+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of human Wnt7a bound to WLS and CALR | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpostsynapse assembly / positive regulation of excitatory synapse assembly / positive regulation of protein localization to presynapse / skeletal muscle satellite cell activation / Wnt protein secretion / Calnexin/calreticulin cycle / asymmetric protein localization involved in cell fate determination / response to biphenyl / cerebellar granule cell differentiation / excitatory synapse assembly ...postsynapse assembly / positive regulation of excitatory synapse assembly / positive regulation of protein localization to presynapse / skeletal muscle satellite cell activation / Wnt protein secretion / Calnexin/calreticulin cycle / asymmetric protein localization involved in cell fate determination / response to biphenyl / cerebellar granule cell differentiation / excitatory synapse assembly / cytolytic granule / regulation of axon diameter / positive regulation of Wnt protein secretion / lens fiber cell development / positive regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis / WNT ligand biogenesis and trafficking / ATF6 (ATF6-alpha) activates chaperone genes / oviduct development / Assembly of Viral Components at the Budding Site / synaptic vesicle recycling / cortical granule / negative regulation of trophoblast cell migration / central nervous system vasculogenesis / cell proliferation in forebrain / nuclear receptor-mediated glucocorticoid signaling pathway / cellular response to electrical stimulus / complement component C1q complex binding / uterus morphogenesis / response to peptide / embryonic axis specification / regulation of meiotic nuclear division / negative regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / cementum mineralization / sequestering of calcium ion / endoplasmic reticulum quality control compartment / secondary palate development / somatic stem cell division / protein folding in endoplasmic reticulum / skeletal muscle satellite cell maintenance involved in skeletal muscle regeneration / sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen / response to glycoside / sex differentiation / presynapse assembly / hindbrain development / hormone binding / positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in wound healing / Wnt-protein binding / negative regulation of intracellular steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway / stem cell development / nuclear export signal receptor activity / establishment of blood-brain barrier / cardiac muscle cell differentiation / neurotransmitter secretion / dendritic spine morphogenesis / exocrine pancreas development / frizzled binding / dorsal/ventral pattern formation / embryonic forelimb morphogenesis / Class B/2 (Secretin family receptors) / positive regulation of synapse assembly / embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis / regulation of postsynapse organization / anterior/posterior axis specification / cortical actin cytoskeleton organization / wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / cartilage condensation / embryonic digit morphogenesis / nuclear androgen receptor binding / Scavenging by Class F Receptors / cellular response to lithium ion / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / establishment of cell polarity / midbrain development / organelle membrane / response to testosterone / positive regulation of protein metabolic process / mesoderm formation / molecular sequestering activity / somatic stem cell population maintenance / positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of presynapse assembly / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / cell fate commitment / negative regulation of neuron differentiation / protein localization to nucleus / chondrocyte differentiation / canonical Wnt signaling pathway / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / positive regulation of phagocytosis / cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus / positive regulation of cell cycle / ERAD pathway / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / positive regulation of endothelial cell migration / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / endocytic vesicle lumen / extracellular matrix / protein folding chaperone Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Qi X / Hu Q / Li X | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Cell / Year: 2023Title: Molecular basis of Wnt biogenesis, secretion, and Wnt7-specific signaling. Authors: Xiaofeng Qi / Qinli Hu / Nadia Elghobashi-Meinhardt / Tao Long / Hongwen Chen / Xiaochun Li /   Abstract: Wnt proteins are enzymatically lipidated by Porcupine (PORCN) in the ER and bind to Wntless (WLS) for intracellular transport and secretion. Mechanisms governing the transfer of these low-solubility ...Wnt proteins are enzymatically lipidated by Porcupine (PORCN) in the ER and bind to Wntless (WLS) for intracellular transport and secretion. Mechanisms governing the transfer of these low-solubility Wnts from the ER to the extracellular space remain unclear. Through structural and functional analyses of Wnt7a, a crucial Wnt involved in central nervous system angiogenesis and blood-brain barrier maintenance, we have elucidated the principles of Wnt biogenesis and Wnt7-specific signaling. The Wnt7a-WLS complex binds to calreticulin (CALR), revealing that CALR functions as a chaperone to facilitate Wnt transfer from PORCN to WLS during Wnt biogenesis. Our structures, functional analyses, and molecular dynamics simulations demonstrate that a phospholipid in the core of Wnt-bound WLS regulates the association and dissociation between Wnt and WLS, suggesting a lipid-mediated Wnt secretion mechanism. Finally, the structure of Wnt7a bound to RECK, a cell-surface Wnt7 co-receptor, reveals how RECK engages the N-terminal domain of Wnt7a to activate Wnt7-specific signaling. