[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9qpr: Single particle cryo-EM structure of the multidrug efflux pump Md... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9qpr | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Single particle cryo-EM structure of the multidrug efflux pump MdtF from Escherichia coli | ||||||
 Components Components | Multidrug resistance protein MdtF | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / multidrug / pump / anaerobic / lipid | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationxenobiotic transmembrane transport / bile acid transmembrane transporter activity / bile acid and bile salt transport / efflux transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transport / response to toxic substance / response to antibiotic / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.56 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lawrence, R. / Adams, C. / Sousa, J.S. / Ahdash, Z. / Reading, E. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025Title: Molecular basis for multidrug efflux by an anaerobic RND transporter. Authors: Ryan Lawrence / Mohd Athar / Muhammad R Uddin / Christopher Adams / Joana S Sousa / Oliver Durrant / Sophie Lellman / Lucy Sutton / C William Keevil / Nisha Patel / Christine Prosser / David ...Authors: Ryan Lawrence / Mohd Athar / Muhammad R Uddin / Christopher Adams / Joana S Sousa / Oliver Durrant / Sophie Lellman / Lucy Sutton / C William Keevil / Nisha Patel / Christine Prosser / David McMillan / Helen I Zgurskaya / Attilio V Vargiu / Zainab Ahdash / Eamonn Reading Abstract: Bacteria can resist antibiotics and toxic substances within demanding ecological settings, such as low oxygen, extreme acid, and during nutrient starvation. MdtEF, a proton motive force-driven efflux ...Bacteria can resist antibiotics and toxic substances within demanding ecological settings, such as low oxygen, extreme acid, and during nutrient starvation. MdtEF, a proton motive force-driven efflux pump from the resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND) superfamily, is upregulated in these conditions but its molecular mechanism is unknown. Here, we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of Escherichia coli multidrug transporter MdtF within native-lipid nanodiscs, including a single-point mutant with an altered multidrug phenotype and associated substrate-bound form. We reveal that drug binding domain and channel conformational plasticity likely governs promiscuous substrate specificity, analogous to its closely related, constitutively expressed counterpart, AcrB. Whereas we discover distinct transmembrane state transitions within MdtF, which create a more engaged proton relay network, altered drug transport allostery and an acid-responsive increase in efflux efficiency. Physiologically, this provides means of xenobiotic and metabolite disposal within remodelled cell membranes that presage encounters with acid stresses, as endured in the gastrointestinal tract. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9qpr.cif.gz 9qpr.cif.gz | 630.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9qpr.ent.gz pdb9qpr.ent.gz | 432.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9qpr.json.gz 9qpr.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qp/9qpr https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qp/9qpr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qp/9qpr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qp/9qpr | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  53281MC  9qpsC  9qptC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 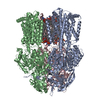
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 113759.867 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: MdtF protein with a C-terminal 6x His (hexahistidine) tag, separated by a linker sequence including a TEV cleavage site Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Chemical | ChemComp-PTY / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-D12 / Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Homotrimer of WT multidrug resistance protein MdtF in SMALP nanodisc Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.334551 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.25 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 190000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 48.82 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2501990 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.56 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 583735 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Source name: SwissModel / Type: in silico model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 39.8 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj