPLSR TAGVGSVQLF GSEYAMRIWL DPQKLNKYNL VPSDVISQIK VQNNQISGGQ LGGMPQAADQ QLNASIIVQT RL QTPEEFG KILLKVQQDG SQVLLRDVAR VELGAEDYST VARYNGKPAA GIAIKLAAGA NALDTSRAVK EELNRLSAYF PAS LKTVYP YDTTPFIEIS IQEVFKTLVE AIILVFLVMY LFLQNFRATI IPTIAVPVVI LGTFAILSAV GFTINTLTMF GMVL AIGLL VDDAIVVVEN VERVIAEDKL PPKEATHKSM GQIQRALVGI AVVLSAVFMP MAFMSGATGE IYRQFSITLI SSMLL SVFV AMSLTPALCA TILKAAPEGG HKPNALFARF NTLFEKSTQH YTDSTRSLLR CTGRYMVVYL LICAGMAVLF LRTPTS FLP EEDQGVFMTT AQLPSGATMV NTTKVLQQVT DYYLTKEKDN VQSVFTVGGF GFSGQGQNNG LAFISLKPWS ERVGEEN SV TAIIQRAMIA LSSINKAVVF PFNLPAVAEL GTASGFDMEL LDNGNLGHEK LTQARNELLS LAAQSPNQVT GVRPNGLE D TPMFKVNVNA AKAEAMGVAL SDINQTISTA FGSSYVNDFL NQGRVKKVYV QAGTPFRMLP DNINQWYVRN ASGTMAPLS AYSSTEWTYG SPRLERYNGI PSMEILGEAA AGKSTGDAMK FMADLVAKLP AGVGYSWTGL SYQEALSSNQ APALYAISLV VVFLALAAL YESWSIPFSV MLVVPLGVVG ALLATDLRGL SNDVYFQVGL LTTIGLSAKN AILIVEFAVE MMQKEGKTPI E AIIEAARM RLRPILMTSL AFILGVLPLV ISHGAGSGAQ NAVGTGVMGG MFAATVLAIY FVPVFFVVVE HLFARFKKAA SG ENLYFQS LEHHHHHH UniProtKB: Multidrug resistance protein MdtF |
-分子 #2: PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE
| 分子 | 名称: PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE / タイプ: ligand / ID: 2 / コピー数: 21 / 式: PTY |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 理論値: 734.039 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PTY: |
-分子 #3: DODECANE
| 分子 | 名称: DODECANE / タイプ: ligand / ID: 3 / コピー数: 7 / 式: D12 |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 理論値: 170.335 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-D12: |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 濃度 | 0.25 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.4 |
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE / チャンバー内湿度: 100 % / チャンバー内温度: 277.15 K / 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) 平均電子線量: 48.82 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 200 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2.2 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 0.8 µm / 倍率(公称値): 190000 |
+ 画像解析
画像解析
-原子モデル構築 1
| 初期モデル | Chain - Source name: SwissModel / Chain - Initial model type: in silico model |
|---|---|
| 精密化 | 空間: REAL / プロトコル: AB INITIO MODEL |
| 得られたモデル |  PDB-9qpr: |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






