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_41764.map.gz emd_41764.map.gz | 117.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-41764-v30.xml emd-41764-v30.xml emd-41764.xml emd-41764.xml | 20.3 KB 20.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_41764.png emd_41764.png | 56.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-41764.cif.gz emd-41764.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_41764_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41764_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41764_half_map_2.map.gz emd_41764_half_map_2.map.gz | 115.9 MB 115.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41764 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41764 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41764 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41764 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8tzoMC 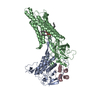 8tzpC 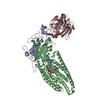 8tzrC  8tzsC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_41764.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_41764.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.83 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_41764_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_41764_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Wnt7a-WLS-CALR Complex
| Entire | Name: Wnt7a-WLS-CALR Complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Wnt7a-WLS-CALR Complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Wnt7a-WLS-CALR Complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Protein Wnt-7a
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein Wnt-7a / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.062977 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MNRKARRCLG HLFLSLGMVY LRIGGFSSVV ALGASIICNK IPGLAPRQRA ICQSRPDAII VIGEGSQMGL DECQFQFRNG RWNCSALGE RTVFGKELKV GSREAAFTYA IIAAGVAHAI TAACTQGNLS DCGCDKEKQG QYHRDEGWKW GGCSADIRYG I GFAKVFVD ...String: MNRKARRCLG HLFLSLGMVY LRIGGFSSVV ALGASIICNK IPGLAPRQRA ICQSRPDAII VIGEGSQMGL DECQFQFRNG RWNCSALGE RTVFGKELKV GSREAAFTYA IIAAGVAHAI TAACTQGNLS DCGCDKEKQG QYHRDEGWKW GGCSADIRYG I GFAKVFVD AREIKQNART LMNLHNNEAG RKILEENMKL ECKCHGVSGS CTTKTCWTTL PQFRELGYVL KDKYNEAVHV EP VRASRNK RPTFLKIKKP LSYRKPMDTD LVYIEKSPNY CEEDPVTGSV GTQGRACNKT APQASGCDLM CCGRGYNTHQ YAR VWQCNC KFHWCCYVKC NTCSERTEMY TCK UniProtKB: Protein Wnt-7a |
-Macromolecule #2: Protein wntless homolog
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein wntless homolog / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 62.317973 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAGAIIENMS TKKLCIVGGI LLVFQIIAFL VGGLIAPGPT TAVSYMSVKC VDARKNHHKT KWFVPWGPNH CDKIRDIEEA IPREIEAND IVFSVHIPLP HMEMSPWFQF MLFILQLDIA FKLNNQIREN AEVSMDVSLA YRDDAFAEWT EMAHERVPRK L KCTFTSPK ...String: MAGAIIENMS TKKLCIVGGI LLVFQIIAFL VGGLIAPGPT TAVSYMSVKC VDARKNHHKT KWFVPWGPNH CDKIRDIEEA IPREIEAND IVFSVHIPLP HMEMSPWFQF MLFILQLDIA FKLNNQIREN AEVSMDVSLA YRDDAFAEWT EMAHERVPRK L KCTFTSPK TPEHEGRYYE CDVLPFMEIG SVAHKFYLLN IRLPVNEKKK INVGIGEIKD IRLVGIHQNG GFTKVWFAMK TF LTPSIFI IMVWYWRRIT MMSRPPVLLE KVIFALGISM TFINIPVEWF SIGFDWTWML LFGDIRQGIF YAMLLSFWII FCG EHMMDQ HERNHIAGYW KQVGPIAVGS FCLFIFDMCE RGVQLTNPFY SIWTTDIGTE LAMAFIIVAG ICLCLYFLFL CFMV FQVFR NISGKQSSLP AMSKVRRLHY EGLIFRFKFL MLITLACAAM TVIFFIVSQV TEGHWKWGGV TVQVNSAFFT GIYGM WNLY VFALMFLYAP SHKNYGEDQS NGDLGVHSGE ELQLTTTITH VDGPTEIYKL TRKEAQE UniProtKB: Protein wntless homolog |
-Macromolecule #3: Calreticulin
| Macromolecule | Name: Calreticulin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 48.198379 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MLLSVPLLLG LLGLAVAEPA VYFKEQFLDG DGWTSRWIES KHKSDFGKFV LSSGKFYGDE EKDKGLQTSQ DARFYALSAS FEPFSNKGQ TLVVQFTVKH EQNIDCGGGY VKLFPNSLDQ TDMHGDSEYN IMFGPDICGP GTKKVHVIFN YKGKNVLINK D IRCKDDEF ...String: MLLSVPLLLG LLGLAVAEPA VYFKEQFLDG DGWTSRWIES KHKSDFGKFV LSSGKFYGDE EKDKGLQTSQ DARFYALSAS FEPFSNKGQ TLVVQFTVKH EQNIDCGGGY VKLFPNSLDQ TDMHGDSEYN IMFGPDICGP GTKKVHVIFN YKGKNVLINK D IRCKDDEF THLYTLIVRP DNTYEVKIDN SQVESGSLED DWDFLPPKKI KDPDASKPED WDERAKIDDP TDSKPEDWDK PE HIPDPDA KKPEDWDEEM DGEWEPPVIQ NPEYKGEWKP RQIDNPDYKG TWIHPEIDNP EYSPDPSIYA YDNFGVLGLD LWQ VKSGTI FDNFLITNDE AYAEEFGNET WGVTKAAEKQ MKDKQDEEQR LKEEEEDKKR KEEEEAEDKE DDEDKDEDEE DEED KEEDE EEDVPGQAKD EL UniProtKB: Calreticulin |
-Macromolecule #5: PALMITOLEIC ACID
| Macromolecule | Name: PALMITOLEIC ACID / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PAM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 254.408 Da |
| Chemical component information | 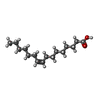 ChemComp-PAM: |
-Macromolecule #6: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(tri...
| Macromolecule | Name: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl phosphate type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: POV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 760.076 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-POV: |
-Macromolecule #7: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)