+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
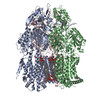
| Title | Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB / NCMN / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationalkane transmembrane transporter activity / alkane transport / Iron assimilation using enterobactin / Antimicrobial resistance / enterobactin transport / enterobactin transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic detoxification by transmembrane export across the cell outer membrane / periplasmic side of plasma membrane / efflux pump complex / bile acid transmembrane transporter activity ...alkane transmembrane transporter activity / alkane transport / Iron assimilation using enterobactin / Antimicrobial resistance / enterobactin transport / enterobactin transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic detoxification by transmembrane export across the cell outer membrane / periplasmic side of plasma membrane / efflux pump complex / bile acid transmembrane transporter activity / Secretion of toxins / bile acid and bile salt transport / efflux transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transport / fatty acid transport / response to toxic substance / response to xenobiotic stimulus / response to antibiotic / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / negative staining / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Trinh TKH / Cabezas A | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Chem Sci / Year: 2023 Journal: Chem Sci / Year: 2023Title: pH-tunable membrane-active polymers, NCMNP2a-, and their potential membrane protein applications. Authors: Thi Kim Hoang Trinh / Andres Jorge Cabezas / Soumil Joshi / Claudio Catalano / Abu Bakkar Siddique / Weihua Qiu / Sanket Deshmukh / Amedee des Georges / Youzhong Guo /  Abstract: Accurate 3D structures of membrane proteins are essential for comprehending their mechanisms of action and designing specific ligands to modulate their activities. However, these structures are still ...Accurate 3D structures of membrane proteins are essential for comprehending their mechanisms of action and designing specific ligands to modulate their activities. However, these structures are still uncommon due to the involvement of detergents in the sample preparation. Recently, membrane-active polymers have emerged as an alternative to detergents, but their incompatibility with low pH and divalent cations has hindered their efficacy. Herein, we describe the design, synthesis, characterization, and application of a new class of pH-tunable membrane-active polymers, NCMNP2a-. The results demonstrated that NCMNP2a- could be used for high-resolution single-particle cryo-EM structural analysis of AcrB in various pH conditions and can effectively solubilize TSPO with the function preserved. Molecular dynamic simulation is consistent with experimental data that shed great insights into the working mechanism of this class of polymers. These results demonstrated that NCMNP2a- might have broad applications in membrane protein research. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24653.map.gz emd_24653.map.gz | 168.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24653-v30.xml emd-24653-v30.xml emd-24653.xml emd-24653.xml | 16.7 KB 16.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
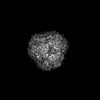
| Images |  emd_24653.png emd_24653.png | 109.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24653.cif.gz emd-24653.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_24653_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24653_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24653_half_map_2.map.gz emd_24653_half_map_2.map.gz | 165.2 MB 165.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24653 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24653 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24653 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24653 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7rr6MC  7rr7C  7rr8C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24653.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24653.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
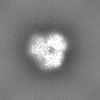
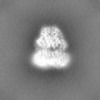
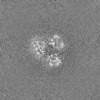
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.8465 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_24653_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
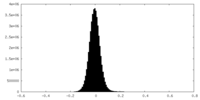
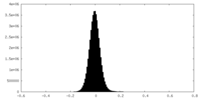
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_24653_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
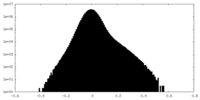
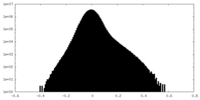
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB
| Entire | Name: Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB
| Supramolecule | Name: Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB
| Macromolecule | Name: Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 114.736289 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPNFFIDRPI FAWVIAIIIM LAGGLAILKL PVAQYPTIAP PAVTISASYP GADAKTVQDT VTQVIEQNMN GIDNLMYMSS NSDSTGTVQ ITLTFESGTD ADIAQVQVQN KLQLAMPLLP QEVQQQGVSV EKSSSSFLMV VGVINTDGTM TQEDISDYVA A NMKDAISR ...String: MPNFFIDRPI FAWVIAIIIM LAGGLAILKL PVAQYPTIAP PAVTISASYP GADAKTVQDT VTQVIEQNMN GIDNLMYMSS NSDSTGTVQ ITLTFESGTD ADIAQVQVQN KLQLAMPLLP QEVQQQGVSV EKSSSSFLMV VGVINTDGTM TQEDISDYVA A NMKDAISR TSGVGDVQLF GSQYAMRIWM NPNELNKFQL TPVDVITAIK AQNAQVAAGQ LGGTPPVKGQ QLNASIIAQT RL TSTEEFG KILLKVNQDG SRVLLRDVAK IELGGENYDI IAEFNGQPAS GLGIKLATGA NALDTAAAIR AELAKMEPFF PSG LKIVYP YDTTPFVKIS IHEVVKTLVE AIILVFLVMY LFLQNFRATL IPTIAVPVVL LGTFAVLAAF GFSINTLTMF GMVL AIGLL VDDAIVVVEN VERVMAEEGL PPKEATRKSM GQIQGALVGI AMVLSAVFVP MAFFGGSTGA IYRQFSITIV SAMAL SVLV ALILTPALCA TMLKPIAKGD HGEGKKGFFG WFNRMFEKST HHYTDSVGGI LRSTGRYLVL YLIIVVGMAY LFVRLP SSF LPDEDQGVFM TMVQLPAGAT QERTQKVLNE VTHYYLTKEK NNVESVFAVN GFGFAGRGQN TGIAFVSLKD WADRPGE EN KVEAITMRAT RAFSQIKDAM VFAFNLPAIV ELGTATGFDF ELIDQAGLGH EKLTQARNQL LAEAAKHPDM LTSVRPNG L EDTPQFKIDI DQEKAQALGV SINDINTTLG AAWGGSYVND FIDRGRVKKV YVMSEAKYRM LPDDIGDWYV RAADGQMVP FSAFSSSRWE YGSPRLERYN GLPSMEILGQ AAPGKSTGEA MELMEQLASK LPTGVGYDWT GMSYQERLSG NQAPSLYAIS LIVVFLCLA ALYESWSIPF SVMLVVPLGV IGALLAATFR GLTNDVYFQV GLLTTIGLSA KNAILIVEFA KDLMDKEGKG L IEATLDAV RMRLRPILMT SLAFILGVMP LVISTGAGSG AQNAVGTGVM GGMVTATVLA IFFVPVFFVV VRRRFSRKNE DI EHSHTVD HHLEHHHHHH UniProtKB: Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB |
-Macromolecule #2: PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 27 / Formula: PTY |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 734.039 Da |
| Chemical component information | 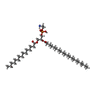 ChemComp-PTY: |
-Macromolecule #3: DODECANE
| Macromolecule | Name: DODECANE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: D12 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 170.335 Da |
| Chemical component information | 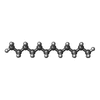 ChemComp-D12: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining, cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 5 |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: 2% uranyl acetate |
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R0.6/1 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 75.9 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: RANDOM CONICAL TILT |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 73352 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)