+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Dephosphorylated CFTR in 1:2 complex with PKA-C | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Dephosphorylated CFTR in 1:2 complex with PKA-C | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CFTR / PKA / complex / HYDROLASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of voltage-gated chloride channel activity / : / Sec61 translocon complex binding / channel-conductance-controlling ATPase / intracellularly ATP-gated chloride channel activity / CD209 (DC-SIGN) signaling / HDL assembly / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of enamel mineralization / Rap1 signalling ...positive regulation of voltage-gated chloride channel activity / : / Sec61 translocon complex binding / channel-conductance-controlling ATPase / intracellularly ATP-gated chloride channel activity / CD209 (DC-SIGN) signaling / HDL assembly / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of enamel mineralization / Rap1 signalling / Ion homeostasis / transepithelial water transport / RHO GTPases regulate CFTR trafficking / PKA activation in glucagon signalling / DARPP-32 events / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / GPER1 signaling / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / RET signaling / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / amelogenesis / Interleukin-3, Interleukin-5 and GM-CSF signaling / intracellular pH elevation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / PKA activation / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / chloride channel inhibitor activity / : / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Hedgehog 'off' state / multicellular organismal-level water homeostasis / Golgi-associated vesicle membrane / cholesterol transport / bicarbonate transport / bicarbonate transmembrane transporter activity / chloride channel regulator activity / membrane hyperpolarization / vesicle docking involved in exocytosis / chloride transmembrane transporter activity / cAMP-dependent protein kinase / regulation of protein processing / cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity / protein localization to lipid droplet / regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly / cAMP-dependent protein kinase complex / cellular response to parathyroid hormone stimulus / Mitochondrial protein degradation / cholesterol biosynthetic process / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / regulation of osteoblast differentiation / cellular response to cold / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / sperm capacitation / negative regulation of glycolytic process through fructose-6-phosphate / ciliary base / RHOQ GTPase cycle / chloride channel activity / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / intracellular potassium ion homeostasis / mesoderm formation / positive regulation of exocytosis / plasma membrane raft / ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity / axoneme / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / ABC-type transporter activity / chloride channel complex / sperm flagellum / postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / 14-3-3 protein binding / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity / cellular response to glucagon stimulus / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / acrosomal vesicle / cellular response to forskolin / chloride transmembrane transport / protein export from nucleus / positive regulation of phagocytosis / cellular response to cAMP / response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / positive regulation of protein export from nucleus / PDZ domain binding / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / neural tube closure / neuromuscular junction / clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane / cellular response to glucose stimulus / establishment of localization in cell / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / positive regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / Late endosomal microautophagy Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fiedorczuk K / Chen J / Csanady L | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024Title: The structures of protein kinase A in complex with CFTR: Mechanisms of phosphorylation and noncatalytic activation. Authors: Karol Fiedorczuk / Iordan Iordanov / Csaba Mihályi / Andras Szollosi / László Csanády / Jue Chen /   Abstract: Protein kinase A (PKA) is a key regulator of cellular functions by selectively phosphorylating numerous substrates, including ion channels, enzymes, and transcription factors. It has long served as a ...Protein kinase A (PKA) is a key regulator of cellular functions by selectively phosphorylating numerous substrates, including ion channels, enzymes, and transcription factors. It has long served as a model system for understanding the eukaryotic kinases. Using cryoelectron microscopy, we present complex structures of the PKA catalytic subunit (PKA-C) bound to a full-length protein substrate, the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)-an ion channel vital to human health. CFTR gating requires phosphorylation of its regulatory (R) domain. Unphosphorylated CFTR engages PKA-C at two locations, establishing two "catalytic stations" near to, but not directly involving, the R domain. This configuration, coupled with the conformational flexibility of the R domain, permits transient interactions of the eleven spatially separated phosphorylation sites. Furthermore, we determined two structures of the open-pore CFTR stabilized by PKA-C, providing a molecular basis to understand how PKA-C stimulates CFTR currents even in the absence of phosphorylation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_47237.map.gz emd_47237.map.gz | 303.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-47237-v30.xml emd-47237-v30.xml emd-47237.xml emd-47237.xml | 20.8 KB 20.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_47237_fsc.xml emd_47237_fsc.xml | 14.