[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-4708: The structure of a Ty3 retrotransposon capsid C-terminal domain dimer -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-4708 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
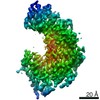
| Title | The structure of a Ty3 retrotransposon capsid C-terminal domain dimer | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | The structure of a Ty3 capsid C-terminal domain dimer | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ty3 / retrotransposon / retrovirus / capsid / Gag polyprotein / capsid-CTD / VIRUS LIKE PARTICLE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationribonuclease H / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Aspartic endopeptidases / DNA integration / RNA-directed DNA polymerase / RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / RNA-DNA hybrid ribonuclease activity / DNA recombination / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / aspartic-type endopeptidase activity / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity ...ribonuclease H / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Aspartic endopeptidases / DNA integration / RNA-directed DNA polymerase / RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / RNA-DNA hybrid ribonuclease activity / DNA recombination / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / aspartic-type endopeptidase activity / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / viral translational frameshifting / proteolysis / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Dodonova SO / Prinz S | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, Germany,  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2019 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2019Title: Structure of the Ty3/Gypsy retrotransposon capsid and the evolution of retroviruses. Authors: Svetlana O Dodonova / Simone Prinz / Virginia Bilanchone / Suzanne Sandmeyer / John A G Briggs /    Abstract: Retroviruses evolved from long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposons by acquisition of envelope functions, and subsequently reinvaded host genomes. Together, endogenous retroviruses and LTR ...Retroviruses evolved from long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposons by acquisition of envelope functions, and subsequently reinvaded host genomes. Together, endogenous retroviruses and LTR retrotransposons represent major components of animal, plant, and fungal genomes. Sequences from these elements have been exapted to perform essential host functions, including placental development, synaptic communication, and transcriptional regulation. They encode a Gag polypeptide, the capsid domains of which can oligomerize to form a virus-like particle. The structures of retroviral capsids have been extensively described. They assemble an immature viral particle through oligomerization of full-length Gag. Proteolytic cleavage of Gag results in a mature, infectious particle. In contrast, the absence of structural data on LTR retrotransposon capsids hinders our understanding of their function and evolutionary relationships. Here, we report the capsid morphology and structure of the archetypal Gypsy retrotransposon Ty3. We performed electron tomography (ET) of immature and mature Ty3 particles within cells. We found that, in contrast to retroviruses, these do not change size or shape upon maturation. Cryo-ET and cryo-electron microscopy of purified, immature Ty3 particles revealed an irregular fullerene geometry previously described for mature retrovirus core particles and a tertiary and quaternary arrangement of the capsid (CA) C-terminal domain within the assembled capsid that is conserved with mature HIV-1. These findings provide a structural basis for studying retrotransposon capsids, including those domesticated in higher organisms. They suggest that assembly via a structurally distinct immature capsid is a later retroviral adaptation, while the structure of mature assembled capsids is conserved between LTR retrotransposons and retroviruses. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_4708.map.gz emd_4708.map.gz | 465.1 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-4708-v30.xml emd-4708-v30.xml emd-4708.xml emd-4708.xml | 14.4 KB 14.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_4708_fsc.xml emd_4708_fsc.xml | 5.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_4708.png emd_4708.png | 154 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-4708.cif.gz emd-4708.cif.gz | 6.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4708 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4708 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4708 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4708 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_4708_validation.pdf.gz emd_4708_validation.pdf.gz | 366.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_4708_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_4708_full_validation.pdf.gz | 365.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_4708_validation.xml.gz emd_4708_validation.xml.gz | 8.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_4708_validation.cif.gz emd_4708_validation.cif.gz | 11.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-4708 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-4708 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-4708 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-4708 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6r23MC 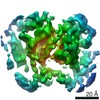 4707C  4709C 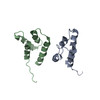 6r22C  6r24C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_4708.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_4708.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | The structure of a Ty3 capsid C-terminal domain dimer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ty3 capsid C-terminal domain dimer
| Entire | Name: Ty3 capsid C-terminal domain dimer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ty3 capsid C-terminal domain dimer
| Supramolecule | Name: Ty3 capsid C-terminal domain dimer / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: The 9 non-symmetry related copies of the Ty3 Capsid-CTD from the complete capsid shell structure were aligned and averaged to generate a higher resolution 4.9 A structure |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Transposon Ty3-I Gag-Pol polyprotein
| Macromolecule | Name: Transposon Ty3-I Gag-Pol polyprotein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: D336I mutation in the active center of the Ty3 protease Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Aspartic endopeptidases |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 36.382371 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSFMDQIPGG GNYPKLPVEC LPNFPIQPSL TFRGRNDSHK LKNFISEIML NMSMISWPND ASRIVYCRRH LLNPAAQWAN DFVQEQGIL EITFDTFIQG LYQHFYKPPD INKIFNAITQ LSEAKLGIER LNQRFRKIWD RMPPDFMTEK AAIMTYTRLL T KETYNIVR ...String: MSFMDQIPGG GNYPKLPVEC LPNFPIQPSL TFRGRNDSHK LKNFISEIML NMSMISWPND ASRIVYCRRH LLNPAAQWAN DFVQEQGIL EITFDTFIQG LYQHFYKPPD INKIFNAITQ LSEAKLGIER LNQRFRKIWD RMPPDFMTEK AAIMTYTRLL T KETYNIVR MHKPETLKDA MEEAYQTTAL TERFFPGFEL DADGDTIIGA TTHLQEEYDS DYDSEDNLTQ NRYVHTVRTR RS YNKPMSN HRNRRNNNAS REECIKNRLC FYCKKEGHRL NECRARKAVL TDLELESKDQ QTLFIKTLPI VH UniProtKB: Transposon Ty3-I Gag-Pol polyprotein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: C-flat / Material: COPPER / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 85 % / Chamber temperature: 296 K / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER Details: The sample was applied onto glow-discharged C-flat (Protochips Inc.) holey carbon grids. The grids were blotted from the back side for 11 seconds at room temperature in a chamber at 85% ...Details: The sample was applied onto glow-discharged C-flat (Protochips Inc.) holey carbon grids. The grids were blotted from the back side for 11 seconds at room temperature in a chamber at 85% humidity and plunge-frozen into liquid ethane using a manual plunger.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Details | Cryo-grids containing purified PR- Ty3 particles were imaged in a Titan Krios electron microscope equipped with a Falcon II direct electron detector, operated at 300 kV. Images were collected with a nominal magnification of 75000, giving a pixel size of 1.08 A. Images were collected in integrating mode with a total electron dose of 20 e/A2. The range of applied defocus values was between -1.0 um and -3.5 um. |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Number grids imaged: 1 / Average electron dose: 20.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 75000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6r23: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















