+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Phosphorylated (E1371Q)CFTR in complex with PKA-C | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Phosphorylated (E1371Q)CFTR in complex with PKA-C | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CFTR / PKA / complex / HYDROLASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of voltage-gated chloride channel activity / : / Sec61 translocon complex binding / channel-conductance-controlling ATPase / intracellularly ATP-gated chloride channel activity / CD209 (DC-SIGN) signaling / HDL assembly / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of enamel mineralization / Rap1 signalling ...positive regulation of voltage-gated chloride channel activity / : / Sec61 translocon complex binding / channel-conductance-controlling ATPase / intracellularly ATP-gated chloride channel activity / CD209 (DC-SIGN) signaling / HDL assembly / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of enamel mineralization / Rap1 signalling / Ion homeostasis / transepithelial water transport / RHO GTPases regulate CFTR trafficking / PKA activation in glucagon signalling / DARPP-32 events / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / GPER1 signaling / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / RET signaling / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / amelogenesis / Interleukin-3, Interleukin-5 and GM-CSF signaling / intracellular pH elevation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / PKA activation / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / chloride channel inhibitor activity / : / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Hedgehog 'off' state / Golgi-associated vesicle membrane / multicellular organismal-level water homeostasis / cholesterol transport / bicarbonate transport / bicarbonate transmembrane transporter activity / vesicle docking involved in exocytosis / chloride channel regulator activity / membrane hyperpolarization / cAMP-dependent protein kinase / regulation of protein processing / chloride transmembrane transporter activity / cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity / protein localization to lipid droplet / cAMP-dependent protein kinase complex / regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly / cellular response to parathyroid hormone stimulus / regulation of osteoblast differentiation / cellular response to cold / Mitochondrial protein degradation / sperm capacitation / cholesterol biosynthetic process / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / negative regulation of glycolytic process through fructose-6-phosphate / ciliary base / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / RHOQ GTPase cycle / chloride channel activity / intracellular potassium ion homeostasis / mesoderm formation / positive regulation of exocytosis / plasma membrane raft / axoneme / ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity / sperm flagellum / chloride channel complex / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / ABC-type transporter activity / postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / 14-3-3 protein binding / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity / cellular response to glucagon stimulus / acrosomal vesicle / cellular response to forskolin / protein export from nucleus / positive regulation of phagocytosis / chloride transmembrane transport / response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / cellular response to cAMP / positive regulation of protein export from nucleus / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / neural tube closure / PDZ domain binding / neuromuscular junction / cellular response to glucose stimulus / establishment of localization in cell / clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane / positive regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / Late endosomal microautophagy Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fiedorczuk K / Chen J / Csanady L | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024Title: The structures of protein kinase A in complex with CFTR: Mechanisms of phosphorylation and noncatalytic activation. Authors: Karol Fiedorczuk / Iordan Iordanov / Csaba Mihályi / Andras Szollosi / László Csanády / Jue Chen /   Abstract: Protein kinase A (PKA) is a key regulator of cellular functions by selectively phosphorylating numerous substrates, including ion channels, enzymes, and transcription factors. It has long served as a ...Protein kinase A (PKA) is a key regulator of cellular functions by selectively phosphorylating numerous substrates, including ion channels, enzymes, and transcription factors. It has long served as a model system for understanding the eukaryotic kinases. Using cryoelectron microscopy, we present complex structures of the PKA catalytic subunit (PKA-C) bound to a full-length protein substrate, the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)-an ion channel vital to human health. CFTR gating requires phosphorylation of its regulatory (R) domain. Unphosphorylated CFTR engages PKA-C at two locations, establishing two "catalytic stations" near to, but not directly involving, the R domain. This configuration, coupled with the conformational flexibility of the R domain, permits transient interactions of the eleven spatially separated phosphorylation sites. Furthermore, we determined two structures of the open-pore CFTR stabilized by PKA-C, providing a molecular basis to understand how PKA-C stimulates CFTR currents even in the absence of phosphorylation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_47239.map.gz emd_47239.map.gz | 307.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-47239-v30.xml emd-47239-v30.xml emd-47239.xml emd-47239.xml | 22.5 KB 22.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_47239_fsc.xml emd_47239_fsc.xml | 14.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_47239.png emd_47239.png | 107.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-47239.cif.gz emd-47239.cif.gz | 7.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_47239_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47239_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47239_half_map_2.map.gz emd_47239_half_map_2.map.gz | 301.2 MB 301.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47239 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47239 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47239 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47239 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_47239_validation.pdf.gz emd_47239_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_47239_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_47239_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_47239_validation.xml.gz emd_47239_validation.xml.gz | 23.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_47239_validation.cif.gz emd_47239_validation.cif.gz | 31.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47239 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47239 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47239 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47239 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9dw9MC  9dw4C  9dw5C 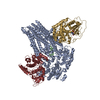 9dw7C  9dw8C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_47239.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_47239.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Phosphorylated (E1371Q)CFTR in complex with PKA-C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.676 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: half-map 1
| File | emd_47239_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-map 2
| File | emd_47239_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Phosphorylated (E1371Q)CFTR in complex with PKA-C
+Supramolecule #1: Phosphorylated (E1371Q)CFTR in complex with PKA-C
+Macromolecule #1: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
+Macromolecule #2: cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha
+Macromolecule #3: CHOLESTEROL
+Macromolecule #4: DECANE
+Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #6: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #7: CHLORIDE ION
+Macromolecule #8: UNDECANE
+Macromolecule #9: water
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R0.6/1 / Material: COPPER / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 52.5 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)