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_47237.png emd_47237.png | 147.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-47237.cif.gz emd-47237.cif.gz | 7.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_47237_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47237_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47237_half_map_2.map.gz emd_47237_half_map_2.map.gz | 302 MB 302 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47237 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47237 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47237 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47237 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_47237_validation.pdf.gz emd_47237_validation.pdf.gz | 1022.2 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_47237_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_47237_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1021.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_47237_validation.xml.gz emd_47237_validation.xml.gz | 23.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_47237_validation.cif.gz emd_47237_validation.cif.gz | 30.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47237 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47237 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47237 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47237 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 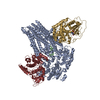 9dw7MC  9dw4C  9dw5C  9dw8C  9dw9C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_47237.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_47237.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Dephosphorylated CFTR in 1:2 complex with PKA-C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.676 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: half-map 1
| File | emd_47237_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-map 2
| File | emd_47237_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : dephosphorylated CFTR in 1:2 complex with PKA-C
| Entire | Name: dephosphorylated CFTR in 1:2 complex with PKA-C |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: dephosphorylated CFTR in 1:2 complex with PKA-C
| Supramolecule | Name: dephosphorylated CFTR in 1:2 complex with PKA-C / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 210 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha
| Macromolecule | Name: cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: cAMP-dependent protein kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.677652 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MGNAAAAKKG SEQESVKEFL AKAKEDFLKK WENPAQNTAH LDQFERIKTL GTGSFGRVML VKHMETGNHY AMKILDKQKV VKLKQIEHT LNEKRILQAV NFPFLVKLEF SFKDNSNLYM VMEYVPGGEM FSHLRRIGRF SEPHARFYAA QIVLTFEYLH S LDLIYRDL ...String: MGNAAAAKKG SEQESVKEFL AKAKEDFLKK WENPAQNTAH LDQFERIKTL GTGSFGRVML VKHMETGNHY AMKILDKQKV VKLKQIEHT LNEKRILQAV NFPFLVKLEF SFKDNSNLYM VMEYVPGGEM FSHLRRIGRF SEPHARFYAA QIVLTFEYLH S LDLIYRDL KPENLLIDQQ GYIQVTDFGF AKRVKGRTWT LCGTPEYLAP EIILSKGYNK AVDWWALGVL IYEMAAGYPP FF ADQPIQI YEKIVSGKVR FPSHFSSDLK DLLRNLLQVD LTKRFGNLKN GVNDIKNHKW FATTDWIAIY QRKVEAPFIP KFK GPGDTS NFDDYEEEEI RVSINEKCGK EFSEF UniProtKB: cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha |
-Macromolecule #2: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
| Macromolecule | Name: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: channel-conductance-controlling ATPase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 168.335453 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MQRSPLEKAS VVSKLFFSWT RPILRKGYRQ RLELSDIYQI PSVDSADNLS EKLEREWDRE LASKKNPKLI NALRRCFFWR FMFYGIFLY LGEVTKAVQP LLLGRIIASY DPDNKEERSI AIYLGIGLCL LFIVRTLLLH PAIFGLHHIG MQMRIAMFSL I YKKTLKLS ...String: MQRSPLEKAS VVSKLFFSWT RPILRKGYRQ RLELSDIYQI PSVDSADNLS EKLEREWDRE LASKKNPKLI NALRRCFFWR FMFYGIFLY LGEVTKAVQP LLLGRIIASY DPDNKEERSI AIYLGIGLCL LFIVRTLLLH PAIFGLHHIG MQMRIAMFSL I YKKTLKLS SRVLDKISIG QLVSLLSNNL NKFDEGLALA HFVWIAPLQV ALLMGLIWEL LQASAFCGLG FLIVLALFQA GL GRMMMKY RDQRAGKISE RLVITSEMIE NIQSVKAYCW EEAMEKMIEN LRQTELKLTR KAAYVRYFNS SAFFFSGFFV VFL SVLPYA LIKGIILRKI FTTISFCIVL RMAVTRQFPW AVQTWYDSLG AINKIQDFLQ KQEYKTLEYN LTTTEVVMEN VTAF WEEGF GELFEKAKQN NNNRKTSNGD DSLFFSNFSL LGTPVLKDIN FKIERGQLLA VAGSTGAGKT SLLMVIMGEL EPSEG KIKH SGRISFCSQF SWIMPGTIKE NIIFGVSYDE YRYRSVIKAC QLEEDISKFA EKDNIVLGEG GITLSGGQRA RISLAR AVY KDADLYLLDS PFGYLDVLTE KEIFESCVCK LMANKTRILV TSKMEHLKKA DKILILHEGS SYFYGTFSEL QNLQPDF SS KLMGCDSFDQ FSAERRNSIL TETLHRFSLE GDAPVSWTET KKQSFKQTGE FGEKRKNSIL NPINSIRKFS IVQKTPLQ M NGIEEDSDEP LERRLSLVPD SEQGEAILPR ISVISTGPTL QARRRQSVLN LMTHSVNQGQ NIHRKTTAST RKVSLAPQA NLTELDIYSR RLSQETGLEI SEEINEEDLK ECFFDDMESI PAVTTWNTYL RYITVHKSLI FVLIWCLVIF LAEVAASLVV LWLLGNTPL QDKGNSTHSR NNSYAVIITS TSSYYVFYIY VGVADTLLAM GFFRGLPLVH TLITVSKILH HKMLHSVLQA P MSTLNTLK AGGILNRFSK DIAILDDLLP LTIFDFIQLL LIVIGAIAVV AVLQPYIFVA TVPVIVAFIM LRAYFLQTSQ QL KQLESEG RSPIFTHLVT SLKGLWTLRA FGRQPYFETL FHKALNLHTA NWFLYLSTLR WFQMRIEMIF VIFFIAVTFI SIL TTGEGE GRVGIILTLA MNIMSTLQWA VNSSIDVDSL MRSVSRVFKF IDMPTEGKPT KSTKPYKNGQ LSKVMIIENS HVKK DDIWP SGGQMTVKDL TAKYTEGGNA ILENISFSIS PGQRVGLLGR TGSGKSTLLS AFLRLLNTEG EIQIDGVSWD SITLQ QWRK AFGVIPQKVF IFSGTFRKNL DPYEQWSDQE IWKVADEVGL RSVIEQFPGK LDFVLVDGGC VLSHGHKQLM CLARSV LSK AKILLLDEPS AHLDPVTYQI IRRTLKQAFA DCTVILCEHR IEAMLECQQF LVIEENKVRQ YDSIQKLLNE RSLFRQA IS PSDRVKLFPH RNSSKCKSKP QIAALKEETE EEVQDTRL UniProtKB: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator |
-Macromolecule #3: cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
| Macromolecule | Name: cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.635006 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ANP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 506.196 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ANP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 52.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






































